Related Research Articles
The Republic of South Africa is a unitary parliamentary democratic republic. The President of South Africa serves both as head of state and as head of government. The President is elected by the National Assembly and must retain the confidence of the Assembly in order to remain in office. South Africans also elect provincial legislatures which govern each of the country's nine provinces.

Bophuthatswana, officially the Republic of Bophuthatswana, was a Bantustan that was declared (nominally) independent by the apartheid regime of South Africa in 1977. However, its independence, like the other Bantustans of was not recognized by any country other than South Africa.
Kgosi Lucas Manyane Mangope was the leader of the Bantustan (homeland) of Bophuthatswana. The territory he ruled over was distributed between the Orange Free State – what is now Free State – and North West Province. He was also the founder and leader of the United Christian Democratic Party, a political party based in the North West of South Africa.

The United Christian Democratic Party is a minor political party in South Africa. It was founded by Lucas Mangope, leader of the Bophuthatswana bantustan in 1997, as a successor to the Tswana National Party, and led by him for the first fifteen years of its existence. Mavis Matladi was elected as its leader on 29 January 2011 after the expulsion of Mangope. Matladi died in December 2011. Isaac Sipho Mfundisi was elected president on Saturday, 7 January 2012.


Elections in Guinea-Bissau take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a semi-presidential system. Both the President and the National People's Assembly are directly elected by voters.

The National Assembly is the directly elected house of the Parliament of South Africa, located in Cape Town, Western Cape. It consists of four hundred members who are elected every five years using a party-list proportional representation system where half of the members are elected proportionally from nine provincial lists and the remaining half from national lists so as to restore proportionality.

Elections in Kenya take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. The President, Senate and National Assembly are directly elected by voters, with elections organised by the Independent Electoral and Boundaries Commission (IEBC).

Elections in Zambia take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. The President and National Assembly are simultaneously elected for five-year terms.
1994 in South Africa saw the transition from South Africa's National Party government who had ruled the country since 1948 and had advocated the apartheid system for most of its history, to the African National Congress (ANC) who had been outlawed in South Africa since the 1950s for its opposition to apartheid. The ANC won a majority in the first multiracial election held under universal suffrage. Previously, only white people were allowed to vote. There were some incidents of violence in the Bantustans leading up to the elections as some leaders of the Bantusans opposed participation in the elections, while other citizens wanted to vote and become part of South Africa. There were also bombings aimed at both the African National Congress and the National Party and politically-motivated murders of leaders of the opposing ANC and Inkatha Freedom Party (IFP).

General elections were held in South Africa on 6 September 1989, the last under apartheid. Snap elections had been called early by the recently elected head of the National Party (NP), F. W. de Klerk, who was in the process of replacing P. W. Botha as the country's president, and his expected program of reform to include further retreat from the policy of apartheid. The creation of the Conservative Party had realigned the NP as a moderate party, now almost certain to initiate negotiations with the black opposition, with liberal opposition openly seeking a new constitutional settlement on liberal democratic and federalist principles.
The system of racial segregation and oppression in South Africa known as apartheid was implemented and enforced by many acts and other laws. This legislation served to institutionalize racial discrimination and the dominance by white people over people of other races. While the bulk of this legislation was enacted after the election of the National Party government in 1948, it was preceded by discriminatory legislation enacted under earlier British and Afrikaner governments. Apartheid is distinguished from segregation in other countries by the systematic way in which it was formalized in law.
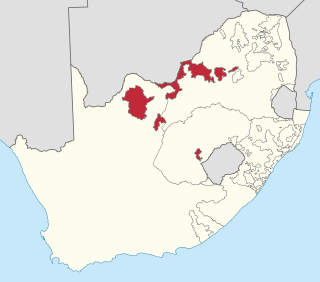
The 1994 Bophuthatswana crisis was a major political crisis which began after Lucas Mangope, the president of Bophuthatswana, a nominally independent South African bantustan created under apartheid, attempted to crush widespread labour unrest and popular demonstrations demanding the incorporation of the territory into South Africa pending non-racial elections later that year. Violent protests immediately broke out following President Mangope's announcement on 7 March that Bophuthatswana would boycott the South African general elections. This was escalated by the arrival of right-wing Afrikaner militias seeking to preserve the Mangope government. The predominantly black Bophuthatswana Defence Force and police refused to cooperate with the white extremists and mutinied, then forced the Afrikaner militias to leave Bophuthatswana.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Gambia on 29 March 2012. The ruling Alliance for Patriotic Reorientation and Construction (APRC) won 43 of the 48 elected seats.
Like South Africa's eight other provinces, the Northern Cape is governed by a parliamentary system, in which the Premier of the Northern Cape is elected by the Northern Cape Provincial Legislature and in turn selects the Northern Cape Executive Council. As in most other provinces, the African National Congress (ANC) has led the Northern Cape Provincial Government since the end of apartheid. In the most recent provincial election, held in 2019, the ANC won 18 of 30 seats in the provincial legislature and the Democratic Alliance was the official opposition in the legislature. Pursuant to the same election, Zamani Saul was elected Premier of the province.
Parliamentary elections were held in Bophuthatswana on 4 October 1972. The Bophuthatswana National Party led by Lucas Mangope won 20 of the 24 elected seats in the Legislative Assembly.
Parliamentary elections were held in Bophuthatswana in October 1982. The Bophuthatswana Democratic Party won all 72 of the elected seats in the National Assembly.
Parliamentary elections were held in Bophuthatswana on 22 October 1987. The Bophuthatswana Democratic Party won 66 of the 72 of the elected seats in the National Assembly.

The Gauteng Division of the High Court of South Africa is a superior court of law which has general jurisdiction over the South African province of Gauteng and the eastern part of North West province. The main seat of the division is at Pretoria, while a local seat at Johannesburg has concurrent jurisdiction over the southern parts of Gauteng. Dunstan Mlambo has been the Judge President of the division since 1 November 2012.
Kgomotso Paul Harry Ditshetelo was a South African politician who represented the United Christian Democratic Party (UCDP) in the National Assembly from 1999 to 2009. He was also the deputy president of the UCDP from 1998 to 2011. During apartheid, he was a politician and civil servant in Bophuthatswana.
References
- 1 2 3 Elections in South Africa's Apartheid-Era Homelands "Bantustans" African Elections Database