
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula C
6H
8O
6, originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent.

Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical "serum" ingredient to treat melasma and wrinkles on the face. It is used to prevent and treat scurvy. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Most animals are able to synthesize their own vitamin C. However, apes and monkeys, most bats, most fish, some rodents, and certain other animals must acquire it from dietary sources because a gene for a synthesis enzyme has mutations.

E numbers, short for Europe numbers, are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly found on food labels, their safety assessment and approval are the responsibility of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The fact that an additive has an E number implies that its use was at one time permitted in products for sale in the European Single Market; some of these additives are no longer allowed today.
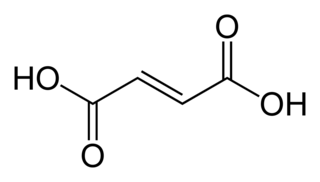
Fumaric acid is an organic compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. A white solid, fumaric acid occurs widely in nature. It has a fruit-like taste and has been used as a food additive. Its E number is E297. The salts and esters are known as fumarates. Fumarate can also refer to the C
4H
2O2−
4 ion (in solution). Fumaric acid is the trans isomer of butenedioic acid, while maleic acid is the cis isomer.

The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are vitamers of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Retinoids have found use in medicine where they regulate epithelial cell growth.

Canthaxanthin is a keto-carotenoid pigment widely distributed in nature. Carotenoids belong to a larger class of phytochemicals known as terpenoids. The chemical formula of canthaxanthin is C40H52O2. It was first isolated in edible mushrooms. It has also been found in green algae, bacteria, crustaceans, and bioaccumulates in fish such as carp, golden grey mullet, seabream and trush wrasse.

Erythorbic acid is a stereoisomer of ascorbic acid. It is synthesized by a reaction between methyl 2-keto-D-gluconate and sodium methoxide. It can also be synthesized from sucrose or by strains of Penicillium that have been selected for this feature. It is denoted by E number E315, and is widely used as an antioxidant in processed foods.

Sodium propanoate or sodium propionate is the sodium salt of propionic acid which has the chemical formula Na(C2H5COO). This white crystalline solid is deliquescent in moist air.
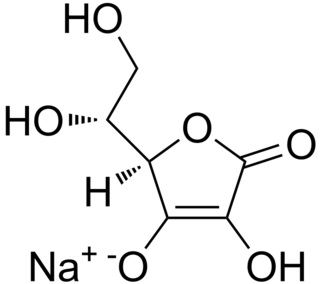
Sodium erythorbate (C6H7NaO6) is a food additive used predominantly in meats, poultry, and soft drinks. Chemically, it is the sodium salt of erythorbic acid. When used in processed meat such as hot dogs and beef sticks, it increases the rate at which nitrite reduces to nitric oxide, thus facilitating a faster cure and retaining the pink coloring. As an antioxidant structurally related to vitamin C, it helps improve flavor stability and prevents the formation of carcinogenic nitrosamines. When used as a food additive, its E number is E316. The use of erythorbic acid and sodium erythorbate as a food preservative has increased greatly since the U.S. Food and Drug Administration banned the use of sulfites as preservatives in foods intended to be eaten fresh (such as ingredients for fresh salads) and as food processors have responded to the fact that some people are allergic to sulfites. It can also be found in bologna, and is occasionally used in beverages, baked goods, and potato salad. Sodium erythorbate is produced from sugars derived from different sources, such as beets, sugarcane, and corn. Sodium erythorbate is usually produced via a fermentation process from D-glucose by Pseudomonas fluorescens bacteria. Most syntheses proceed through the 2-keto-D-gluconic acid intermediate. An urban myth claims that sodium erythorbate is made from ground earthworms; however, there is no truth to the myth. It is thought that the origin of the legend comes from the similarity of the chemical name to the words earthworm and bait.

Apocarotenal, or trans-β-apo-8'-carotenal, is a carotenoid found in spinach and citrus fruits. Like other carotenoids, apocarotenal plays a role as a precursor of vitamin A, even though it has 50% less pro-vitamin A activity than β-carotene. The empirical chemical formula for apocarotenal is C30H40O.

Mineral ascorbates are a group of salts of ascorbic acid. They are composed of a mineral cation bonded to ascorbate.
Ascorbyl stearate (C24H42O7) is an ester formed from ascorbic acid and stearic acid. In addition to its use as a source of vitamin C, it is used as an antioxidant food additive in margarine (E number E305). The USDA limits its use to 0.02% individually or in conjunction with other antioxidants.

Calcium benzoate refers to the calcium salt of benzoic acid. When used in the food industry as a preservative, its E number is E213 ; it is approved for use as a food additive in the EU, USA and Australia and New Zealand.

Calcium ascorbate is a compound with the molecular formula CaC12H14O12. It is the calcium salt of ascorbic acid, one of the mineral ascorbates. It is approximately 10% calcium by mass.

Sodium ascorbate is one of a number of mineral salts of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). The molecular formula of this chemical compound is C6H7NaO6. As the sodium salt of ascorbic acid, it is known as a mineral ascorbate. It has not been demonstrated to be more bioavailable than any other form of vitamin C supplement.

Potassium ascorbate is a compound with formula KC6H7O6. It is the potassium salt of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and a mineral ascorbate. As a food additive, it has E number E303, INS number 303. Although it is not a permitted food additive in the UK, USA and the EU, it is approved for use in Australia and New Zealand. According to some studies, it has shown a strong antioxidant activity and antitumoral properties.
Benzene in soft drinks is of potential concern due to the carcinogenic nature of the molecule. This contamination is a public health concern and has caused significant outcry among environmental and health advocates. Benzene levels are regulated in drinking water nationally and internationally, and in bottled water in the United States, but only informally in soft drinks. The benzene forms from decarboxylation of the preservative benzoic acid in the presence of ascorbic acid and metal ions that act as catalysts, especially under heat and light. Hot peppers naturally contain vitamin C so the observation about soft drinks applies to pepper sauces containing sodium benzoate, like Texas Pete.

A dough conditioner, flour treatment agent, improving agent or bread improver is any ingredient or chemical added to bread dough to strengthen its texture or otherwise improve it in some way. Dough conditioners may include enzymes, yeast nutrients, mineral salts, oxidants and reductants, bleaching agents and emulsifiers. They are food additives combined with flour to improve baking functionality. Flour treatment agents are used to increase the speed of dough rising and to improve the strength and workability of the dough.
Food orange 7, the ethyl ester of beta-apo-8'-carotenic acid, is a carotenoid with an orange-red color. It is found in small quantities in some plants, but is often produced commercially from apocarotenal (E160e). It is used as a food coloring under the E number E160f and is approved for use in the EU and Australia and New Zealand where it is listed as food additive 160f; it is banned in the United States.
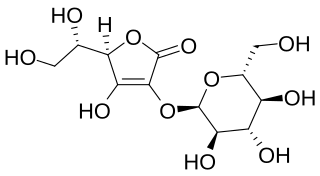
Ascorbyl glucoside (AA-2G) is an ascorbic acid derivative that contains at least one glycosyl group. Ascorbyl glucoside is commonly used in cosmetic products to administer vitamin C topically. Ascorbyl glucoside exhibits superior stability and penetration ability compared to ascorbyl phosphate salts, but the rate of its in vivo conversion to ascorbic acid is not known. Ascorbyl glucosides such as AA-2G, like many other derivatives of the ascorbic acid, show antiscorbutic effects. It is also sometimes used in skin whitening products.
















