
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma and the extreme southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover a significant portion of northern Arkansas and most of the southern half of Missouri, extending from Interstate 40 in central Arkansas to Interstate 70 in central Missouri.

The Buffalo River, located in Northern Arkansas, was the first National River to be designated in the United States. The Buffalo River is 153 miles (246 km) long. The lower 135 miles (217 km) flow within the boundaries of an area managed by the National Park Service, where the stream is designated the Buffalo National River. The river flows through Newton, Searcy, Marion, and Baxter Counties, from west to east. The river originates in the highest part of the Boston Mountains of the Ozarks, flows out onto the Springfield Plateau near the historic community of Erbie, and finally crosses a portion of the Salem Plateau just before joining the White River. The Park is home to the state's only elk herd. The upper section of the river in the Ozark National Forest is managed by the U.S. Forest Service and is designated as a National Scenic River and a National Wild River; that section is not part of the area managed as a park by the Park Service but is managed as a part of the Ozark National Forest.

The Current River forms in the southeastern portion of the Ozarks of Missouri and becomes a 7th order stream as it flows southeasterly out of the Ozarks into northeastern Arkansas where it becomes a tributary of the Black River, which is a tributary of the White River, a tributary of the Mississippi River. The Current River is approximately 184 miles (296 km) long and drains about 2,641 square miles (6,840 km2) of land mostly in Missouri and a small portion of land in northeastern Arkansas. The headwaters of the Current River are nearly 900 feet (270 m) above sea level, while the mouth of the river lies around 280 feet (85 m) above sea level. The basin drains a rural area that is dominated by karst topography, underlain by dolomite and sandstone bedrock with a small area of igneous rock southeast of Eminence, Missouri. The annual daily mean discharge of the river near Doniphan, Missouri is 2,815 cubic feet (79.7 m3) per second. In 1964, over 134 mi (160 km) of the upper course of the river and its tributaries were federally protected as the Ozark National Scenic Riverways, the first national park in America to protect a river system.
The Cave Research Foundation (CRF) is an American private, non-profit group dedicated to the exploration, research, and conservation of caves. The group arose in the early 1950s from the exploration efforts at Floyd Collins Crystal Cave, now within Mammoth Cave National Park. Its stated goals were: to promote exploration and documentation of caves and karst areas, initiate and support cave and karst research, aid in cave conservation and protection, and to assist with the interpretation of caves and karst to the public.

Route 103 is a short highway in southeastern Missouri. Its southern terminus is at Route Z inside the Ozark National Scenic Riverways. The route travels north and intersects a few county roads as it leaves the national park. The road ends at U.S. Route 60 in a three-way junction. After being proposed in 1930, a road was built from the national park to US 60 in 1933. The gravel road was designated as Route 103, and it was paved five years later.

Mark Twain National Forest (MTNF) is a U.S. National Forest located in the southern half of Missouri. MTNF was established on September 11, 1939. It is named for author Mark Twain, a Missouri native. The MTNF covers 3,068,800 acres (12,419 km2) of which 1,506,100 acres (6,095 km2) is public owned, 78,000 acres (320 km2) of which are Wilderness, and National Scenic River area. MTNF spans 29 counties and represents 11% of all forested land in Missouri. MTNF is divided into six distinct ranger districts: Ava-Cassville-Willow Springs, Eleven Point, Houston-Rolla, Cedar Creek, Poplar Bluff, Potosi-Fredericktown, and the Salem. The six ranger districts actually comprise nine overall unique tracts of forests. Its headquarters are in Rolla, Missouri.

Maramec Spring is located on the Meramec River near St. James in the east-central Ozarks of Missouri. The fifth largest spring in the state with an average discharge of 153 cubic feet (4.3 m3) of water per second, it is part of a Karst topographical area, with many springs and caves. The spring and 1800 acres (7.28 km²) are owned by the James Foundation, which maintains the area as a public park, donated by Lucy Wortham James. The Missouri Department of Conservation operates a trout hatchery and fishery at the spring. Ruins of the Maramec Iron Works are still visible at the site; its machinery was partly powered by the spring's waterflow. The spring was declared a National Natural Landmark in October 1971.

The Gasconade River is about 280 miles (450 km) long and is located in central and south-central Missouri.

The Spring River is a 129-mile-long (208 km) waterway located in southwestern Missouri, southeastern Kansas, and northeastern Oklahoma.

