
Fort Duquesne was a fort established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers. It was later taken over by the British, and later the Americans, and developed as Pittsburgh in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. Fort Duquesne was destroyed by the French before its British conquest during the Seven Years' War, known as the French and Indian War on the North American front. The British replaced it, building Fort Pitt between 1759 and 1761. The site of both forts is now occupied by Point State Park, where the outlines of the two forts have been laid in brick.

John Forbes was a Scottish professional soldier who served in the British Army from 1729 until his death in 1759.

Events from the year 1758 in Canada.

Henry Bouquet was a Swiss mercenary who rose to prominence in British service during the French and Indian War and Pontiac's War. He is best known for his victory over a Native American force at the Battle of Bushy Run, lifting the siege of Fort Pitt during Pontiac's War. During the conflict Bouquet gained lasting infamy in an exchange of letters with his commanding officer, Jeffery Amherst, who suggested a form of biological warfare in the use of blankets infected with smallpox which were to be distributed to Native Americans. Despite this indictment historians have praised Bouquet for leading British forces in several demanding campaigns on the Western Frontier in which they "protected and rescued" settlers from increasingly frequent attacks.
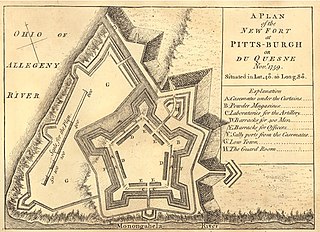
Fort Pitt was a fort built by British forces between 1759 and 1761 during the French and Indian War at the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers, where the Ohio River is formed in western Pennsylvania. It was near the site of Fort Duquesne, a French colonial fort built in 1754 as tensions increased between Great Britain and France in both Europe and North America. The French destroyed Fort Duquesne in 1758 when they retreated under British attack.

The Battle of Bushy Run was fought on August 5–6, 1763, in western Pennsylvania, between a British column under the command of Colonel Henry Bouquet and a combined force of Delaware, Shawnee, Mingo, and Huron warriors. This action occurred during Pontiac's Rebellion. Though the British suffered serious losses, they routed the tribesmen and successfully relieved the garrison of Fort Pitt.
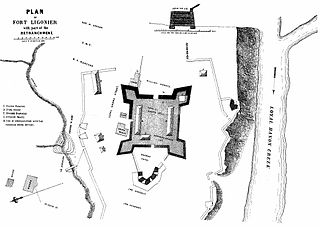
The Battle of Fort Ligonier was a battle of the French and Indian War. On 12 October 1758, French and Indian forces directed from nearby Fort Duquesne were repulsed in an attack on the British outpost of Fort Ligonier, then still under construction.
Fort Bedford was a French and Indian War-era British military fortification located at the present site of Bedford, Pennsylvania. The fort was a star-shaped log fortress erected in the summer of 1758.

Fort Ligonier is a British fortification from the French and Indian War located in Ligonier, Pennsylvania, United States. The fort served as a staging area for the Forbes Expedition of 1758. During the eight years of its existence as a garrison, Fort Ligonier was never taken by an enemy. It served as a post of passage to the new Fort Pitt, and during Pontiac's War of 1763, was a vital link in the British communication and supply lines. It was attacked twice and besieged by the Native Americans, prior to the decisive victory at Bushy Run in August of that year. The fort was decommissioned from active service in 1766. Today, there is a museum next to the reconstructed fort. Inside the museum there are artifacts from the battle. An individual can take a guided tour of the fort, and on Fort Ligonier Days, the fort's cannons are fired.

Fort Loudoun was a fort in colonial Pennsylvania, one of several forts in colonial America named after John Campbell, 4th Earl of Loudoun. The fort was built in 1756 during the French and Indian War by the Second Battalion of the Pennsylvania Regiment under Colonel John Armstrong, and served as a post on the Forbes Road during the Forbes expedition that successfully drove the French away from Fort Duquesne. The fort remained occupied through Pontiac's War and served as a base for Colonel Henry Bouquet's 1764 campaign. In the 1765 Black Boys Rebellion, Fort Loudoun was assaulted by angry settlers, when their guns were confiscated after they destroyed supplies intended for Native Americans. The garrison retreated to Fort Bedford and the fort was abandoned.
The 77th Regiment of Foot (Montgomerie's Highlanders) was a Highland Scots Regiment raised in 1757. The 77th Regiment was one of the first three Highland Regiments to fight in North America. During the Seven Years' War, the regiment lost 110 soldiers and 259 were wounded.
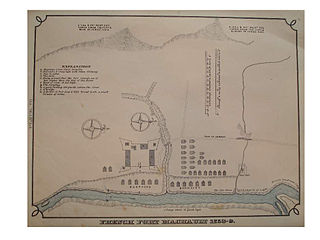
Fort Machault was a fort built by the French in 1754 near the confluence of French Creek with the Allegheny River, in northwest Pennsylvania. The fort helped the French control these waterways, part of what was known as the Venango Path from Lake Erie to the Ohio River. It was one of four forts designed to protect French access to the Ohio Country and connections between its northern and southern colonies. From north to south the forts were Fort Presque Isle, Fort Le Boeuf, Fort Machault, and Fort Duquesne, at the Forks of the Ohio. The fort was abandoned by the French in 1759, and burned so that the British could not use it. It was replaced by the British in 1760 with Fort Venango.

