Softball is a sport similar to baseball, and it is played with a larger ball on a smaller field and with only underhand pitches permitted. Softball is played competitively at club levels, the college level, and the professional level. The game was first created in 1887 in Chicago by George Hancock.
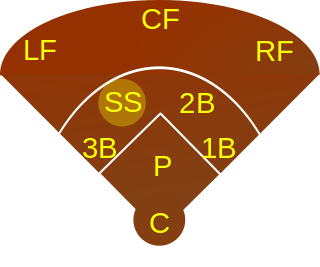
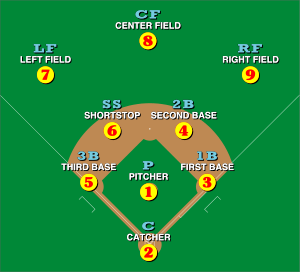
Shortstop, abbreviated SS, is the baseball or softball fielding position between second and third base, which is considered to be among the most demanding defensive positions. Historically, the position was assigned to defensive specialists who were typically poor at batting and were often placed at the bottom of the batting order. Today, shortstops are often able to hit well and many are placed at the top of the lineup. In the numbering system used by scorers to record defensive plays, the shortstop is assigned the number 6.

In baseball and softball, a double play is the act of making two outs during the same continuous play. Double plays can occur any time there is at least one baserunner and fewer than two outs.

Catcher is a position in baseball and softball. When a batter takes their turn to hit, the catcher crouches behind home plate, in front of the (home) umpire, and receives the ball from the pitcher. In addition to this primary duty, the catcher is also called upon to master many other skills in order to field the position well. The role of the catcher is similar to that of the wicket-keeper in cricket.

An outfielder is a person playing in one of the three defensive positions in baseball or softball, farthest from the batter. These defenders are the left fielder, the center fielder, and the right fielder. As an outfielder, their duty is to catch fly balls and ground balls then to return them to the infield for the out or before the runner advances, if there are any runners on the bases. As an outfielder, they normally play behind the six players located in the field. By convention, each of the nine defensive positions in baseball is numbered. The outfield positions are 7, 8 and 9. These numbers are shorthand designations useful in baseball scorekeeping and are not necessarily the same as the squad numbers worn on player uniforms.

A first baseman, abbreviated 1B, is the player on a baseball or softball team who fields the area nearest first base, the first of four bases a baserunner must touch in succession to score a run. The first baseman is responsible for the majority of plays made at that base. In the numbering system used to record defensive plays, the first baseman is assigned the number 3.
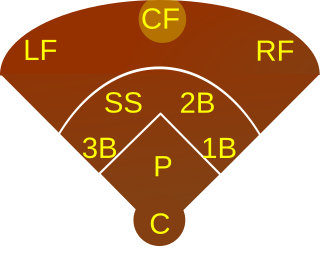
A center fielder, abbreviated CF, is the outfielder in baseball who plays defense in center field – the baseball and softball fielding position between left field and right field. In the numbering system used to record defensive plays, the center fielder is assigned the number 8.
An infielder is a baseball player stationed at one of four defensive "infield" positions on the baseball field, between first base and third base.

Throughout the history of baseball, the rules have frequently changed as the game continues to evolve. A few common rules most professional leagues have in common is that four balls is a base on balls, three strikes is a strikeout, and three outs end a half-inning.

In baseball and softball, while there are nine named fielding positions, players, with the exception of the pitcher and catcher, may move around freely. The positioning for the other seven positions is very flexible, although they all have regular depths—distances from home plate, and sometimes lateral positioning. A shift means that a player is playing in a noticeably different location than the norm for his positioning. A fielder who is playing shallow or in is playing closer to home plate, while a player playing deep is playing farther from home plate than normal.
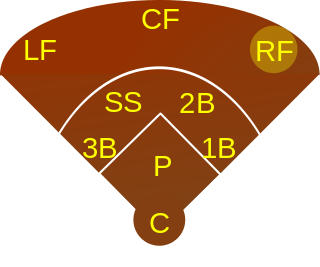
A right fielder, abbreviated RF, is the outfielder in baseball or softball who plays defense in right field. Right field is the area of the outfield to the right of a person standing at home plate and facing towards the pitcher's mound. In the numbering system used to record defensive plays, the right fielder is assigned the number 9.
A hit and run is a high risk, high reward offensive strategy used in baseball. It uses a stolen base attempt to try to place the defending infielders out of position for an attempted base hit.

Baseball scorekeeping is the practice of recording the details of a baseball game as it unfolds. Professional baseball leagues hire official scorers to keep an official record of each game, but many fans keep score as well for their own enjoyment. Scorekeeping is usually done on a printed scorecard and, while official scorers must adhere precisely to one of the few different scorekeeping notations, most fans exercise some amount of creativity and adopt their own symbols and styles.
This is an alphabetical list of selected unofficial and specialized terms, phrases, and other jargon used in baseball, along with their definitions, including illustrative examples for many entries.