
The Boeing Vertol CH-46 Sea Knight is a medium-lift tandem-rotor transport helicopter powered by twin turboshaft engines. It was designed by Vertol and manufactured by Boeing Vertol following Vertol's acquisition by Boeing.

The Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk is a four-blade, twin-engine, medium-lift utility military helicopter manufactured by Sikorsky Aircraft. Sikorsky submitted the S-70 design for the United States Army's Utility Tactical Transport Aircraft System (UTTAS) competition in 1972. The Army designated the prototype as the YUH-60A and selected the Black Hawk as the winner of the program in 1976, after a fly-off competition with the Boeing Vertol YUH-61.

The Sikorsky MH-60G/HH-60G Pave Hawk is a four-blade, twin-engine, medium-lift utility military helicopter manufactured by Sikorsky Aircraft. It is a derivative of the UH-60 Black Hawk and incorporates the US Air Force PAVE electronic systems program. The HH-60/MH-60 is a member of the Sikorsky S-70 family.
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1963:

Hurlburt Field is a United States Air Force installation located in Okaloosa County, Florida, immediately west of the town of Mary Esther. It is part of the greater Eglin Air Force Base reservation and is home to Headquarters Air Force Special Operations Command (AFSOC), the 1st Special Operations Wing (1 SOW), the USAF Special Operations School (USAFSOS) and the Air Combat Command's (ACC) 505th Command and Control Wing. It was named for First Lieutenant Donald Wilson Hurlburt, who died in a crash at Eglin. The installation is nearly 6,700 acres (27 km2) and employs nearly 8,000 military personnel.

The Sikorsky H-34 "Choctaw" is an American piston-engined military helicopter originally designed by Sikorsky as an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) aircraft for the United States Navy. It has seen extended use when adapted to turbine power by the British licensee as the Westland Wessex and Sikorsky as the later S-58T.

Marine Light Attack Helicopter Squadron 167 (HMLA-167) is a United States Marine Corps helicopter squadron consisting of AH-1W SuperCobra attack helicopters and UH-1Y Venom utility helicopters. Known as the "Warriors", they are based at Marine Corps Air Station New River, North Carolina and fall under the command of Marine Aircraft Group 29 (MAG-29) and the 2nd Marine Aircraft Wing.

United States Marine Forces Special Operations Command (MARSOC) is a component command of the United States Special Operations Command (SOCOM) that comprises the Marine Corps' contribution to SOCOM. Its core capabilities are direct action, special reconnaissance and foreign internal defense. MARSOC has also been directed to conduct counter-terrorism and information operations.

Marine Medium Tiltrotor Squadron 261 (VMM-261) is a United States Marine Corps tiltrotor squadron consisting of MV-22 Osprey transport aircraft. The squadron, known as the "Raging Bulls", is based at Marine Corps Air Station (MCAS) New River, North Carolina and typically falls under the command of Marine Aircraft Group 26 (MAG-26) and the 2nd Marine Aircraft Wing. They are the fourth squadron in the Marine Corps to transition to the MV-22 Osprey.

Marine Aircraft Group 16 is a United States Marine Corps aviation unit based at Marine Corps Air Station Miramar that is currently composed of four V-22 Osprey squadrons, four CH-53 Super Stallion squadrons, one Personnel Support Detachment, and an aviation logistics squadron. The group falls under the command of the 3rd Marine Aircraft Wing and the I Marine Expeditionary Force.

Marine Medium Tiltrotor Squadron 162 (VMM-162) is a United States Marine Corps tiltrotor squadron consisting of MV-22 Osprey transport aircraft. The squadron, known as the "Golden Eagles", is based at Marine Corps Air Station New River, North Carolina and falls under the command of Marine Aircraft Group 26 (MAG-26) and the 2nd Marine Aircraft Wing. HMM-162 officially stood down December 9, 2005 to begin the process of transitioning to the MV-22 Osprey. On August 31, 2006, the squadron was reactivated as the second operational Osprey squadron in the Marine Corps.

