
Buffalo is the second-largest city in the U.S. state of New York and the seat of Erie County. It is at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of the Niagara River, and is next to the Canadian border with Southern Ontario. With a population of 278,349 according to the 2020 census, Buffalo is the 76th-largest city in the United States. The city and nearby Niagara Falls together make up the two-county Buffalo–Niagara Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA), which had an estimated population of 1.1 million in 2020, making it the 49th largest MSA in the United States. Buffalo is in Western New York, which is the largest population and economic center between Boston and Cleveland.

Erie County is a county along the shore of Lake Erie in western New York State. As of the 2020 census, the population was 954,236. The county seat is Buffalo, which makes up about 28% of the county's population. Both the county and Lake Erie were named for the regional Iroquoian language-speaking Erie tribe of Native Americans, who lived in the area before 1654. They were later pushed out by the more powerful Iroquoian nations tribes.

Niagara County is in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 212,666. The county seat is Lockport. The county name is from the Iroquois word Onguiaahra; meaning the strait or thunder of waters.

North Tonawanda is a city in Niagara County, New York, United States. The population was 31,568 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Buffalo–Niagara Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area. The city is named after Tonawanda Creek, its south border.

Lewiston is a town in Niagara County, New York, United States. The population was 16,262 at the 2010 census. The town and its contained village are named after Morgan Lewis, a governor of New York.

The Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, connecting Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. It forms a key section of the St. Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway. Traversing the Niagara Peninsula from Port Weller in St. Catharines to Port Colborne, it enables ships to ascend and descend the Niagara Escarpment and bypass Niagara Falls. It is the fourth canal connecting these waterways; three smaller predecessors also bore the same name.
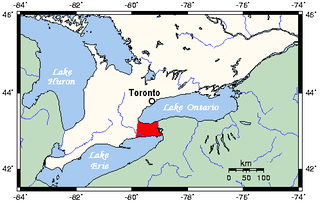
The Niagara Peninsula is the portion of Golden Horseshoe, Southern Ontario, Canada, lying between the southwestern shore of Lake Ontario and the northeastern shore of Lake Erie. Technically an isthmus rather than a peninsula, it stretches from the Niagara River in the east to Hamilton, Ontario, in the west. The population of the peninsula is roughly 1,000,000 people. The region directly across the Niagara River and Lake Erie in New York State is known as the Niagara Frontier.

Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the portion of New York State lying north of the New York City metropolitan area. Although the precise boundary is debated, Upstate New York excludes New York City and Long Island, and most definitions of the region exclude all or part of Westchester and Rockland counties. Major cities across Upstate New York from east to west include Albany, Utica, Binghamton, Syracuse, Rochester, and Buffalo.

Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves “Western New Yorkers.” Almost all sources agree WNY includes the cities of Buffalo, Niagara Falls, Jamestown, and the surrounding suburbs, as well as the outlying rural areas of the Great Lakes lowlands and Niagara Frontier, and Chautauqua-Alleghany Many would also place Rochester and the Genesee Valley in the region while some would also include the western Finger Lakes within the region. Others would describe the latter three areas as being in a separate Finger Lakes region.

The Onondaga Limestone is a group of hard limestones and dolomites of Devonian age that form an important geographic feature in some areas in which it outcrops; in others, especially its Southern Ontario portion, the formation can be less prominent as a local surface feature.

The Snowbelt is the region near the Great Lakes in North America where heavy snowfall in the form of lake-effect snow is particularly common. Snowbelts are typically found downwind of the lakes, principally off the eastern and southern shores.

The blizzard of 1977 hit Western New York and Southern Ontario's Niagara Peninsula from January 28 to February 1. Daily peak wind gusts ranging from 46 to 69 mph were recorded by the National Weather Service in Buffalo, with snowfall as high as 100 in (254 cm) recorded in areas, and the high winds blew this into drifts of 30 to 40 ft. There were 23 total storm-related deaths in Western New York, with five more in northern New York.
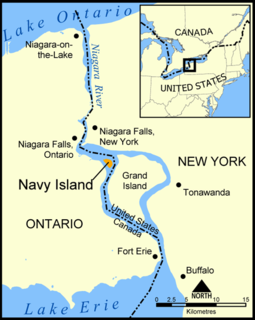
Navy Island is a small, uninhabited island in the Niagara River in the province of Ontario, managed by Parks Canada as a National Historic Site of Canada. It is located about 4.5 kilometres upstream from Horseshoe Falls, and has an area of roughly 1.2 km2. It is across from the town of Grand Island, New York, US. It was designated a national historic site in 1921 in recognition of its role in shipbuilding and the location of the short-lived Republic of Canada. The site is closed to the public, has no visitor facilities, and has not allowed camping since the expiration of a lease with the Niagara Parks Commission.

Bayview Junction is a major railway junction in southern Ontario, Canada. It is located at the intersection of three of the nation's busiest rail lines and is a popular location for railfans and trainspotters.

The Niagara Frontier refers to the stretch of land in the United States that is south of Lake Ontario and Lake Erie, and extends westward to Cleveland, Ohio. The term dates to the War of 1812, when the northern border was in contention between the United States and British forces in Canada. It refers only to the land east of the Niagara River and south of Lake Erie within the United States. The western side of the Niagara River, on the Canada/Ontario side, is the Niagara Peninsula; it is considered part of the Golden Horseshoe.

The October 2006 Buffalo storm was an unusual early-season lake effect snow storm that hit the Buffalo, New York area and other surrounding areas of the United States and Canada, from the afternoon of Thursday, October 12 through the morning of Friday, October 13, 2006. It was called Lake Storm Aphid by the National Weather Service office in Buffalo, in accordance with their naming scheme for lake-effect snowstorms for that year, which related to insects, though locals never used that terminology and have simply referred to it as the October Surprise or the October Storm or Arborgeddon.

The Buffalo–Niagara Falls Metropolitan Statistical Area is a metropolitan area, designated by the United States Census Bureau, encompassing two counties — Erie and Niagara in Western New York. It has a population of almost 1.2 million people. It is the second-largest metropolitan area in the state of New York, centering on the urbanized area of Buffalo.

The Southtowns is a region of Western New York, United States, that lies within the snowbelt or ski country. It includes the southern suburbs of Buffalo, New York. This is the common name for the southern part of Erie County, New York.

The Buffalo area economy consists of a mix of industrial, light manufacturing, high technology and service-oriented private sector companies. Instead of relying on a single industry or sector for its economic future, the region has taken a diversified approach that has the potential to create opportunities for growth and expansion in the 21st century.

The Niagara Falls Country Club, located at 505 Mountain View Drive, is an exclusive country club and golf course located in the Lewiston Heights neighborhood of Lewiston, New York, just outside Niagara Falls, New York.























