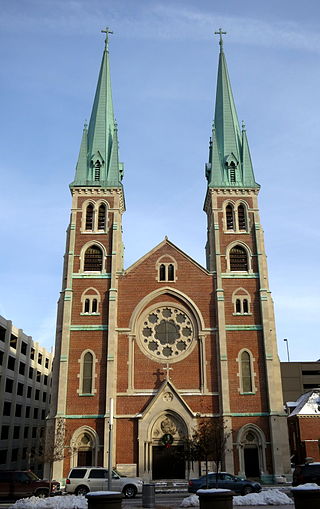Columbia is a city in and the county seat of Maury County, Tennessee. The population was 41,690 as of the 2020 United States census. Columbia is included in the Nashville metropolitan area.

Rugby is an unincorporated community in Morgan and Scott counties in the U.S. state of Tennessee. Founded in 1880 by English author Thomas Hughes, Rugby was built as an experimental utopian colony. While Hughes's experiment largely failed, a small community lingered at Rugby throughout the 20th century. In the 1960s, residents, friends and descendants of Rugby began restoring the original design and layout of the community, preserving surviving structures and reconstructing others. Rugby's Victorian architecture and picturesque setting have since made it a popular tourist attraction. In 1972, Rugby's historic area was listed under the name Rugby Colony on the National Register of Historic Places as a historic district.

Borley Rectory was a house located in Borley, Essex, famous for being described as "the most haunted house in England" by psychic researcher Harry Price. Built in 1862 to house the rector of the parish of Borley and his family, the house was badly damaged by fire in 1939 and demolished in 1944.

The University of the South, familiarly known as Sewanee, is a private Episcopal liberal arts college in Sewanee, Tennessee. It is owned by 28 southern dioceses of the Episcopal Church, and its School of Theology is an official seminary of the church. The university's School of Letters offers graduate degrees in American Literature and Creative Writing. The campus consists of 13,000 acres (53 km2) of scenic mountain property atop the Cumberland Plateau, with the developed portion occupying about 1,000 acres (4.0 km2).

Lieutenant-General Leonidas Polk was a bishop of the Episcopal Diocese of Louisiana and founder of the Protestant Episcopal Church in the Confederate States of America, which separated from the Episcopal Church of the United States of America. He was a planter in Maury County, Tennessee, and a second cousin of President James K. Polk. He resigned his ecclesiastical position to become a major-general in the Confederate States Army, when he was called "Sewanee's Fighting Bishop". His official portrait at the University of the South depicts him as a bishop with his army uniform hanging nearby. He is often erroneously referred to as "Leonidas K. Polk," but he had no middle name and never signed any documents as such.

James Hervey Otey, Christian educator, author, and the first Episcopal Bishop of Tennessee, having established the Anglican church in the state, including its first parish churches and what became the University of the South.

TMI Episcopal is a private school in San Antonio. Previously known as Texas Military Institute, TMI is a selective coeducational Episcopal college preparatory school with a military tradition in San Antonio, Texas for boarding and day students. It is the flagship school, and sole secondary school, of the Episcopal Diocese of West Texas. TMI is the oldest Episcopal college preparatory school in the American Southwest. Founded as West Texas School for Boys, the school was later known as West Texas Military Academy, and popularly nicknamed 'West Point on the Rio Grande', though it is several hours from the Rio Grande itself.
Barclay Martin was an American politician and a member of the United States House of Representatives for Tennessee's 6th congressional district.

Charles Todd Quintard was an American physician and clergyman who became the second bishop of the Episcopal Diocese of Tennessee and the first Vice-Chancellor of the University of the South.

The Church of the Holy Trinity is an historic Episcopal church at 381 Main Street in Middletown, Connecticut. Completed in 1874, it is one of the city's finest examples of Gothic Revival architecture. Its nearby former rectory, also known as the Bishop Acheson House, is one of its finest Colonial Revival houses. The two buildings were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979.

St. Mary's Episcopal Cathedral, designed by Memphis architect Bayard Snowden Cairns, located near downtown Memphis, Tennessee, is the cathedral church of the Episcopal Diocese of West Tennessee and the former cathedral of the old statewide Episcopal Diocese of Tennessee.

Christ Episcopal Church is an Episcopal congregation in South Pittsburg, Tennessee, part of the Episcopal Diocese of East Tennessee. The church building and parish house, located at 302 West 3rd Street, are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

St. John's Episcopal Church is a historic Episcopal church in Ashwood, Maury County, Tennessee, United States. Built from 1839 to 1842 by Bishop Leonidas Polk, it was an active church in the Antebellum South. It was ransacked and later used as a hospital for the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War of 1861–1865. Services resumed after the war, but they were discontinued due to low attendance in 1915. It is now closed, except for an annual pilgrimage.
St. James’ Episcopal Church is an historic Episcopal church located at 2423 SW Bascom Norris Drive in Lake City, Florida. The church is in the Episcopal Diocese of Florida.

Kinder House is a historic house on Ayr Street, in the suburb of Parnell, Auckland, New Zealand.

St. Luke's Episcopal Church is a historic church at 309 E. Baltimore Street in Jackson, Tennessee, United States. The congregation was formed in 1832, the first of five new Episcopal congregations planted in West Tennessee that year after Mrs. Mary Hayes Willis Gloster of La Grange had traveled to Nashville to ask Bishop James H. Otey to bring the Episcopal Church to West Tennessee. The church building dates to 1845, although it was only partially completed that year. It was consecrated by Bishop Otey on May 14, 1853.

St. Peter's Episcopal Church is a historic church located at 311 W. 7th Street in Columbia, Tennessee.
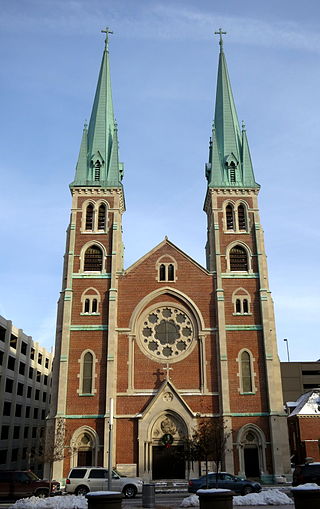
Saint John the Evangelist Catholic Church is a Roman Catholic parish of the Archdiocese of Indianapolis in Indianapolis, Indiana, United States. The parish's origins date to 1837, when it was first named Holy Cross parish. In 1850 it was renamed Saint John the Evangelist parish, and is the oldest Catholic parish in the city and in Marion County, Indiana. Considered the mother of the Catholic parishes in Indianapolis, it played an important role in development of the Catholic Church in the city. Saint John's Church served as the pro-cathedral of the diocese from 1878 until 1906; its rectory served as the bishop's residence and chancery from 1878 until 1892. In 1900 the church served as the site of first episcopal consecration held in Indianapolis.

Ashwood is an unincorporated community in Maury County, Tennessee, in the United States. Most of the community has been annexed by the city of Mount Pleasant.