
The coast, also known as the coastline, shoreline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. Shores are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape, as well as by water induced erosion, such as waves. The geological composition of rock and soil dictates the type of shore which is created. The Earth has around 620,000 kilometres (390,000 mi) of coastline. Coasts are important zones in natural ecosystems, often home to a wide range of biodiversity. On land, they harbor important ecosystems such as freshwater or estuarine wetlands, which are important for bird populations and other terrestrial animals. In wave-protected areas they harbor saltmarshes, mangroves or seagrasses, all of which can provide nursery habitat for finfish, shellfish, and other aquatic species. Rocky shores are usually found along exposed coasts and provide habitat for a wide range of sessile animals and various kinds of seaweeds. In physical oceanography, a shore is the wider fringe that is geologically modified by the action of the body of water past and present, while the beach is at the edge of the shore, representing the intertidal zone where there is one. Along tropical coasts with clear, nutrient-poor water, coral reefs can often be found between depths of 1–50 meters.

Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone through lithification.

A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high discharge. The soils usually consist of clays, silts, sands, and gravels deposited during floods.

An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world.

A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by the deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs at a river mouth, when it enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, or another river that cannot carry away the supplied sediment. It is so named because its triangle shape resembles the uppercase Greek letter delta, Δ. The size and shape of a delta are controlled by the balance between watershed processes that supply sediment, and receiving basin processes that redistribute, sequester, and export that sediment. The size, geometry, and location of the receiving basin also plays an important role in delta evolution.

In geography and geology, fluvial sediment processes or fluvial sediment transport are associated with rivers and streams and the deposits and landforms created by sediments. It can result in the formation of ripples and dunes, in fractal-shaped patterns of erosion, in complex patterns of natural river systems, and in the development of floodplains and the occurrence of flash floods. Sediment moved by water can be larger than sediment moved by air because water has both a higher density and viscosity. In typical rivers the largest carried sediment is of sand and gravel size, but larger floods can carry cobbles and even boulders. When the stream or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, the term glaciofluvial or fluvioglacial is used, as in periglacial flows and glacial lake outburst floods. Fluvial sediment processes include the motion of sediment and erosion or deposition on the river bed.

In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material, and rises from the bed of a body of water close to the surface or above it, which poses a danger to navigation. Shoals are also known as sandbanks, sandbars, or gravelbars. Two or more shoals that are either separated by shared troughs or interconnected by past or present sedimentary and hydrographic processes are referred to as a shoal complex.
Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as their creating process, shape, elevation, slope, orientation, rock exposure, and soil type.

A streambed or stream bed is the bottom of a stream or river (bathymetry) and is confined within a channel, or the banks (bank of the waterway. Usually the bed does not contain terrestrial vegetation and instead supports different types of aquatic vegetation, depending on the type of streambed material and water velocity. Streambeds are what would be left once a stream is no longer in existence. The beds are usually well preserved even if they get buried because the banks and canyons made by the stream are typically hard, although soft sand and debris often fill the bed. Dry, buried streambeds can actually be underground water pockets. During times of rain, sandy streambeds can soak up and retain water, even during dry seasons, keeping the water table close enough to the surface to be obtainable by local people.

The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud.
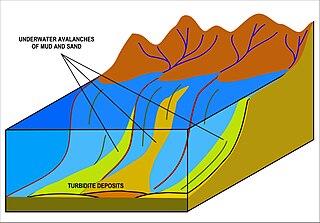
A turbidity current is most typically an underwater current of usually rapidly moving, sediment-laden water moving down a slope; although current research (2018) indicates that water-saturated sediment may be the primary actor in the process. Turbidity currents can also occur in other fluids besides water.
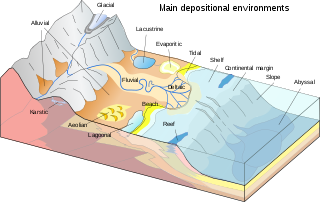
In geology, depositional environment or sedimentary environment describes the combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will be formed after lithification, if the sediment is preserved in the rock record. In most cases, the environments associated with particular rock types or associations of rock types can be matched to existing analogues. However, the further back in geological time sediments were deposited, the more likely that direct modern analogues are not available.
Aeolian landforms are produced by either the erosive or depositive action of wind. These features may be built up from sand or snow, or eroded into rock, snow, or ice.

In sedimentary geology and fluvial geomorphology, avulsion is the rapid abandonment of a river channel and the formation of a new river channel. Avulsions occur as a result of channel slopes that are much less steep than the slope that the river could travel if it took a new course.

A bar in a river is an elevated region of sediment that has been deposited by the flow. Types of bars include mid-channel bars, point bars, and mouth bars. The locations of bars are determined by the geometry of the river and the flow through it. Bars reflect sediment supply conditions, and can show where sediment supply rate is greater than the transport capacity.
A mouth bar is an element of a deltaic system, which refers to the typically mid-channel deposition of the sediment transported by the river channel at the river mouth.

An alluvial river is one in which the bed and banks are made up of mobile sediment and/or soil. Alluvial rivers are self-formed, meaning that their channels are shaped by the magnitude and frequency of the floods that they experience, and the ability of these floods to erode, deposit, and transport sediment. For this reason, alluvial rivers can assume a number of forms based on the properties of their banks; the flows they experience; the local riparian ecology; and the amount, size, and type of sediment that they carry.

A marine habitat is a habitat that supports marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea. A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species. The marine environment supports many kinds of these habitats.

A river plume is a freshened water mass that is formed in the sea as a result of mixing of river discharge and saline seawater. River plumes are formed in coastal sea areas at many regions in the World. River plumes generally occupy wide-but-shallow sea surface layers bounded by sharp density gradients. The area of a river plume is 3-5 orders of magnitude greater than its depth; therefore, even small rivers with discharge rates ~1–10 m/s form river plumes with horizontal spatial extents ~10–100 m. Areas of river plumes formed by the largest rivers are ~100–1000 km2. Despite the relatively small volume of total freshwater runoff to the World Ocean, river plumes occupy up to 21% of shelf areas of the ocean, i.e., several million square kilometers.
Legacy sediment (LS) is depositional bodies of sediment inherited from the increase of human activities since the Neolithic. These include a broad range of land use and land cover changes, such as agricultural clearance, lumbering and clearance of native vegetation, mining, road building, urbanization, as well as alterations brought to river systems in the form of dams and other engineering structures meant to control and regulate natural fluvial processes (erosion, deposition, lateral migration, meandering). The concept of LS is used in geomorphology, ecology, as well as in water quality and toxicological studies.


