Alley Spring is an unincorporated community in Shannon County, Missouri, United States. It is located six miles west of Eminence on Route 106. The scenic Alley Mill, or "Old Red Mill" is located there on a spring and is located in the Ozark National Scenic Riverways. The Mill is operated as an Ozarks history museum. Nearby a one room schoolhouse and general store add to the feeling of the restored historic hamlet. It once had a post office, but it is now closed and mail now comes from Eminence. The community is named after John Alley, a miller. It was originally named Mammoth Spring and later Barksdale Spring. These names were deemed too long by the Post Office Department of the time, so the village was renamed after a prominent local citizen, John Alley.

Montauk State Park is a public recreation area occupying nearly 3,000 acres (1,200 ha) at the headwaters of the Current River, fifteen miles (24 km) southwest of Salem, Missouri. The state park contains a fish hatchery and is noted for its rainbow and brown trout angling. It was acquired in 1926. The park has several natural springs including Montauk Spring with a daily average flow of 53 million gallons of water.

The Ozark National Scenic Riverways is a recreational unit of the National Park Service in the Ozarks of southern Missouri in the U.S.
The Owl's Bend Site is a location in the Ozark National Scenic Riverways, at Owls Bend, Missouri in eastern Shannon County adjacent to the Current River. It was placed on the National Register of Historic Places on March 22, 1988.
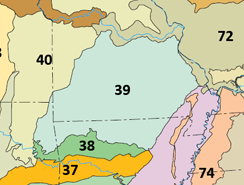
The Ozark Highlands is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in four U.S. states. Most of the region is within Missouri, with a part in Arkansas and small sections in Oklahoma and Kansas. It is the largest subdivision of the region known as the Ozark Mountains, less rugged in comparison to the Boston Mountains in Arkansas, the highest part of the Ozarks.

Greer Spring is a first magnitude spring located in the southeast portion of the Ozark Plateau, in Oregon County in south-central Missouri within the boundaries of the Mark Twain National Forest. The spring is the second largest spring in the Ozarks, with an average discharge of 360 cubic feet (10 m3) of water per second. Greer Spring was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1980.

The Eleven Point National Wild and Scenic River is a 44-mile (71 km) stretch of the spring-fed Eleven Point River in the Ozarks of southern Missouri set aside through eminent domain for preservation by Congress in 1968. The designated part of the river stretches from Thomasville to State Highway 142. The river was included in the original proposal for the Ozark National Scenic Riverways, but it was ultimately excluded when the Riverways were designated on the Current and Jacks Fork rivers in 1964.
Devils Well is a sinkhole cave near Akers in the U.S. state of Missouri, containing an underground lake that is the largest in the state. It is a part of the Ozark National Scenic Riverways and can be viewed by the public any day during daylight hours. The U.S. Park Service has set up a metal staircase and a switch-activated light; however, it is recommended that visitors bring additional light sources.

Big Spring Historic District is a national historic district located at Van Buren, Carter County, Missouri. It encompasses 26 contributing buildings, 1 contributing site, and contributing structure in the Ozark National Scenic Riverways. It includes the Big Spring, rental cabins, service building, storage shed, garage, a museum, dining lodge, restroom, shelter house, ranger station, pump house, footbridge, and two picnic shelters. The structures represent the best features of park construction by the Civilian Conservation Corps in Missouri.

The Alley Spring Roller Mill, also known as Red Mill, is a historic grist mill located in the Ozark National Scenic Riverways near Eminence, Shannon County, Missouri. It was built in 1893, and is a 2 1/2-story, rectangular frame building on a limestone block foundation. It measures 32 feet by 42 feet and houses four steel rollers and a single stone burr.

The Missouri Lumber and Mining Company (MLM) was a large timber corporation with headquarters and primary operations in southeast Missouri. The company was formed by Pennsylvania lumbermen who were eager to exploit the untapped timber resources of the Missouri Ozarks to supply lumber, primarily used in construction, to meet the demand of U.S. westward expansion. Its primary operations were centered in Grandin, a company town it built starting c. 1888. The lumber mill there grew to be the largest in the country at the turn of the century and Grandin's population peaked around 2,500 to 3,000. As the timber resources were exhausted, the company had to abandon Grandin around 1910. It continued timber harvesting in other parts of Missouri for another decade. While some of the buildings in Grandin were relocated, many of the remaining buildings were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980 as part of the state's historic preservation plan which considered the MLM a significant technological and economic contributor to Missouri.


















