A codec is a device or computer program that encodes or decodes a data stream or signal. Codec is a portmanteau of coder/decoder.
Windows Media Audio (WMA) is a series of audio codecs and their corresponding audio coding formats developed by Microsoft. It is a proprietary technology that forms part of the Windows Media framework. WMA consists of four distinct codecs. The original WMA codec, known simply as WMA, was conceived as a competitor to the popular MP3 and RealAudio codecs. WMA Pro, a newer and more advanced codec, supports multichannel and high-resolution audio. A lossless codec, WMA Lossless, compresses audio data without loss of audio fidelity. WMA Voice, targeted at voice content, applies compression using a range of low bit rates. Microsoft has also developed a digital container format called Advanced Systems Format to store audio encoded by WMA.

Windows Media Player, is the first media player and media library application that Microsoft developed to play audio and video on personal computers. It has been a component of the Microsoft Windows operating system, including Windows 9x, Windows NT, Pocket PC, and Windows Mobile. Microsoft also released editions of Windows Media Player for classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, and Solaris, but has since discontinued them.
Helix DNA was a project to produce computer software that can play audio and video media in various formats and aid in creating such media. It is intended as a largely free and open-source digital media framework that runs on numerous operating systems and processors and it was started by RealNetworks, which contributed much of the code. The Helix Community was an open collaborative effort to develop and extend the Helix DNA platform. The Helix Project has been discontinued.

DivX is a brand of video codec products developed by DivX, LLC. There are three DivX codecs: the original MPEG-4 Part 2 DivX codec, the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC DivX Plus HD codec and the High Efficiency Video Coding DivX HEVC Ultra HD codec. The most recent version of the codec itself is version 6.9.2, which is several years old. New version numbers on the packages now reflect updates to the media player, converter, etc.
Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) is an audio coding standard for lossy digital audio compression. It was designed to be the successor of the MP3 format and generally achieves higher sound quality than MP3 at the same bit rate.

Advanced Systems Format is Microsoft's proprietary digital audio/digital video container format, especially meant for streaming media. ASF is part of the Media Foundation framework.
Windows Media is a discontinued multimedia framework for media creation and distribution for Microsoft Windows. It consists of a software development kit (SDK) with several application programming interfaces (API) and a number of prebuilt technologies, and is the replacement of NetShow technologies.
SMPTE 421, informally known as VC-1, is a video coding format. Most of it was initially developed as Microsoft's proprietary video format Windows Media Video 9 in 2003. With some enhancements including the development of a new Advanced Profile, it was officially approved as a SMPTE standard on April 3, 2006. It was primarily marketed as a lower-complexity competitor to the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC standard. After its development, several companies other than Microsoft asserted that they held patents that applied to the technology, including Panasonic, LG Electronics and Samsung Electronics.
DVR-MS is a proprietary video and audio file container format, developed by Microsoft used for storing TV content recorded by Windows XP Media Center Edition, Windows Vista and Windows 7.
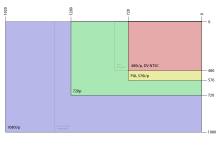
Windows Media High Definition Video is the marketing name for high definition videos encoded using Microsoft Windows Media Video 9 codecs. These low-complexity codecs make it possible to watch high definition movies in 1280×720 (720p) or 1920×1080 (1080p) resolutions on many modern personal computers running Microsoft Windows XP or Windows Vista, although the hardware requirements are steep. Microsoft's Xbox 360 and Sony's PlayStation 3 video game consoles can also play WMV HD.
A container format or metafile is a file format that allows multiple data streams to be embedded into a single file, usually along with metadata for identifying and further detailing those streams. Notable examples of container formats include archive files and formats used for multimedia playback. Among the earliest cross-platform container formats were Distinguished Encoding Rules and the 1985 Interchange File Format.
These tables compare features of multimedia container formats, most often used for storing or streaming digital video or digital audio content. To see which multimedia players support which container format, look at comparison of media players.

Windows Media Components for QuickTime, also known as Flip4Mac WMV Player by Telestream, Inc. was one of the few commercial products that allow playback of Microsoft's proprietary audio and video codecs inside QuickTime for macOS.

Flip4Mac from Telestream, Inc. was a digital media software for the macOS operating system. It was known for being the only QuickTime component for macOS to support Windows Media Video, and was distributed by Microsoft as a substitute after they discontinued their media player for Macintosh computers.
The first attempt at producing pre-recorded HDTV media was a scarce Japanese analog MUSE-encoded laser disc which is no longer produced.

K-Multimedia Player is an Adware-supported media player for Windows and iOS that can play most current audio and video formats, including VCD, HDML, DVD, AVI, MKV, Ogg, OGM, 3GP, MPEG-1/2/4, AAC, WMA 7, 8, WMV, RealMedia, FLV and QuickTime.

Microsoft Expression Encoder is a transcoding and non-linear video editing software application for Microsoft Windows. It can create video streams for distribution via Microsoft Silverlight. This utility is created to record the screen for various purposes like YouTube, Twitch, Sharing etc.
.m2ts is a filename extension used for the Blu-ray disc Audio-Video (BDAV) MPEG-2 Transport Stream (M2TS) container file format. It is used for multiplexing audio, video and other streams, such as subtitles. It is based on the MPEG-2 transport stream container. This container format is commonly used for high definition video on Blu-ray Disc and AVCHD.