
Electrical discharge machining (EDM), also known as spark machining, spark eroding, die sinking, wire burning or wire erosion, is a metal fabrication process whereby a desired shape is obtained by using electrical discharges (sparks). Material is removed from the work piece by a series of rapidly recurring current discharges between two electrodes, separated by a dielectric liquid and subject to an electric voltage. One of the electrodes is called the tool-electrode, or simply the tool or electrode, while the other is called the workpiece-electrode, or work piece. The process depends upon the tool and work piece not making physical contact. Extremely hard materials like carbides, ceramics, titanium alloys and heat treated tool steels that are very difficult to machine using conventional machining can be precisely machined by EDM.

Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) also known as computer-aided modeling or computer-aided machining is the use of software to control machine tools in the manufacturing of work pieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most common. It may also refer to the use of a computer to assist in all operations of a manufacturing plant, including planning, management, transportation and storage. Its primary purpose is to create a faster production process and components and tooling with more precise dimensions and material consistency, which in some cases, uses only the required amount of raw material, while simultaneously reducing energy consumption. CAM is now a system used in schools and lower educational purposes. CAM is a subsequent computer-aided process after computer-aided design (CAD) and sometimes computer-aided engineering (CAE), as the model generated in CAD and verified in CAE can be input into CAM software, which then controls the machine tool. CAM is used in many schools alongside CAD to create objects.
Mastercam is a suite of computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) and CAD/CAM software applications developed by CNC Software, LLC. Founded in Massachusetts in 1983, CNC Software are headquartered in Tolland, Connecticut.
Creo Parametric, formerly known, together with Creo Elements/Pro, as Pro/Engineer and Wildfire, is a solid modeling or CAD, CAM, CAE, and associative 3D modeling application, running on Microsoft Windows.

In machining, numerical control, also called computer numerical control (CNC), is the automated control of tools by means of a computer. It is used to operate tools such as drills, lathes, mills, grinders, routers and 3D printers. CNC transforms a piece of material into a specified shape by following coded programmed instructions and without a manual operator directly controlling the machining operation.

Tebis is a CAD/CAM software provided by Tebis AG, with headquarters in Martinsried near Munich/Germany. Development locations: Martinsried and Norderstedt, Germany International locations: China, Spain, France, Italy, Portugal, Sweden, United Kingdom, USA.

A Tool and Cutter Grinder is used to sharpen milling cutters and tool bits along with a host of other cutting tools.
A cutter location (CLData) refers to the position which a CNC milling machine has been instructed to hold a milling cutter by the instructions in the program.
Delcam is a supplier of advanced CAD/CAM software for the manufacturing industry. The company has grown steadily since being founded formally in 1977, after initial development work at Cambridge University, UK. It is now a global developer of product design and manufacturing software, with subsidiaries and joint ventures in North America, South America, Europe and Asia with a total staff of over 800 people and local support provided from over 300 re-seller offices worldwide. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange until 6 February 2014, when it was acquired by Autodesk. It now operates as a wholly owned, independently operated subsidiary of Autodesk.

Vero Software is a company based in Cheltenham, England, that specialises in CAD CAM.
Surfware, Inc. is a Camarillo, CA-based company involved in the development of CAD/CAM software.

STEP-NC is a machine tool control language that extends the ISO 10303 STEP standards with the machining model in ISO 14649, adding geometric dimension and tolerance data for inspection, and the STEP PDM model for integration into the wider enterprise. The combined result has been standardized as ISO 10303-238.
Cimatron is an Israeli software company that produces CAD/CAM software for manufacturing, toolmaking and CNC programming applications.

Multiaxis machining is a manufacturing process that involves tools that move in 4 or more directions and are used to manufacture parts out of metal or other materials by milling away excess material, by water jet cutting or by laser cutting. This type of machining was originally performed mechanically on large complex machines. These machines operated on 4, 5, 6, and even 12 axes which were controlled individually via levers that rested on cam plates. The cam plates offered the ability to control the tooling device, the table in which the part is secured, as well as rotating the tooling or part within the machine. Due to the machines size and complexity it took extensive amounts of time to set them up for production. Once computer numerically controlled machining was introduced it provided a faster, more efficient method for machining complex parts.

Sescoi is a developer of industrial software for computer-aided manufacturing, enterprise resource planning and extended enterprise productivity. Its WorkNC software is one of the market leaders in the CAD/CAM field and is used by more than 25% of companies in demanding countries such as Japan. Sescoi also develops WorkPLAN, a range of ERP software products for custom manufacturers and project based companies. As of 2011 Sescoi had more than 5000 customers and 11000 licenses sold worldwide. Sescoi and its products were acquired by Vero Software in January 2013.

SprutCAM X is a high-level Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software that provides off-line features for programming of various CNC machines used for cutting, wire electrical discharge (EDM), 2, 3, and multi axial machining.
PartXplore is a computer aided design (CAD) file viewer developed by Sescoi for reading, analyzing, and sharing 3D and 2D CAD files. It was introduced in 2008 and is supported from local Vero offices. The software is available as a viewer and an evaluation version.
SmartCAM is a suite of Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) and CAD/CAM software applications that uses toolpath modeling to assist CNC machinists in creating computer-numerically controlled (CNC) programs that direct CNC machine tools.
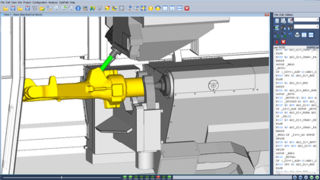
Vericut, is a software program used for simulating CNC machining. It is used to simulate tool motion and the material removal process, detecting errors or areas of inefficiency in NC programs. It was developed by CGTech Inc. and first released in 1988.
A Post Processor is a unique "driver" specific to a CNC machine, robot or mechanism; some machines start at different locations or require extra movement between each operation, the Post-Processor works with the CAM software or off-line programming software to make sure the G-Code output or program is correct for a specific Trademark machine Control Cabinet CAM software uses geometry from a CAD model and converts it to G-code. The CAM software analyzes the CAD model and determines what tooling and toolpaths will be used to mill the desired features. Doing so requires a CAM post processor that generates the exact G-code dialect used by the machine Control Module that is being targeted. An instance of such a translation is often referred to as a "post". There will be a different “post” for each G-code dialect the CAM software supports. Post Processors, rather the “post” uses an intermediate format that captures the G-code commands in a dialect-independent form. Most CAM software accomplishes this with an intermediate format called "CL.Data."













