
Holmium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ho and atomic number 67. It is a rare-earth element and the eleventh member of the lanthanide series. It is a relatively soft, silvery, fairly corrosion-resistant and malleable metal. Like many other lanthanides, holmium is too reactive to be found in native form, as pure holmium slowly forms a yellowish oxide coating when exposed to air. When isolated, holmium is relatively stable in dry air at room temperature. However, it reacts with water and corrodes readily, and also burns in air when heated.

Thulium is a chemical element; it has symbol Tm and atomic number 69. It is the thirteenth and third-last element in the lanthanide series. Like the other lanthanides, the most common oxidation state is +3, seen in its oxide, halides and other compounds; however, the +2 oxidation state can also be stable. In aqueous solution, like compounds of other late lanthanides, soluble thulium compounds form coordination complexes with nine water molecules.
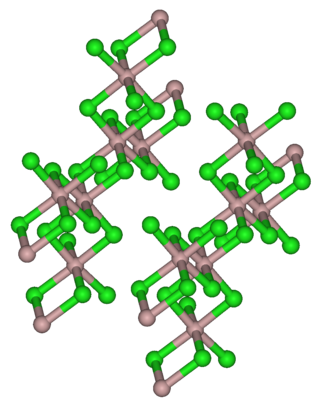
Thulium(III) chloride or thulium trichloride is as an inorganic salt composed of thulium and chlorine with the formula TmCl3. It forms yellow crystals. Thulium(III) chloride has the YCl3 (AlCl3) layer structure with octahedral thulium ions. It has been used as a starting material for some exotic nanostructures prepared for NIR photocatalysis.
The selenide iodides are chemical compounds that contain both selenide ions (Se2−) and iodide ions (I−) and one or metal atoms. They are in the class of mixed anion compounds or chalcogenide halides.
The telluride bromides are chemical compounds that contain both telluride ions (Te2−) and bromide ions (Br−). They are in the class of mixed anion compounds or chalcogenide halides.
The sulfate fluorides are double salts that contain both sulfate and fluoride anions. They are in the class of mixed anion compounds. Some of these minerals are deposited in fumaroles.
The telluride oxides or oxytellurides are double salts that contain both telluride and oxide anions. They are in the class of mixed anion compounds.
The telluride iodides are chemical compounds that contain both telluride ions (Te2−) and iodide ions (I−). They are in the class of mixed anion compounds or chalcogenide halides.
The borate bromides are mixed anion compounds that contain borate and bromide anions. They are in the borate halide family of compounds which also includes borate fluorides, borate chlorides, and borate iodides.
The borate iodides are mixed anion compounds that contain both borate and iodide anions. They are in the borate halide family of compounds which also includes borate fluorides, borate chlorides, and borate bromides.
Sulfidogermanates or thiogermanates are chemical compounds containing anions with sulfur atoms bound to germanium. They are in the class of chalcogenidotetrelates. Related compounds include thiosilicates, thiostannates, selenidogermanates, telluridogermanates and selenidostannates.
Tellurogallates are chemical compounds which contain anionic units of tellurium connected to gallium. They can be considered as gallates where tellurium substitutes for oxygen. Similar compounds include the thiogallates, selenogallates, telluroaluminates, telluroindates and thiostannates. They are in the category of chalcogenotrielates or more broadly tellurometallates or chalcogenometallates.

Holmium acetylacetonate is a coordination complex, with the chemical formula of Ho(C5H7O2)3 or Ho(acac)3. It can be obtained via the reaction between metallic holmium or holmium(III) hydride with acetylacetone, or via the reaction between holmium(III) chloride and ammonium acetylacetonate. Its anhydrous form is stable in a dry atmosphere but forms a hydrate in humid air.

Thulium(III) acetate is the acetate salt of thulium, with the chemical formula of Tm(CH3COO)3. It can exist in the tetrahydrate or the anhydrous form.

Thulium(III) iodide is an iodide of thulium, with the chemical formula of TmI3. Thulium(III) iodide is used as a component of metal halide lamps.
Thulium(III) selenide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Tm2Se3.
A selenophosphate is a chemical compound containing phosphate anions substituted with selenium. Over 7000 compounds are known with a bond between selenium and phosphorus. Compared to phosphorus-sulfur compounds selenophosphates are less thermally stable, and more easily destroyed by water. However they are more stable than tellurophosphates which have an even weaker phosphorus-tellurium bond. Selenophosphates have an oxidation number for phosphorus of +5. But in many there are bonds between phosphorus atoms, reducing the oxidation state to +4, Some may be termed selenophosphites.
Holmium(III) telluride is an inorganic compound, one of the tellurides of holmium, with the chemical formula Ho2Te3.
Lutetium(III) telluride is an inorganic compound, one of the tellurides of lutetium, with the chemical formula Lu2Te3. It has the structure Sc2S3 and space group Fddd. It can be obtained by arc melting with lutetium metal, and Lu7Te, Lu11Te4 or LuTe could also be obtained.
Ytterbium monotelluride is an inorganic compound, one of the tellurides of ytterbium, with the chemical formula YbTe.





