
Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings, as well as related disciplines, such as vexillology, together with the study of ceremony, rank and pedigree. Armory, the best-known branch of heraldry, concerns the design and transmission of the heraldic achievement. The achievement, or armorial bearings usually includes a coat of arms on a shield, helmet and crest, together with any accompanying devices, such as supporters, badges, heraldic banners and mottoes.

The overhand knot is one of the most fundamental knots, and it forms the basis of many others, including the simple noose, overhand loop, angler's loop, reef knot, fisherman's knot, half hitch, and water knot. The overhand knot is a stopper, especially when used alone, and hence it is very secure, to the point of jamming badly. It should be used if the knot is intended to be permanent. It is often used to prevent the end of a rope from unraveling. An overhand knot becomes a trefoil knot, a true knot in the mathematical sense, by joining the ends. It can also be adjusted, faired, or mis-tied as a half hitch.
Flag terminology is the nomenclature, or system of terms, used in vexillology, the study of flags, to describe precisely the parts, patterns, and other attributes of flags and their display.

Lødingen is a municipality in Nordland county in Norway. Lødingen is located on the southeastern corner of the island of Hinnøya, and is part of the traditional district of Ofoten. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Lødingen. The other main part of the municipality is Vestbygda. Lødingen has the nickname "Biketown" because it hosts several annual bicycle races, including "Lofoten Insomnia" and Vestbygd-rittet.

Three Crowns is the national emblem of Sweden, present in the coat of arms of Sweden, and composed of three yellow or gilded coronets ordered two above and one below, placed on a blue background. Similar designs are found on a number of other coats of arms or flags.

In heraldry, the field (background) of a shield can be divided into more than one area, or subdivision, of different tinctures, usually following the lines of one of the ordinaries and carrying its name. Shields may be divided this way for differencing or for purposes of marshalling, or simply for style. The lines that divide a shield may not always be straight, and there is a system of terminology for describing patterned lines, which is also shared with the heraldic ordinaries.

The coat of arms of Bulgaria consists of a crowned golden lion rampant over a dark red shield; above the shield is the Bulgarian historical crown. The shield is supported by two crowned golden lions rampant; below the shield there is compartment in the shape of oak twigs and white bands with the national motto "Unity makes strength" inscribed on them.

In heraldry, an ordinary is one of the two main types of charges, beside the mobile charges. An ordinary is a simple geometrical figure, bounded by straight lines and running from side to side or top to bottom of the shield. There are also some geometric charges known as subordinaries, which have been given lesser status by some heraldic writers, though most have been in use as long as the traditional ordinaries. Diminutives of ordinaries and some subordinaries are charges of the same shape, though thinner. Most of the ordinaries are theoretically said to occupy one-third of the shield; but this is rarely observed in practice, except when the ordinary is the only charge.
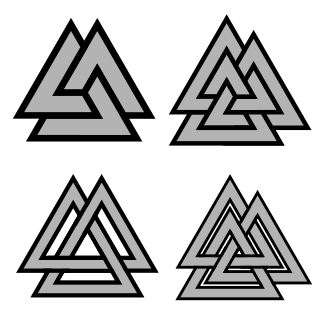
The valknut is a symbol consisting of three interlocked triangles. It appears on a variety of objects from the archaeological record of the ancient Germanic peoples. The term valknut is a modern development; it is not known what term or terms were used to refer to the symbol historically.

The coat of arms of Scotland, colloquially called the Lion Rampant, is the coat of arms historically used as arms of dominion by the monarchs of the Kingdom of Scotland, and later by monarchs of Great Britain and the United Kingdom. The coat of arms, or elements from it, are also used in heraldry to symbolise Scotland in general. The arms consist of a red lion surrounded by a red double border decorated with fleurs-de-lis, all on a gold background. The blazon, or heraldic description, is: Or a lion rampant Gules armed and langued Azure within a double tressure flory-counter-flory of the second.

