
An anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once. For example, the word anagram itself can be rearranged into nag a ram, as well as the word binary into brainy and the word adobe into abode.
Collation is the assembly of written information into a standard order. Many systems of collation are based on numerical order or alphabetical order, or extensions and combinations thereof. Collation is a fundamental element of most office filing systems, library catalogs, and reference books.

Scrabble is a word game in which two to four players score points by placing tiles, each bearing a single letter, onto a game board divided into a 15×15 grid of squares. The tiles must form words that, in crossword fashion, read left to right in rows or downward in columns and are included in a standard dictionary or lexicon.
In cryptography, a transposition cipher is a method of encryption which scrambles the positions of characters (transposition) without changing the characters themselves. Transposition ciphers reorder units of plaintext according to a regular system to produce a ciphertext which is a permutation of the plaintext. They differ from substitution ciphers, which do not change the position of units of plaintext but instead change the units themselves. Despite the difference between transposition and substitution operations, they are often combined, as in historical ciphers like the ADFGVX cipher or complex high-quality encryption methods like the modern Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
Word games are spoken, board, or video games often designed to test ability with language or to explore its properties.
Constrained writing is a literary technique in which the writer is bound by some condition that forbids certain things or imposes a pattern.

A crossword is a word puzzle that usually takes the form of a square or a rectangular grid of white- and black-shaded squares. The goal is to fill the white squares with letters, forming words or phrases, by solving clues which lead to the answers. In languages that are written left-to-right, the answer words and phrases are placed in the grid from left to right ("across") and from top to bottom ("down"). The shaded squares are used to separate the words or phrases.
A cryptic crossword is a crossword puzzle in which each clue is a word puzzle. Cryptic crosswords are particularly popular in the United Kingdom, where they originated, Ireland, Israel, the Netherlands, and in several Commonwealth nations, including Australia, Canada, India, Kenya, Malta, New Zealand, and South Africa. Compilers of cryptic crosswords are commonly called "setters" in the UK and "constructors" in the US. Particularly in the UK, a distinction may be made between cryptics and "quick" crosswords, and sometimes two sets of clues are given for a single puzzle grid.
The Danish and Norwegian alphabets, together called the Dano-Norwegian alphabet, is the set of symbols, forming a variant of the Latin alphabet, used for writing the Danish and Norwegian languages. It has consisted of the following 29 letters since 1917 (Norwegian) and 1948 (Danish):
The Hungarian alphabet is an extension of the Latin alphabet used for writing the Hungarian language.
Alphabetical order is a system whereby character strings are placed in order based on the position of the characters in the conventional ordering of an alphabet. It is one of the methods of collation. In mathematics, a lexicographical order is the generalization of the alphabetical order to other data types, such as sequences of numbers or other ordered mathematical objects.

Jumble is a word puzzle with a clue, a drawing illustrating the clue, and a set of words, each of which is “jumbled” by scrambling its letters. A solver reconstructs the words, and then arranges letters at marked positions in the words to spell the answer phrase to the clue. The clue, and sometimes the illustration, provide hints about the answer phrase, which frequently uses a homophone or pun.

Fill-Ins, also known as Fill-It-Ins or Word Fill-Ins, are a variation of the common crossword puzzle in which words, rather than clues, are given, and the solver must work out where to place them. Fill-Ins are common in puzzle magazines along with word searches, cryptograms, and other logic puzzles. Some people consider Fill-Ins to be an easier version of the crossword. Since the Fill-In requires no outside knowledge of specific subjects, one can solve the puzzle in another language.
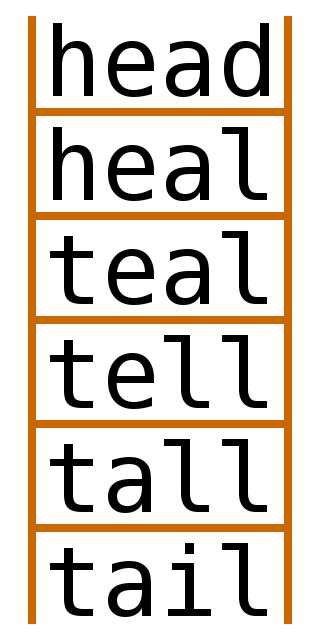
Word ladder is a word game invented by Lewis Carroll. A word ladder puzzle begins with two words, and to solve the puzzle one must find a chain of other words to link the two, in which two adjacent words differ by one letter.

Crosswords DS and as Nintendo presents: Crossword Collection in PAL regions is a puzzle video game developed by American studio Nuevo Retro games released by Nintendo for the Nintendo DS handheld video game console. It was previously released in Australia as CrossworDS but a new OFLC entry confirms that Nintendo Australia is re-releasing it with a European localization. It was first released in North America, and has since been released in Australia. Crosswords DS features over 1,000 crossword puzzles that the player solves by using the stylus. Despite the title, it also features word search puzzles and anagram puzzles. It makes use of similar handwriting mechanics that the Brain Age titles make use of. Crosswords DS is included in the Touch! Generations series of titles, which includes such popular games as Brain Age: Train Your Brain in Minutes a Day! and Nintendogs. The background music was composed by Fabian Del Priore.
Scrabble variants are games created by changing the normal Scrabble rules or equipment.

An acrostic is a type of word puzzle, related somewhat to crossword puzzles, that uses an acrostic form. It typically consists of two parts. The first part is a set of lettered clues, each of which has numbered blanks representing the letters of the answer. The second part is a long series of numbered blanks and spaces, representing a quotation or other text, into which the answers for the clues fit. In some forms of the puzzle, the first letters of each correct clue answer, read in order from clue A on down the list, will spell out the author of the quote and the title of the work it is taken from; this can be used as an additional solving aid.
A letter is a segmental symbol of a phonemic writing system. The inventory of all letters forms an alphabet. Letters broadly correspond to phonemes in the spoken form of the language, although there is rarely a consistent and exact correspondence between letters and phonemes.

Alphablocks is a British interactive children's computer-animated television programme that debuted on CBeebies on 25 January 2010. Alphablocks is designed to teach preschoolers to spell with the use of four families of animated blocks known as Alphablocks, who represent each of their letters referred to as Alphalings. The show is animated by Blue-Zoo and produced by Alphablocks Ltd for the BBC. Once the Alphablocks discover that whenever they make a word it comes to life, many adventures can happen. This is meant to help preschoolers with learning the alphabet, spelling, reading and writing.

An anatree is a data structure designed to solve anagrams. Solving an anagram is the problem of finding a word from a given list of letters. These problems are commonly encountered in word games like Scrabble or in newspaper crossword puzzles. The problem for the wordwheel also has the condition that the central letter appear in all the words framed with the given set. Some other conditions may be introduced regarding the frequency of each of the letters in the given input string. These problems are classified as Constraint satisfaction problem in computer science literature.









