
Southern California Edison (SCE), the largest subsidiary of Edison International, is the primary electric utility company for much of Southern California. It provides 15 million people with electricity across a service territory of approximately 50,000 square miles.

The Manitoba Hydro-Electric Board, operating as Manitoba Hydro, is the electric power and natural gas utility in the province of Manitoba, Canada. Founded in 1961, it is a provincial Crown Corporation, governed by the Manitoba Hydro-Electric Board and the Manitoba Hydro Act. Today the company operates 16 interconnected generating stations. It has more than 527,000 electric power customers and more than 263,000 natural gas customers. Since most of the electrical energy is provided by hydroelectric power, the utility has low electricity rates. Stations in Northern Manitoba are connected by a HVDC system, the Nelson River Bipole, to customers in the south. The internal staff are members of the Canadian Union of Public Employees Local 998 while the outside workers are members of the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers Local 2034.

American Electric Power Company, Inc. (AEP), is a major investor-owned electric utility in the United States, delivering electricity to more than five million customers in 11 states.

The electricity sector in Canada has played a significant role in the economic and political life of the country since the late 19th century. The sector is organized along provincial and territorial lines. In a majority of provinces, large government-owned integrated public utilities play a leading role in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. Ontario and Alberta have created electricity markets in the last decade to increase investment and competition in this sector of the economy.

Constellation Energy Corporation is an American energy company headquartered in Baltimore, Maryland. The company provides electric power, natural gas, and energy management services. It has approximately two million customers across the continental United States.

The AES Corporation is an American utility and power generation company. It owns and operates power plants, which it uses to generate and sell electricity to end users and intermediaries like utilities and industrial facilities. AES is headquartered in Arlington, Virginia, and is one of the world's leading power companies, generating and distributing electric power in 15 countries and employing 10,500 people worldwide. AES Corporation is a global Fortune 500 power company. AES Ranks in the Top Ten of Fast Company's 2022 Best Workplaces for Innovators.

Pine Ridge is an unincorporated community in Hale Township, Caddo County, Oklahoma, United States. It is located 6 miles (10 km) south of Fort Cobb at the junction of County Road 1380 and County Street 2550.

The Bujagali Power Station is a hydroelectric power station across the Victoria Nile that harnesses the energy of its namesake; the Bujagali Falls, in Uganda. Construction began in 2007 and concluded in 2012. It was officially inaugurated on 8 October 2012 by Ugandan President Yoweri Museveni and Aga Khan IV in the presence of African politicians and investors.
The Grand River Dam Authority (GRDA) is an agency of the state of Oklahoma created to control, develop, and maintain the Grand River waterway. It was created by the Oklahoma state legislature in 1935, and is headquartered in Tulsa, Oklahoma. GRDA was designed to be self-funding from the sales of electricity and water. The state of Oklahoma was to provide no funding from taxes. The Authority was authorized to issue revenue bonds to fund large-scale capital investments.

Enel Green Power S.p.A. is an Italian multinational renewable energy corporation, headquartered in Rome. The company was formed as a subsidiary of the power generation firm Enel in December 2008. It has operations in five continents generating energy from solar, geothermal, wind and hydropower sources. As of 2022, it manages a capacity of 60,9 GW and has over 1200 plants worldwide.
Energy in Sudan describes energy and electricity production, consumption and imports in Sudan. The chief sources of energy in 2010 were wood and charcoal, hydroelectric power, and oil. Sudan is a net energy exporter. Primary energy use in Sudan was 179 TWh and 4 TWh per million persons in 2008.
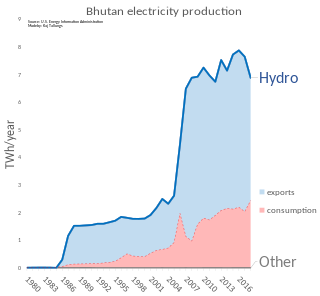
Energy in Bhutan has been a primary focus of development in the kingdom under its Five-Year Plans. In cooperation with India, Bhutan has undertaken several hydroelectric projects whose output is traded between the countries. Though Bhutan's many hydroelectric plants provide energy far in excess of its needs in the summer, dry winters and increased fuel demand makes the kingdom a marginal net importer of energy from India.

As of 2018, hydroelectric power stations in the United Kingdom accounted for 1.87 GW of installed electrical generating capacity, being 2.2% of the UK's total generating capacity and 4.2% of UK's renewable energy generating capacity. This includes four conventional hydroelectric power stations and run-of-river schemes for which annual electricity production is approximately 5,000 GWh, being about 1.3% of the UK's total electricity production. There are also four pumped-storage hydroelectric power stations providing a further 2.8 GW of installed electrical generating capacity, and contributing up to 4,075 GWh of peak demand electricity annually.

The U.S. State of Oklahoma has high potential capacity for wind power in the western half of the state. In 2021, Oklahoma's installed wind generation capacity was almost 10,500 megawatts, supplying over 40% of the state's generated electricity and 85% of Oklahoma's total generating capacity from all renewable resources.
The John W. Turk Jr. Coal Plant is a base load 600-megawatt coal-fired power station in Fulton, Arkansas, operated by the American Electric Power subsidiary Southwestern Electric Power Company (SWEPCO). It provides power to customers in Arkansas, Louisiana, and Texas.
The United States state of Arkansas is a significant producer of natural gas and a minor producer of petroleum.
Wind power in Arkansas remains nearly untapped, with just a single wind turbine in the state. Arkansas does not have a renewable portfolio standard. Studies have concluded that while Arkansas is generally considered to have low wind resources, there are significant pockets of it throughout the state.












