
From May 21 to May 26, 2011, one of the largest tornado outbreaks on record affected the Midwestern and Southern regions of the United States. A six-day tornado outbreak sequence, most of the tornadoes developed in a corridor from Lake Superior southwest to central Texas, while isolated tornadoes occurred in other areas. An especially destructive EF5 tornado destroyed one-third of Joplin, Missouri, resulting in 158 deaths and over 1,000 injuries. The Joplin tornado was the deadliest in the United States since April 9, 1947, when an intense tornado killed 181 in the Woodward, Oklahoma, area. Tornado-related deaths also occurred in Arkansas, Kansas, Minnesota, and Oklahoma. Overall, the tornado outbreak resulted in 186 deaths, 8 of those non-tornadic, making it second only to the 2011 Super Outbreak as the deadliest since 1974. It was the second costliest tornado outbreak in United States history behind that same April 2011 outbreak, with insured damage estimated at $4–7 billion.

This page documents the tornadoes and tornado outbreaks of 2012. Extremely destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Bangladesh, Brazil and eastern India, but they can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also appear regularly in neighboring southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer season, and somewhat regularly in Europe, Asia, Argentina, and Australia.

This page documents the tornadoes and tornado outbreaks of 2013. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Bangladesh, Brazil and Eastern India, but they can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also appear regularly in neighboring southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer season, and somewhat regularly in Europe, Asia, and Australia.

On Sunday, February 10, 2013, a large EF4 multiple-vortex wedge tornado devastated the cities of West Hattiesburg, Hattiesburg, and Petal, Mississippi. The tornado was one of eight that touched down in southern Mississippi and southwestern Alabama that day. It reached a maximum path width of 0.75 miles (1.21 km) in its path through the Hattiesburg area and reached estimated maximum sustained winds of 170 mph (270 km/h) in Oak Grove neighborhood of West Hattiesburg. It destroyed many structures and impacted University of Southern Mississippi and two high schools. Mississippi was declared a federal disaster area by President Barack Obama, and a state of emergency was issued by Mississippi Governor Phil Bryant.

This page documents the tornadoes and tornado outbreaks of 2014. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Bangladesh, Brazil, and Eastern India, but they can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also appear regularly in neighboring southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer season, and somewhat regularly in Europe, Asia, and Australia.

This page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2015. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Bangladesh, Brazil and Eastern India, but they can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, and Australia. Tornadic events are often accompanied with other forms of severe weather including strong thunderstorms, winds and hail. There were 1,178 tornadoes reported in the United States in 2015 according to the Storm Prediction Center (SPC), of which at least 1,178 have been confirmed. Worldwide, 109 fatalities have been reported: 45 in Pakistan, 36 in the United States, 14 in Mexico, seven in China, three in Myanmar, two in Brazil and one each in Italy and Russia.

This page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2017. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Brazil, Bangladesh, and Eastern India, but they can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina and Australia. Tornadic events are often accompanied with other forms of severe weather, including strong thunderstorms, strong winds, and hail. There were 1,522 reports of tornadoes in the United States in 2017, of which 1,418 were confirmed. Worldwide, 43 fatalities were confirmed in 2017: 35 in the United States, five in China, two in Paraguay, and one in Brazil.

The tornado outbreak of February 28 – March 1, 2017 was a widespread and significant outbreak of tornadoes and severe weather that affected the Midwestern United States at the end of February 2017 and beginning of March. Fueled by the combination of ample instability, strong wind shear, and rich low-level moisture, the event led to 71 confirmed tornadoes and thousands of other non-tornadic severe weather reports. The most notable aspect of the outbreak was a long-tracked EF4 tornado—the first violent tornado of 2017 and the first violent tornado during the month of February since the 2013 Hattiesburg, Mississippi tornado—that tracked from Perryville, Missouri to near Christopher, Illinois, killing one person. Three EF3 tornadoes were recorded during the event, including one that caused two fatalities in Ottawa, Illinois, one that caused a fatality near Crossville, and one that heavily damaged or destroyed homes in and around Washburn. In addition to the deaths, 38 people were injured by tornadoes and an additional 30 were injured by non-tornadic impacts, mainly by fallen trees.

