
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects. Classically, the four defects are:

Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a medical condition in which the ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth: this allows a portion of oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs through the aorta, which has a higher blood pressure, to the pulmonary artery, which has a lower blood pressure. Symptoms are uncommon at birth and shortly thereafter, but later in the first year of life there is often the onset of an increased work of breathing and failure to gain weight at a normal rate. With time, an uncorrected PDA usually leads to pulmonary hypertension followed by right-sided heart failure.

dextro-Transposition of the great arteries is a potentially life-threatening birth defect in the large arteries of the heart. The primary arteries are transposed.

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this does not naturally close after birth it is referred to as a patent (open) foramen ovale (PFO). It is common in patients with a congenital atrial septal aneurysm (ASA).

A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms are variable and may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure.

A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. The extent of the opening may vary from pin size to complete absence of the ventricular septum, creating one common ventricle. The ventricular septum consists of an inferior muscular and superior membranous portion and is extensively innervated with conducting cardiomyocytes.

Eisenmenger syndrome or Eisenmenger's syndrome is defined as the process in which a long-standing left-to-right cardiac shunt caused by a congenital heart defect causes pulmonary hypertension and eventual reversal of the shunt into a cyanotic right-to-left shunt. Because of the advent of fetal screening with echocardiography early in life, the incidence of heart defects progressing to Eisenmenger syndrome has decreased.
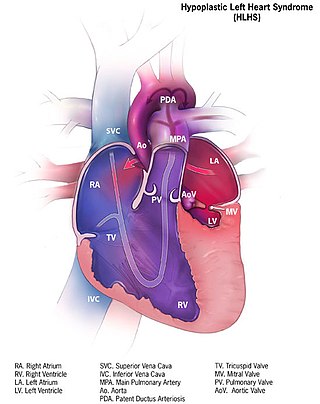
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a rare congenital heart defect in which the left side of the heart is severely underdeveloped and incapable of supporting the systemic circulation. It is estimated to account for 2-3% of all congenital heart disease. Early signs and symptoms include poor feeding, cyanosis, and diminished pulse in the extremities. The etiology is believed to be multifactorial resulting from a combination of genetic mutations and defects resulting in altered blood flow in the heart. Several structures can be affected including the left ventricle, aorta, aortic valve, or mitral valve all resulting in decreased systemic blood flow.

Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior and/or inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenital heart diseases involving only the primary arteries belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries (TGA), which is considered the most common congenital heart lesion that presents in neonates.

Pulmonary atresia is a congenital malformation of the pulmonary valve in which the valve orifice fails to develop. The valve is completely closed thereby obstructing the outflow of blood from the heart to the lungs. The pulmonary valve is located on the right side of the heart between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery. In a normal functioning heart, the opening to the pulmonary valve has three flaps that open and close.

Tricuspid atresia is a form of congenital heart disease whereby there is a complete absence of the tricuspid valve. Therefore, there is an absence of right atrioventricular connection. This leads to a hypoplastic (undersized) or absent right ventricle. This defect is contracted during prenatal development, when the heart does not finish developing. It causes the systemic circulation to be filled with relatively deoxygenated blood. The causes of tricuspid atresia are unknown.

Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) or atrioventricular canal defect (AVCD), also known as "common atrioventricular canal" or "endocardial cushion defect" (ECD), is characterized by a deficiency of the atrioventricular septum of the heart that creates connections between all four of its chambers. It is a very specific combination of 3 defects:
Levo-Transposition of the great arteries is an acyanotic congenital heart defect in which the primary arteries are transposed, with the aorta anterior and to the left of the pulmonary artery; the morphological left and right ventricles with their corresponding atrioventricular valves are also transposed.
Cor triatriatum is a congenital heart defect where the left atrium or right atrium is subdivided by a thin membrane, resulting in three atrial chambers.

Scimitar syndrome, or congenital pulmonary venolobar syndrome, is a rare congenital heart defect characterized by anomalous venous return from the right lung. This anomalous pulmonary venous return can be either partial (PAPVR) or total (TAPVR). The syndrome associated with PAPVR is more commonly known as Scimitar syndrome after the curvilinear pattern created on a chest radiograph by the pulmonary veins that drain to the inferior vena cava. This radiographic density often has the shape of a scimitar, a type of curved sword. The syndrome was first described by Catherine Neill in 1960.
A right-to-left shunt is a cardiac shunt which allows blood to flow from the right heart to the left heart. This terminology is used both for the abnormal state in humans and for normal physiological shunts in reptiles.
A cardiac shunt is a pattern of blood flow in the heart that deviates from the normal circuit of the circulatory system. It may be described as right-left, left-right or bidirectional, or as systemic-to-pulmonary or pulmonary-to-systemic. The direction may be controlled by left and/or right heart pressure, a biological or artificial heart valve or both. The presence of a shunt may also affect left and/or right heart pressure either beneficially or detrimentally.

Anomalous aortic origin of a coronary artery (AAOCA) is a rare congenital heart defect in which a coronary artery inappropriately arises from the aorta, usually from the incorrect sinus of Valsalva. This anomalous coronary artery often takes an interarterial, intraconal, or intramural course, and is associated with an increased risk of sudden death in children.

Pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect is a rare birth defect characterized by pulmonary valve atresia occurring alongside a defect on the right ventricular outflow tract.
Raghib syndrome is rare a congenital heart defect where the left superior vena cava (LSVC) is draining into the left atrium in addition to an absent coronary sinus and an atrial septal defect. This can be considered a dangerous heart condition because it puts the individual at a high risk of stroke. Other defects that are often associated with Raghib syndrome can include ventricular septal defects, enlargement of the tricuspid annulus, and pulmonary stenosis. While this is considered an extremely rare developmental complex, cases regarding a persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) are relatively common among congenital heart defects. It is also important to note that the PLSVC often drains into the right atrium, and only drains into the left atrium in approximately 10 to 20% of individuals with the defect.