The coat of arms of Denmark has a lesser and a greater version.
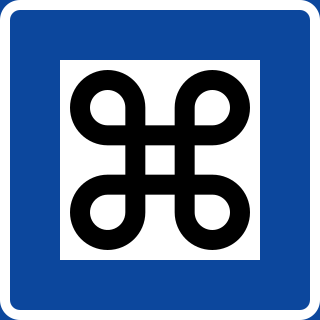
The looped square (⌘), also known as Saint John's Arms, Saint Hannes cross, and as the command-key symbol due to its use on the command key on Apple computer keyboards, is a symbol consisting of a square with outward pointing loops at its corners. It is referred to as a looped square, for example, in works regarding the Mississippian culture. It is also known as the place of interest sign when used on information signs, a practice which started in Finland in the 1950s, spreading to the other Nordic countries in the 1960s.

The lion is a common charge in heraldry. It traditionally symbolises courage, nobility, royalty, strength, stateliness and valour, because historically the lion has been regarded as the "king of beasts". The lion also carries Judeo-Christian symbolism. The Lion of Judah stands in the coat of arms of Jerusalem. Similar-looking lions can be found elsewhere, such as in the coat of arms of the Swedish royal House of Bjelbo, from there in turn derived into the coat of arms of Finland, formerly belonging to Sweden.

In heraldry and heraldic vexillology, a blazon is a formal description of a coat of arms, flag or similar emblem, from which the reader can reconstruct the appropriate image. The verb to blazon means to create such a description. The visual depiction of a coat of arms or flag has traditionally had considerable latitude in design, but a verbal blazon specifies the essentially distinctive elements. A coat of arms or flag is therefore primarily defined not by a picture but rather by the wording of its blazon. Blazon is also the specialized language in which a blazon is written, and, as a verb, the act of writing such a description. Blazonry is the art, craft or practice of creating a blazon. The language employed in blazonry has its own vocabulary, grammar and syntax, which becomes essential for comprehension when blazoning a complex coat of arms.
Heraldry in Wales has a tradition distinct from that of English and Scottish heraldry. There is evidence that heraldry was already being used in Wales by the middle of the thirteenth century; for instance, in Gwynedd, two sons of Llywelyn the Great are recorded as having borne coats of arms in this period. Following the integration of Wales into England in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, the Welsh heraldic tradition became merged into that of England.
Irish heraldry is the forms of heraldry, such as coats of arms, in Ireland. Since 1 April 1943 it is regulated in the Republic of Ireland by the Office of the Chief Herald of Ireland and in Northern Ireland by Norroy and Ulster King of Arms. Prior to that, heraldry on the whole island of Ireland was a function of the Ulster King of Arms, a crown office dating from 1552. Despite its name the Ulster King of Arms was based in Dublin.

A heraldic knot is a knot, unknot, or design incorporating a knot used in European heraldry. While a given knot can be used on more than one family's achievement of arms, the family on whose coat the knot originated usually gives its name to the said knot. These knots can be used to charge shields and crests, but can also be used in badges or as standalone symbols of the families for whom they are named. The simplest of these patterns, the Bowen knot, is often referred to as the heraldic knot in symbolism and art outside of heraldry.

Icelandic heraldry is the study of coats of arms and other insignia used in Iceland. It belongs to the German-Nordic heraldic tradition, as the heraldry of Iceland has been primarily influenced by the heraldic traditions of Norway, Denmark and other Nordic countries. Iceland does not have a strong sense of heraldic tradition, however, because the country lacks a governing body to oversee this. As a result, coats of arms registered as such are virtually nonexistent in modern Iceland. While many municipalities use more or less heraldic logos, there are no heraldic standards to which these must adhere, and they are registered as graphic designs rather than as coats of arms.

A number of cross symbols were developed for the purpose of the emerging system of heraldry, which appeared in Western Europe in about 1200. This tradition is partly in the use of the Christian cross an emblem from the 11th century, and increasingly during the age of the Crusades. Many cross variants were developed in the classical tradition of heraldry during the late medieval and early modern periods. Heraldic crosses are inherited in modern iconographic traditions and are used in numerous national flags.
A national coat of arms is a symbol which denotes an independent state in the form of a heraldic achievement. While a national flag is usually used by the population at large and is flown outside and on ships, a national coat of arms is normally considered a symbol of the government or the head of state personally and tends to be used in print, on armorial ware, and as a wall decoration in official buildings. The royal arms of a monarchy, which may be identical to the national arms, are sometimes described as arms of dominion or arms of sovereignty.






















