
Wilkinson's catalyst is the common name for chloridotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I), a coordination complex of rhodium with the formula [RhCl(PPh3)3], where 'Ph' denotes a phenyl group). It is a red-brown colored solid that is soluble in hydrocarbon solvents such as benzene, and more so in tetrahydrofuran or chlorinated solvents such as dichloromethane. The compound is widely used as a catalyst for hydrogenation of alkenes. It is named after chemist and Nobel laureate Sir Geoffrey Wilkinson, who first popularized its use.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation.

Iron pentacarbonyl, also known as iron carbonyl, is the compound with formula Fe(CO)5. Under standard conditions Fe(CO)5 is a free-flowing, straw-colored liquid with a pungent odour. Older samples appear darker. This compound is a common precursor to diverse iron compounds, including many that are useful in small scale organic synthesis.

Metal carbonyls are coordination complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide ligands. Metal carbonyls are useful in organic synthesis and as catalysts or catalyst precursors in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation and Reppe chemistry. In the Mond process, nickel tetracarbonyl is used to produce pure nickel. In organometallic chemistry, metal carbonyls serve as precursors for the preparation of other organometallic complexes.

Triiron dodecarbonyl is the organoiron compound with the formula Fe3(CO)12. It is a dark green solid that sublimes under vacuum. It is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents to give intensely green solutions. Most low-nuclearity clusters are pale yellow or orange. Hot solutions of Fe3(CO)12 decompose to an iron mirror, which can be pyrophoric in air.The solid decomposes slowly in air, and thus samples are typically stored cold under an inert atmosphere. It is a more reactive source of iron(0) than iron pentacarbonyl.

Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [( 3P)2N]Cl, often abbreviated [(Ph3P)2N]Cl, where Ph is phenyl C6H5, or even abbreviated [PPN]Cl or [PNP]Cl or PPNCl or PNPCl, where PPN or PNP stands for (Ph3P)2N. This colorless salt is a source of the [(Ph3P)2N]+ cation, which is used as an unreactive and weakly coordinating cation to isolate reactive anions. [(Ph3P)2N]+ is a phosphazene.

Stryker's reagent ([(PPh3)CuH]6), also known as the Osborn complex, is a hexameric copper hydride ligated with triphenylphosphine. It is a brick red, air-sensitive solid. Stryker's reagent is a mildly hydridic reagent, used in homogeneous catalysis of conjugate reduction reactions of enones, enoates, and related substrates.
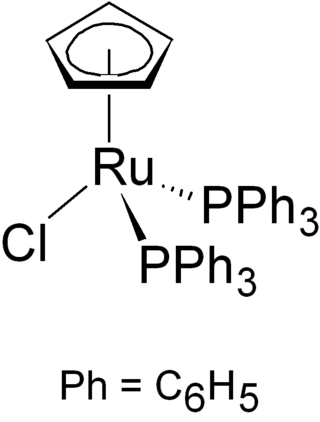
Chloro(cyclopentadienyl)bis(triphenylphosphine)ruthenium is the organoruthenium half-sandwich compound with formula RuCl(PPh3)2(C5H5). It as an air-stable orange crystalline solid that is used in a variety of organometallic synthetic and catalytic transformations. The compound has idealized Cs symmetry. It is soluble in chloroform, dichloromethane, and acetone.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. While iron adopts oxidation states from Fe(−II) through to Fe(VII), Fe(IV) is the highest established oxidation state for organoiron species. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.

Organoruthenium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to ruthenium chemical bond. Several organoruthenium catalysts are of commercial interest and organoruthenium compounds have been considered for cancer therapy. The chemistry has some stoichiometric similarities with organoiron chemistry, as iron is directly above ruthenium in group 8 of the periodic table. The most important reagents for the introduction of ruthenium are ruthenium(III) chloride and triruthenium dodecacarbonyl.

Iron tetracarbonyl dihydride is the organometallic compound with the formula H2Fe(CO)4. This compound was the first transition metal hydride discovered. The complex is stable at low temperatures but decomposes rapidly at temperatures above –20 °C.

A metal-phosphine complex is a coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0).

Carbonyl hydrido tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I) [Carbonyl(hydrido)tris(triphenylphosphane)rhodium(I)] is an organorhodium compound with the formula [RhH(CO)(PPh3)3] (Ph = C6H5). It is a yellow, benzene-soluble solid, which is used industrially for hydroformylation.
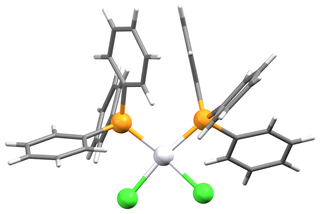
Bis(triphenylphosphine)platinum chloride is a metal phosphine complex with the formula PtCl2[P(C6H5)3]2. Cis- and trans isomers are known. The cis isomer is a white crystalline powder, while the trans isomer is yellow. Both isomers are square planar about the central platinum atom. The cis isomer is used primarily as a reagent for the synthesis of other platinum compounds.

Dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine)nickel(II) refers to a pair of metal phosphine complexes with the formula NiCl2[P(C6H5)3]2. The compound exists as two isomers, a paramagnetic dark blue solid and a diamagnetic red solid. These complexes function as catalysts for organic synthesis.

Bis(triphenylphosphine)rhodium carbonyl chloride is the organorhodium complex with the formula [RhCl(CO)(PPh3)2]. This complex of rhodium(I) is a bright yellow, air-stable solid. It is the Rh analogue of Vaska's complex, the corresponding iridium complex. With regards to its structure, the complex is square planar with mutually trans triphenylphosphine (PPh3) ligands. The complex is a versatile homogeneous catalyst.

Tricarbonylbis(triphenylphosphine)iron(0) is a coordination complex with the formula Fe(CO)3(PPh3)2 (Ph = C6H5). A yellow solid, this complex is derived from iron pentacarbonyl by replacement of two carbonyl ligands by triphenylphosphine (PPh3).
Potassium tetracarbonyliron hydride is the inorganic salt with the formula K[HFe(CO)4]. A pale yellow solid, it is the potassium salt of [HFe(CO)4]−, which is the conjugate base of iron tetracarbonyl dihydride:
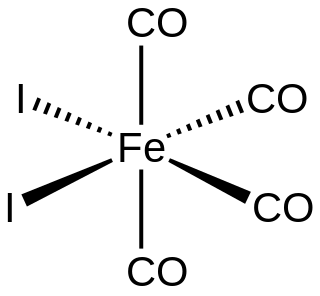
Iron tetracarbonyl diiodide is the inorganic compound with the formula FeI2(CO)4. The molecule features four carbonyl ligands and two iodides. It is a low-spin complex of ferrous iron. As confirmed by X-ray crystallography, the compound has cis stereochemistry. It is a black solid that is soluble in dichloromethane and related organic solvents.


















