
Anomochilus is a genus of snakes, it is the only genus in the monogeneric family Anomochilidae and has three species classified within it. Members of the genus are known as anomochilids, or by the common names dwarf pipesnake, lesser pipesnake, and giant blind snake. Initially created as Anomalochilus in 1890 for the species A. weberi, the genus was renamed in 1901 because the original name was already in use for a genus of beetles. Dwarf pipesnakes are small and cylindrical, with short, conical tails and small, rounded heads that are continuous with the neck. They have blackish to purplish-brown uppersides and dark brown or black undersides, with orange-red bands around the tail and a variety of pale markings on the snout and belly. All three species of dwarf pipesnake are endemic to Sundaland, where they are found on the Malay Peninsula and the islands of Sumatra and Borneo.

The hog-nosed skunks belong to the genus Conepatus and are members of the family Mephitidae (skunks). They are native to the Americas. They have white backs and tails and black underparts.

The greater hog badger is a very large terrestrial mustelid native to Southeast Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species because the global population is thought to be declining due to high levels of poaching.

The Sumatran striped rabbit, also known as the Sumatra short-eared rabbit or Sumatran rabbit, is a rabbit found only in forests in the Barisan Mountains in western Sumatra, Indonesia, and surrounding areas. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Doria's tree-kangaroo is a long-tailed, furry, bear-like mammal found only in tropical mountain forests on the island of New Guinea. It is one of the largest tree-kangaroos, living alone in trees and active at night to feed on leaves or fruit. It belongs to the macropod family (Macropodidae) with kangaroos, and carries its young in a pouch like other marsupials. Threats include hunting and habitat loss.

The broad-striped dasyure is a species of marsupial in the family Dasyuridae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests.

The ursine tree-kangaroo is a long-tailed, furry, bear-like mammal found only in tropical forests on the island of New Guinea. Slightly larger than a cat, it lives alone in trees and is active at night to feed on leaves and fruit. It belongs to the macropod family (Macropodidae) with kangaroos, and carries its young in a pouch like other marsupials. It has a small range in northwestern New Guinea and is threatened by habitat loss and hunting. Other common names for this species include the black tree-kangaroo, the Vogelkop tree-kangaroo and the white-throated tree-kangaroo.

The black-crested Sumatran langur is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. It is endemic to Sumatra in Indonesia. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The swift fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae.

Humboldt's hog-nosed skunk, also known as the Patagonian hog-nosed skunk, is a species of hog-nosed skunk indigenous to the open grassy areas in the Patagonian regions of South Argentina and Chile. It belongs to the order Carnivora and the family Mephitidae.

The Bougainville monkey-faced bat or Bougainville flying monkey is a megabat endemic to Bougainville Island of Papua New Guinea and Choiseul Island of the Solomon Islands in Melanesia. It inhabits mature forests in upland areas, within the Autonomous Region of Bougainville and Bougouriba Province.
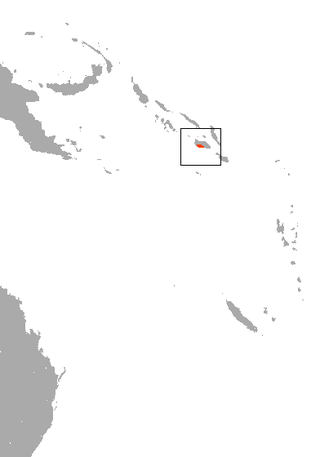
The montane monkey-faced bat or montane flying monkey is a megabat endemic to the Solomon Islands. It is listed as a critically endangered species. Due to its imperilled status, it is identified by the Alliance for Zero Extinction as a species in danger of imminent extinction. In 2013, Bat Conservation International listed this species as one of the 35 species of its worldwide priority list of conservation. Only one individual has ever been found.

The American hog-nosed skunk is a species of hog-nosed skunk from Central and North America, and is one of the largest skunks in the world, growing to lengths of up to 2.7 feet (82 cm). Recent work has concluded the western hog-nosed skunk is the same species, and Conepatus leuconotus is the correct name of the merged populations.

The greater monkey-faced bat or greater flying monkey is a megabat endemic to Solomon Islands, Bougainville, in Papua New Guinea, and nearby small islands. It is listed as a critically endangered species and the population is decreasing. It is the largest monkey-faced bat.
Chalcorana chalconota is a species of "true frog", family Ranidae. It is endemic to Indonesia and occurs in southern Sumatra, Java, Bali, and a few smaller islands. Populations previously assigned to this species now belong to a number of other Chalcorana species, leading to the current delineation of Chalcorana chalconota with a much narrower range. This species is also known as the Schlegel's frog, brown stream frog, copper-cheeked frog, or, among with many other species, white-lipped frog.

The Wondiwoi tree-kangaroo is a critically endangered, bear-like mammal native to tropical mountain forests on the island of New Guinea in Western Papua. Elusive and rare, it was considered extinct until rediscovery in 2018. It is a species of tree-kangaroo, a group of long-tailed, bear-like animals native to Australia and New Guinea that mostly live in trees and feed on plant matter. Tree-kangaroos belong to the macropod family (Macropodidae) with kangaroos, and carry their young in a pouch like most other marsupials. The Wondiwoi tree-kangaroo is likely threatened by hunting, and is known only from remote mountains on the Wondiwoi Peninsula in northwest New Guinea.

Hog badgers are three species of mustelid in the genus Arctonyx. They represent one of the two genera in the subfamily Melinae, alongside the true badgers.

The northern hog badger is a species of mustelid native to South and East Asia.
















