
George Corley Wallace Jr. was an American politician who served as the 45th governor of Alabama for four terms. A member of the Democratic Party, he is best remembered for his staunch segregationist and populist views. During his tenure, he promoted "industrial development, low taxes, and trade schools." Wallace sought the United States presidency as a Democrat three times, and once as an American Independent Party candidate, unsuccessfully each time. Wallace opposed desegregation and supported the policies of "Jim Crow" during the Civil Rights Movement, declaring in his 1963 inaugural address that he stood for "segregation now, segregation tomorrow, segregation forever."

Henry Louis Bellmon was an American Republican politician from the U.S. State of Oklahoma. A member of the Oklahoma Legislature, he went on to become both the 18th and 23rd governor of Oklahoma, mainly in the 1960s and again in the 1980s, as well as a two-term United States Senator in the 1970s. He was the first Republican to serve as Governor of Oklahoma and, after his direct predecessor George Nigh, only the second governor to be reelected.

Lurleen Burns Wallace was the 46th governor of Alabama for 16 months from January 16, 1967 until her untimely death on May 7, 1968. She was the first wife of Alabama governor George Wallace, whom she succeeded as governor because the Alabama constitution forbade consecutive terms. She was Alabama's first female governor and was the only female governor to hold the position until Kay Ivey became the second woman to succeed to the office in 2017. She is also the only female governor in U.S. history to have died in office as well as being the first and so far currently to date only female Democrat to have serve as Alabama state governor in Alabama's state history. In 1973, she was posthumously inducted into the Alabama Women's Hall of Fame.

William Haydon Burns was an American politician. He was Mayor of Jacksonville, Florida from 1949 to 1965, and served as the 35th Governor of Florida from 1965 to 1967.
The 1968 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate. Held on November 5, the 34 seats of Class 3 were contested in regular elections. They coincided with the presidential election of the same year. Although Richard Nixon won the presidential election narrowly, the Republicans picked up five net seats in the Senate. This saw Republicans win a Senate seat in Florida for the first time since Reconstruction.

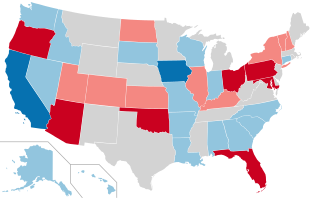
United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 3, 1998, in 36 states and two territories. Going into the election 24 of the seats were held by Republicans, 11 by Democrats, and one by an Independent. The elections changed the national balance of power by the loss of one Republican and the gain of one Independent, although it shifted in nine states. Democrats gained open seats in California and Iowa and defeated incumbents Fob James of Alabama and David Beasley of South Carolina, while Republicans won open seats in Colorado, Florida, Nebraska, and Nevada and the Reform Party won an open Republican governorship in Minnesota. By the end of the election, 23 seats were held by Republicans, 11 by Democrats, one by the Reform Party, and one by an Independent.
In the United States, a governor serves as the chief executive and commander-in-chief in each of the fifty states and in the five permanently inhabited territories, functioning as head of state and head of government therein. As such, governors are responsible for implementing state laws and overseeing the operation of the state executive branch. As state leaders, governors advance and pursue new and revised policies and programs using a variety of tools, among them executive orders, executive budgets, and legislative proposals and vetoes. Governors carry out their management and leadership responsibilities and objectives with the support and assistance of department and agency heads, many of whom they are empowered to appoint. A majority of governors have the authority to appoint state court judges as well, in most cases from a list of names submitted by a nominations committee.

United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 8, 1994, in 36 states and two territories. Many seats held by Democratic governors switched to the Republicans during the time known as the Republican Revolution. Indeed, this would be the first election since 1969 that Republicans won the majority of governorships.

United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 6, 1990, in 36 states and two territories. Most elected in these elections would serve for a 4-year term, while those in New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont would serve for a 2-year term. The elections coincided with the mid-term elections for the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. Heading into the elections, there were 20 seats held by Democrats and 16 held by Republicans. By the end of the elections, 19 seats would be held by a Democrat, 15 would be held by a Republican, and two would be held by other parties.

The 1970 Florida gubernatorial election took place on November 3, 1970, to determine the Governor and Lieutenant Governor of Florida, concurrent with the election to the United States Senate, elections to the United States House of Representatives, and various state and local elections.

The 1966 Florida gubernatorial election took place on November 8, 1966. During the primary election, the results from the Democratic Party was close among three of the four candidates. Thus, the top two Democrat candidates – incumbent Governor of Florida William "Haydon" Burns and Mayor of Miami Robert King High – competed in a runoff election on May 24, 1966. In an upset outcome, Robert King High was chosen over W. Haydon Burns as the Democratic Gubernatorial nominee. In contrast, the Republican primary was rather uneventful, with businessman Claude Roy Kirk Jr. easily securing the Republican nomination against Richard Muldrew. In the general election, Claude Kirk won by a margin of 55.13%-44.86% against Robert King High, becoming the first Republican Governor of Florida since the Reconstruction Era.
As of January 2023, Arizona's registered voters include 1,443,142 Republicans (34.7%), 1,270,613 Democrats (30.5%), 32,961 Libertarians (0.8%), and 1,415,020 "Other" (34.0%).

United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 4, 2014, in 36 states and three territories, concurrent with other elections during the 2014 United States elections.

United States gubernatorial elections were held on 3 November 1970, in 35 states and two territories.

The 2014 Arizona gubernatorial election was held on November 4, 2014, to elect the Governor of Arizona, concurrently with elections to the United States Senate in other states and elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections.

United States gubernatorial elections were held on 5 November 1968, in 21 states and one territory, concurrent with the House, Senate elections and presidential election. These were the last gubernatorial elections for Arizona, New Mexico, and Wisconsin to take place in a presidential election year, as all would extend their governors' terms from two to four years.
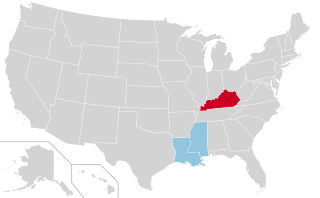
United States gubernatorial elections were held in November 1967, in three states.

The 1924 Arizona gubernatorial election took place on November 4, 1924. Despite being a Republican year nationally, President Coolidge's election in Arizona was rather close. He only took Arizona with 40% of the vote against Davis' 35% and La Follette's 23%. The closest Arizona gubernatorial election since 1916, Hunt's lead in votes would continue to decline.

United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 8, 2022, in 36 states and three territories. As most governors serve four-year terms, the last regular gubernatorial elections for all but two of the seats took place in 2018 U.S. gubernatorial elections. The gubernatorial elections took place concurrently with several other federal, state, and local elections, as part of the 2022 midterm elections.

The 2024 United States elections are scheduled to be held, in large part, on Tuesday, November 5, 2024. During this presidential election year, the President of the United States and Vice President will be elected. In addition, all 435 seats in the United States House of Representatives and 34 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate will be contested to determine the membership of the 119th United States Congress. Thirteen state and territorial governorships and numerous other state and local elections will also be contested.


