This page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2018. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Brazil, Bangladesh and Eastern India, but they can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina and Australia. Tornadic events are often accompanied with other forms of severe weather, including strong thunderstorms, strong winds, and hail. There were 1,169 preliminary filtered reported tornadoes and 1,121 confirmed tornadoes in the United States in 2018. Worldwide, 17 tornado-related deaths were confirmed; 10 in the United States, four in Brazil, two in Indonesia, and one in Canada.

The tornado outbreak sequence of May 2019 was a prolonged series of destructive tornadoes and tornado outbreaks affecting the United States over the course of nearly two weeks, producing a total of 400 tornadoes, including 53 significant events (EF2+). Eighteen of these were EF3 tornadoes, spanning over multiple states, including Nebraska, Kansas, Texas, Missouri, Oklahoma, Indiana, Iowa, and Ohio, with additional tornadoes confirmed across a region extending from California to New Jersey. Two EF4 tornadoes occurred, one in Dayton, Ohio, and the other in Linwood, Kansas. Four tornadoes during this outbreak were fatal, causing a total of eight fatalities. The deadliest of these occurred on May 22 near Golden City, Missouri, where an EF3 tornado took three lives, including an elderly couple in their eighties. The damaging series of tornadoes that occurred in Indiana and Ohio on the evening of May 27 during this event is sometimes locally referred to as the Memorial Day tornado outbreak of 2019, which became the fourth costliest weather event in Ohio history. The near continuous stream of systems also produced to widespread flash and river flooding, along with damaging winds and large hail.

This page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2020. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Argentina, Brazil, Bangladesh, and eastern India, but can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina, Australia and New Zealand. Tornadic events are often accompanied by other forms of severe weather, including strong thunderstorms, strong winds, and hail. There were 1,243 preliminary filtered reported tornadoes in 2020 in the United States in 2020, and 1,086 confirmed tornadoes in the United States in 2020. Worldwide, at least 93 tornado-related deaths were confirmed with 78 in the United States, eight in Vietnam, two each in Canada, Indonesia, and Mexico, and one in South Africa.

A small but deadly tornado outbreak affected West and Middle Tennessee on the night of March 2 and into the morning of March 3, 2020, including a high-end EF3 tornado that hit Nashville and Mount Juliet, becoming the 6th costliest tornado in United States history, and a violent EF4 tornado that impacted areas in and just west of Cookeville. A total of 25 people were killed by the tornadoes, with an additional 309 being injured, and more than 70,000 lost electricity. The path of the Nashville tornado was very similar to the one that hit East Nashville in 1998. A few additional tornadoes were also confirmed in Alabama, southeastern Missouri, and western Kentucky. Total damage from the event reached $1.607 billion according to the National Centers for Environmental Information.

A widespread and deadly tornado outbreak affected the Southeastern United States on Easter Sunday and Monday, April 12–13, 2020. Several tornadoes were responsible for prompting tornado emergencies, including the first one to be issued by the National Weather Service in Charleston, South Carolina. A large squall line formed and tracked through the mid-Atlantic on April 13, prompting more tornado warnings and watches. A total of 15 watches were produced during the course of the event, two of which were designated Particularly Dangerous Situations.

This page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2021. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Argentina, Brazil, Bangladesh, and Eastern India, but can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina, Australia and New Zealand. Tornadic events are often accompanied by other forms of severe weather, including strong thunderstorms, strong winds, and hail. Worldwide, 150 tornado-related deaths were confirmed with 103 in the United States, 28 in China, six in the Czech Republic, four in Russia, three in Italy, two in India, and one each in Canada, New Zealand, Indonesia, and Turkey.