The 171st Special Operations Aviation Squadron is an Australian Army helicopter squadron equipped with NHIndustries MRH-90 Taipan helicopters and provides support to the Special Operations Command. The squadron is based at Luscombe Airfield, Holsworthy Barracks, Sydney and forms part of the 6th Aviation Regiment as the regiment's sole operational squadron. In December 2021, the squadron completed its transition from the retiring Sikorsky S70A Black Hawk helicopter to the MRH-90 Taipan helicopter.

Bryan Douglas "Doug" Brown is a retired four-star United States Army general. He retired in 2007 after four decades of military service. In his final assignment, he served as the seventh commander of U.S. Special Operations Command (USSOCOM), from September 2, 2003, until July 9, 2007. As USSOCOM's commander, he was responsible for all unified special operations forces (SOF), both active duty and reserve.

The Marine Raider Regiment (MRR), formerly known as the Marine Special Operations Regiment (MSOR), is a special operations force of the United States Marine Corps, which is a part of Marine Corps Special Operations Command (MARSOC). Renamed for its predecessor, the World War II Marine Raiders, this unit is the principal combat component of MARSOC, which is the Marine Corps' contribution to the United States Special Operations Command (USSOCOM).
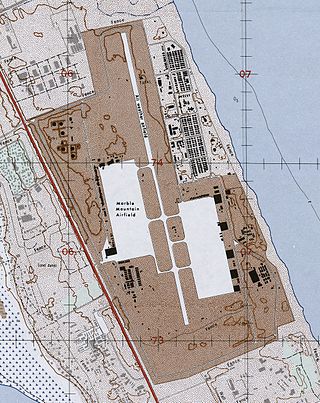
Marble Mountain Air Facility (MMAF), also known as Da Nang East Airfield, Marble Mountain Army Airfield and Nuoc Man Airfield, was an aviation facility used primarily by the United States Marine Corps during the Vietnam War. It was a helicopter facility that was constructed in August 1965 and served as home to Marine Aircraft Group 16 (MAG-16), the 5th Special Forces Group and an assortment of other squadrons until May 1971. It was controlled by the United States Army from May 1971 to August 1972 and finally by the Republic of Vietnam Air Force (RVNAF) from 29 August 1972 to 29 March 1975 when it fell to the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN). It was in Quảng Nam Province 5 miles (8 km) southeast of Da Nang Air Base on a strip of beach between China Beach and the Marble Mountains.

The Sikorsky S-97 Raider is a high-speed scout and attack compound helicopter based on the Advancing Blade Concept (ABC) with a coaxial rotor system under development by Sikorsky Aircraft. Sikorsky planned to offer it for the United States Army's Armed Aerial Scout program, along with other possible uses. The S-97 made its maiden flight on 22 May 2015.

On 12 May 2015, a US Marine Corps Bell UH-1Y Venom of Camp Pendleton-based HMLA-469 squadron crashed in the Charikot region of Nepal during Operation Sahayogi Haat, a humanitarian relief effort following the earthquake that had struck the region earlier. All 13 occupants were killed.

Brothers In Arms Foundation (BIAF) is a charity and veterans service organization that offers a variety of programs, services, and events for wounded veterans. It operates as a nonprofit 501(c)(3) organization.

Operation Shufly was a United States Marine Corps operation to improve the mobility of Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) forces in the early phases of the Vietnam War from 1962 to 1965. Beginning on 15 April 1962, Marine helicopter squadrons, associated maintenance units and air traffic control detachments deployed to Sóc Trăng Airfield in the Mekong Delta and later to Da Nang Air Base rotating every four months in order to provide assault support and CASEVAC assistance during combat operations. By early 1965 half of the Marine Corps' medium helicopter squadrons had rotated through a "Shufly" deployment. The operation ended on 8 March 1965, when the 9th Marine Expeditionary Brigade came ashore in Vietnam as the vanguard of the United States' commitment of large numbers of regular combat units into South Vietnam.




















