Related Research Articles
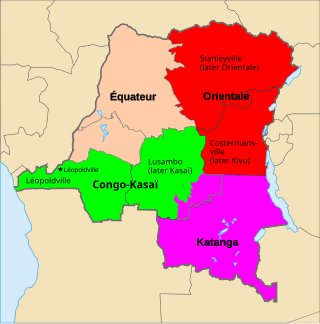
Katanga was one of the four large provinces created in the Belgian Congo in 1914. It was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 1966 and 2015, when it was split into the Tanganyika, Haut-Lomami, Lualaba, and Haut-Katanga provinces. Between 1971 and 1997, its official name was Shaba Province.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo is a country in Central Africa. By land area, the DRC is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 112 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the economic center. The country is bordered by the Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, Angola, the Cabinda exclave of Angola, and the South Atlantic Ocean.

South Kivu is one of 26 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Its capital is Bukavu.

The African Great Lakes are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. The series includes Lake Victoria, the third-largest freshwater lake in the world by area; Lake Tanganyika, the world's second-largest freshwater lake by volume and depth; Lake Malawi, the world's eighth-largest freshwater lake by area; and Lake Turkana, the world's largest permanent desert lake and the world's largest alkaline lake. Collectively, they contain 31,000 km3 (7,400 cu mi) of water, which is more than either Lake Baikal or the North American Great Lakes. This total constitutes about 25% of the planet's unfrozen surface fresh water. The large rift lakes of Africa are the ancient home of great biodiversity, and 10% of the world's fish species live in this region.

The Luvua River is a river in the Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It flows from the northern end of Lake Mweru on the Zambia-Congo border in a northwesterly direction for 350 kilometres (220 mi) to its confluence with the Lualaba River opposite the town of Ankoro. The Lualaba becomes the Congo River below the Boyoma Falls.

Central Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Middle Africa is an analogous term used by the United Nations in its geoscheme for Africa and consists of the following countries: Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Rwanda, and São Tomé and Príncipe. These eleven countries are members of the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS). Six of those countries are also members of the Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEMAC) and share a common currency, the Central African CFA franc.

The Hema people or Bahema (plural) are a Bantu ethnic group who are concentrated in parts of Ituri Province in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo.

The Banda people are an ethnic group of the Central African Republic. They are likewise found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Cameroon, and South Sudan. They were severely affected by slave raids of the 19th century and slave trading out of Africa. Under French colonial rule, most converted to Christianity but retained elements of their traditional religious systems and values.
The Logo people or Logoa (plural) are an ethnic group of Nilotic origin who live predominantly in the north-east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo as well as parts of western Uganda and southern South Sudan. There are believed to be more than 200,000 people who identify as ethnically Logo of whom most live in the Congo's Faradje Territory, a remote region in Haut-Uélé Province, where they form the ethnic majority. Logo people also live in Watsa and Aba, both also in Haut-Uélé, and in Yei in South Sudan.

The mining industry of the Democratic Republic of the Congo produces copper, diamonds, tantalum, tin, gold, and more than 63% of global cobalt production. Minerals and petroleum are central to the DRC's economy, making up more than 95% of the value of its exports.
The Bwa is an African society that is native to Burkina Faso. This society has an approximate population of over 300,000 persons. The Bwa people live in a number of individualized communities. They have no central government, and rely on their community standards. They are most known for their scarification and elaborate plank masks.

The Republic of the Congo is a country located on the western coast of Central Africa to the west of the Congo River. It is bordered to the west by Gabon, to the northwest by Cameroon, to the northeast by the Central African Republic, to the southeast by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda, and to the southwest by the Atlantic Ocean.

The International Criminal Court investigation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo or the situation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is an ongoing investigation by the International Criminal Court (ICC) into crimes committed in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) during the Second Congo War and its aftermath, including the Ituri and Kivu conflicts. The war started in 1998 and despite a peace agreement between combatants in 2003, conflict continued in the eastern parts of the country for several years. In April 2004 the government of the DRC formally referred the situation in the Congo to the International Criminal Court, and in June 2004, prosecutor Luis Moreno Ocampo, formally opened an investigation. To date, arrest warrants have been issued for:
The Turumbu people live in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, mostly in the Isangi Territory of the Tshopo District on both sides of the Congo River. They speak the Lombo language. As of 1971 their population was estimated to be 10,000. A more recent estimate put the population at 32,000.

Bas-Uélé is one of the 21 new provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Bas-Uélé, Haut-Uélé, Ituri, and Tshopo provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Orientale Province. Bas-Uélé was formed from the Bas-Uele District whose town of Buta was elevated to capital city of the new province.

The Lega people are a Bantu ethnic group of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. In 1998 their population was about 250,000.

The Itombwe Mountains are a range of mountains in the South Kivu province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). They run along the west shore of the northern part of Lake Tanganyika. They contain a vast area of contiguous montane forest and are home to a rich diversity of wildlife.

Bas-Uele District was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was formed from part of Uele District in 1912. Later it was merged back into Uele District, then split out again. There were various boundary changes. It roughly corresponded in area to the present Bas-Uélé province.
The Makongo River is a river of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is a left tributary of the Bomokandi River, which in turn is a tributary of the Uele River.
Titulé is a village in the Bas-Uélé province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was the terminus of a branch of the defunct Vicicongo line, a railway. The town is the center of a health zone and has a general referral hospital.
References
- ↑ "Bwa". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2011-10-08.
- 1 2 "BOA (ABABUA, ABABWA, BABOA, BABUA, BABWA, BUA, BWA)". AFRICAN ART MUSEUM. Retrieved 2011-10-08.
- ↑ Emizet F. Kisangani, F. Scott Bobb (2010). Historical Dictionary of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Scarecrow Press. p. 45. ISBN 0-8108-5761-8.
- ↑ Ambroise V. Bukassa (2010). Congo-Zaïre: éternel rebelle au consensus politique. Editions L'Harmattan. p. 8. ISBN 2-296-12502-6.