On the afternoon of March 3, 2019, a violent and long-tracked EF4 tornado struck portions of eastern Alabama and western Georgia, causing extreme damage along its path. This tornado was the deadliest tornado in the United States since the 2013 Moore tornado, killing 23 and injuring 97. This tornado was part of a larger tornado outbreak that affected the Southeastern United States on this same day. This outbreak produced numerous tornadoes across Alabama and Georgia. This was the deadliest and strongest tornado of this outbreak, and the 8th deadliest in Alabama state history.

A deadly late-season tornado outbreak, the deadliest on record in December, produced catastrophic damage and numerous fatalities across portions of the Southern United States and Ohio Valley from the evening of December 10 to the early morning of December 11, 2021. The event developed as a trough progressed eastward across the United States, interacting with an unseasonably moist and unstable environment across the Mississippi Valley. Tornado activity began in northeastern Arkansas, before progressing into Missouri, Illinois, Tennessee, and Kentucky.

During the late evening of Friday, December 10, 2021, a violent, long-tracked EF4 tornado moved across Western Kentucky, producing severe to catastrophic damage in numerous towns, including Mayfield, Princeton, Dawson Springs, and Bremen. The second significant tornado in an exceedingly long-tracked tornado family, this tornado began just inside northern Obion County, Tennessee, a few miles after another long-tracked tornado – which traveled through northeast Arkansas, the Missouri Bootheel, and northwest Tennessee – dissipated in western Obion County. After crossing into Kentucky, the tornado moved through eleven counties of the Jackson Purchase and Western Coal Field regions while at times becoming wrapped in rain during its almost three-hour lifespan that covered 165.6 miles (266.5 km). It was the deadliest and longest-tracked tornado in an outbreak that produced numerous strong tornadoes in several states; 57 fatalities were confirmed in the tornado.
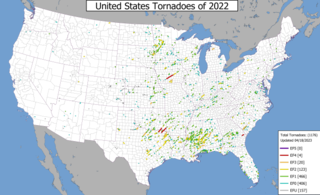
This page documents notable tornadoes and tornado outbreaks worldwide in 2022. Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Argentina, Brazil, Bangladesh, and Eastern India, but can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions. Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina, Australia and New Zealand. Tornadic events are often accompanied by other forms of severe weather, including strong thunderstorms, strong winds, and hail. Worldwide, 32 tornado-related deaths were confirmed: 23 in the United States, three in China, two each in Poland and Russia, and one each in the Netherlands and Ukraine.
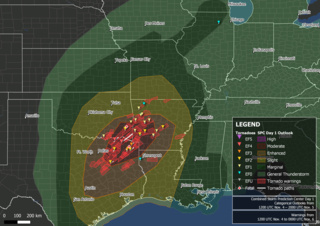
A significant late-season tornado outbreak took place on November 4, 2022, across Northeast Texas, southwestern Arkansas, southeastern Oklahoma, and northwestern Louisiana with multiple large, destructive tornadoes occurring over a span of several hours. Major damage was reported in Sulphur Springs, Powderly, Caviness, Paris, Cason, Daingerfield, Athens, New Boston, Texas, and Idabel, Oklahoma, with the latter two communities being placed under tornado emergencies. Two fatalities occurred in Cason, Texas, and Pickens, Oklahoma respectively. Numerous PDS tornado warnings were issued as well. An additional tornado embedded within a narrow, but intense line of showers with damaging winds was also confirmed in Illinois the following morning as the system progressed eastward. Strong winds affected most of the western Great Lakes throughout the day before moving into Canada that evening. Two fatalities and at least 34 injuries were confirmed from tornadoes, and an additional fatality occurred near Stilwell, Oklahoma from drowning.

On the evening of March 24, 2023, a large and destructive tornado struck the communities of Rolling Fork and Silver City, Mississippi, killing 17 people and injuring at least 165 others. The tornado was the strongest and deadliest of a widespread tornado outbreak in the Southern United States between March 24–27, 2023. The tornado damaged or destroyed much of Rolling Fork, with the most intense damage leading the National Weather Service to assign a rating of high-end EF4 on the Enhanced Fujita scale, with maximum windspeeds estimated at 195 miles per hour (314 km/h).

























