Related Research Articles
The meaning of the word American in the English language varies according to the historical, geographical, and political context in which it is used. American is derived from America, a term originally denoting all of the Americas. In some expressions, it retains this Pan-American sense, but its usage has evolved over time and, for various historical reasons, the word came to denote people or things specifically from the United States of America.

A dictionary is a listing of lexemes from the lexicon of one or more specific languages, often arranged alphabetically, which may include information on definitions, usage, etymologies, pronunciations, translation, etc. It is a lexicographical reference that shows inter-relationships among the data.
A thesaurus or synonym dictionary is a reference work for finding synonyms and sometimes antonyms of words. They are often used by writers to help find the best word to express an idea:
...to find the word, or words, by which [an] idea may be most fitly and aptly expressed

The Royal Spanish Academy is Spain's official royal institution with a mission to ensure the stability of the Spanish language. It is based in Madrid, Spain, and is affiliated with national language academies in 22 other hispanophone nations through the Association of Academies of the Spanish Language. The RAE's emblem is a fiery crucible, and its motto is Limpia, fija y da esplendor.
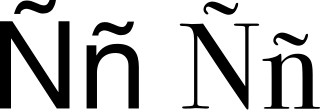
Ñ, or ñ, is a letter of the modern Latin alphabet, formed by placing a tilde on top of an upper- or lower-case N. It became part of the Spanish alphabet in the eighteenth century when it was first formally defined, but it has subsequently been used in other languages, such as Galician, Asturian, the Aragonese Grafía de Uesca, Basque, Chavacano, some Philippine languages, Chamorro, Guarani, Quechua, Mapudungun, Mandinka, and Tetum alphabets, as well as in Latin transliteration of Tocharian and many Indian languages, where it represents or. It represents in Crimean Tatar, Kazakh, ALA-LC romanization for Turkic languages, the Common Turkic Alphabet, Nauruan and romanized Quenya. In Breton and in Rohingya, it denotes nasalization of the preceding vowel. Many Portuguese speakers use this letter in informal internet language to represent the word não (no).

A vernacular or vernacular language refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, normally spoken informally rather than written, and seen as of lower status than more codified forms. It may vary from more prestigious speech varieties in different ways, in that the vernacular can be a distinct stylistic register, a regional dialect, a sociolect, or an independent language. Vernacular is a term for a type of speech variety, generally used to refer to a local language or dialect, as distinct from what is seen as a standard language. The vernacular is contrasted with higher-prestige forms of language, such as national, literary, liturgical or scientific idiom, or a lingua franca, used to facilitate communication across a large area.

Che is an interjection commonly used in Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Rio Grande do Sul (Brazil) and Valencia (Spain), signifying "hey!", "fellow", "guy". Che is mainly used as a vocative to call someone's attention, but it is often used as filler too. The Argentine revolutionary Ernesto "Che" Guevara earned his nickname from his frequent use of the expression, which was perceived as foreign by his Cuban comrades.

Charro has several meanings, but it generally refers to Mexican horse riders, who maintain traditional dress, such as some form of sombrero, which in Mexican Spanish are called sombrero de charro. The charros could also be thought of as old Mexican cowboys who dress like such, although more modern dress is now seen on those who still work the ranches (rancheros). See also, vaquero.

Spanish orthography is the orthography used in the Spanish language. The alphabet uses the Latin script. The spelling is fairly phonemic, especially in comparison to more opaque orthographies like English, having a relatively consistent mapping of graphemes to phonemes; in other words, the pronunciation of a given Spanish-language word can largely be predicted from its spelling and to a slightly lesser extent vice versa. Notable features of Spanish punctuation include the lack of the serial comma and the use of inverted question and exclamation marks: ⟨¿⟩ ⟨¡⟩.

Standard Spanish is a linguistic variety, or lect, of the Spanish language, dominantly used in its written form. There are different standard forms, including the Mexican standard, the Latin American standard, the Peninsular standard or European standard and the Rioplatense standard, in addition to the standard forms developed by international organizations and multinational companies. The term norma culta, 'cultivated norm' is often applied to standard Spanish. The RAE defines standard Spanish as the norm of cultivated, formal speech.
Portuguese and Spanish, although closely related Romance languages, differ in many aspects of their phonology, grammar and lexicon. Both belong to a subset of the Romance languages known as West Iberian Romance, which also includes several other languages or dialects with fewer speakers, all of which are mutually intelligible to some degree. A 1949 study by Italian-American linguist Mario Pei, analyzing the degree of difference from a language's parent by comparing phonology, inflection, syntax, vocabulary, and intonation, indicated the following percentages : In the case of Spanish it was 20%, the third closest Romance language to Latin, only behind Sardinian and Italian. Portuguese was 31%, making it the second furthest language from Latin after French.

The Diccionario de la lengua española, previously known as Diccionario de la Real Academia Española, is produced, edited, and published by the Royal Spanish Academy (RAE) with participation of the Association of Academies of the Spanish Language. It was first published in 1780, and subsequent editions have been published about once a decade. The twenty-third edition was published in 2014; it is available online, incorporating modifications to be included in the twenty-fourth print edition.
In Romani culture, a gadjo (masculine) or gadji (feminine) is a person who has no Romanipen. This usually corresponds to not being an ethnic Romani, but it can also be an ethnic Romani who does not live within Romani culture. It is often used by Romanies to address or denote outsider neighbors living within or very near their community.
Gabacho is a word used in the Spanish language to describe foreigners of different origins in previous history. Its origin is in Peninsular Spain, as a derogatory synonym of "French".

Quixotism is impracticality in pursuit of ideals, especially those ideals manifested by rash, lofty and romantic ideas or extravagantly chivalrous action. It also serves to describe an idealism without regard to practicality. An impulsive person or act might be regarded as quixotic.

Google Dictionary is an online dictionary service of Google that can be accessed with the "define" operator and other similar phrases in Google Search. It is also available in Google Translate and in the form of an extension for Google Chrome. The dictionary content is licensed from Oxford University Press's OxfordDictionaries.com. It is available in different languages such as English, Spanish and French. The service also contains pronunciation audio, Google Translate, word origin chart, Ngram Viewer, and word games among other features for the English-language version. Originally available as a standalone service it was integrated into Google Search with the separate service being discontinued in August 2011.

Taíno is an extinct Arawakan language that was spoken by the Taíno people of the Caribbean. At the time of Spanish contact, it was the most common language throughout the Caribbean. Classic Taíno was the native language of the Taíno tribes living in the northern Lesser Antilles, Puerto Rico, the Turks and Caicos Islands, and most of Hispaniola, and expanding into Cuba. The Ciboney dialect is essentially unattested, but colonial sources suggest it was very similar to Classic Taíno, and was spoken in the westernmost areas of Hispaniola, the Bahamas, Jamaica, and most of Cuba.

The Tesoro de la lengua castellana o española is a dictionary of the Spanish language, written by Sebastián de Covarrubias in 1611.
Elle is a fringe third-person gender-neutral pronoun in Spanish intended as an alternative to the gender-specific él ("he") and ella ("she"). It is supposed to be used when the gender of a person is not known or when it is not desirable to specify the person as either "he" or "she". It is not endorsed by any Spanish-language academy or institution. It is an equivalent of the singular they pronoun when used for gendering purposes.
References
This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2008) |