George Washington's military experience began in the French and Indian War with a commission as a major in the militia of the British Province of Virginia. In 1753 Washington was sent as an ambassador from the British crown to the French officials and Indians as far north as present-day Erie, Pennsylvania. The following year he led another expedition to the area to assist in the construction of a fort at present-day Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Before reaching that point, he and some of his men, along with Mingo allies led by Tanacharison, ambushed a French scouting party. Its leader was killed, although the exact circumstances of his death were disputed. This peacetime act of aggression is seen as one of the first military steps leading to the global Seven Years' War. The French responded by attacking fortifications Washington erected following the ambush, forcing his surrender. Released on parole, Washington and his troops returned to Virginia.

Fort Pitt Museum is an indoor/outdoor museum that is administered by the Senator John Heinz History Center in downtown Pittsburgh, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania in the United States. It is at the confluence of the Monongahela and Allegheny Rivers, where the Ohio River is formed. Fort Pitt Museum is surrounded by Point State Park, a Pennsylvania state park named for the geographically and historically significant point that is between the rivers. This piece of land was key to controlling the upper reaches of the Ohio River Valley and western Pennsylvania, before, during and after the French and Indian War as well as the American Revolution.
The Battle of La Belle-Famille occurred on July 24, 1759, during the French and Indian War along the Niagara River portage trail. François-Marie Le Marchand de Lignery's French relief force for the besieged French garrison at Fort Niagara fell into Eyre Massey's British and Iroquois ambush. This action formed part of the larger Battle of Fort Niagara.

The Forbes Expedition was a British military campaign to capture Fort Duquesne, led by Brigadier-General John Forbes in 1758, during the French and Indian War. While advancing to the fort, the expedition built the Forbes Road. The Treaty of Easton served to cause a loss of Native American support for the French, resulting in the French destroying the fort before the expedition could arrive on November 24.
François-Marie Le Marchand de Lignery was a colonial military leader in the French province of Canada. Active in the defense of New France during the Seven Years' War, he died of wounds sustained in the 1759 Battle of La Belle-Famille.
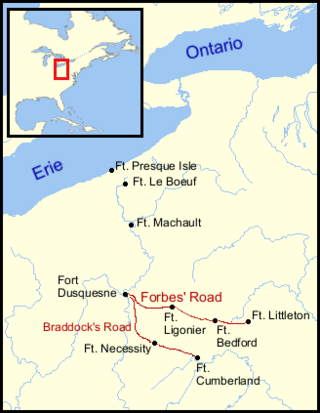
The Forbes Road, a historic military roadway in what was then British America, was initially completed in 1758 from Carlisle, Pennsylvania, to the French Fort Duquesne at the junction of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers in what is now downtown Pittsburgh, via Fort Loudon, Fort Lyttleton, Fort Bedford and Fort Ligonier. The road, initially about 220 miles long, was named for Brigadier General John Forbes, the commander of the 1758 British-led expedition that built the road during the French and Indian War. The Forbes Road and Braddock's Road were the two main land routes that the British cut west through the wilderness during the war. The task was complicated by the Appalachian Mountains' steep northeast-to-southwest ridges, a generally broken terrain between the ridges, heavy forestation, and numerous swamps and rivers.
Keekyuscung aka Kickyuscung, Kaquehuston, Kikyuskung, Ketiuscund, Kekeuscund, or Ketiushund, was a Delaware (Lenape) chief. In the 1750s he took part in peace negotiations to end Lenape participation in the French and Indian War. In 1754 he briefly engaged in some spying and smuggled some letters into and out of Fort Duquesne for George Washington. He was sympathetic to the British for many years, but in 1763 he and his son Wolf sided with the French after a failed assassination attempt by Colonel Henry Bouquet. He is known for being one of the Native American leaders that attacked Colonel Bouquet's forces at the Battle of Bushy Run, where Keekyuscung was killed.

Mercer's Fort was a temporary fort built by Colonel Hugh Mercer during the winter of 1758–1759, to secure the "forks of the Ohio," at the confluence of the Monongahela River and the Allegheny River, where Mercer was preparing to build Fort Pitt. At the time it was loosely known as "the fort at Pittsburgh," and when work on Fort Pitt had progressed, it was sometimes referred to as "the first Fort Pitt." Only later did people call it "Mercer's Fort," leading to confusion with Fort Mercer in New Jersey. The fort initially served to defend the site, but as Fort Pitt neared completion, it was used mostly to lodge workers and to store supplies. In mid-1760 it was partially dismantled, with some buildings converted into a hospital.
















