Related Research Articles

The candela is the unit of luminous intensity in the International System of Units (SI). It measures luminous power per unit solid angle emitted by a light source in a particular direction. Luminous intensity is analogous to radiant intensity, but instead of simply adding up the contributions of every wavelength of light in the source's spectrum, the contribution of each wavelength is weighted by the luminous efficiency function, the model of the sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths, standardized by the CIE and ISO. A common wax candle emits light with a luminous intensity of roughly one candela. If emission in some directions is blocked by an opaque barrier, the emission would still be approximately one candela in the directions that are not obscured.

Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle.
In optics, Lambert's cosine law says that the radiant intensity or luminous intensity observed from an ideal diffusely reflecting surface or ideal diffuse radiator is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle θ between the observer's line of sight and the surface normal; I = I0 cos θ. The law is also known as the cosine emission law or Lambert's emission law. It is named after Johann Heinrich Lambert, from his Photometria, published in 1760.

The lux is the unit of illuminance, or luminous flux per unit area, in the International System of Units (SI). It is equal to one lumen per square metre. In photometry, this is used as a measure of the intensity, as perceived by the human eye, of light that hits or passes through a surface. It is analogous to the radiometric unit watt per square metre, but with the power at each wavelength weighted according to the luminosity function, a model of human visual brightness perception, standardized by the CIE and ISO. In English, "lux" is used as both the singular and plural form. The word is derived from the Latin word for "light", lux.
In photometry, luminous intensity is a measure of the wavelength-weighted power emitted by a light source in a particular direction per unit solid angle, based on the luminosity function, a standardized model of the sensitivity of the human eye. The SI unit of luminous intensity is the candela (cd), an SI base unit.

Photometry is a branch of optics that deals with the measurement of light in terms of its perceived brightness to the human eye. It is concerned with quantifying the amount of light that is emitted, transmitted, or received by an object or a system.

In photometry, luminous flux or luminous power is the measure of the perceived power of light. It differs from radiant flux, the measure of the total power of electromagnetic radiation, in that luminous flux is adjusted to reflect the varying sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of light.

sRGB is a standard RGB color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61966-2-1:1999. sRGB is the current defined standard colorspace for the web, and it is usually the assumed colorspace for images that are neither tagged for a colorspace nor have an embedded color profile.
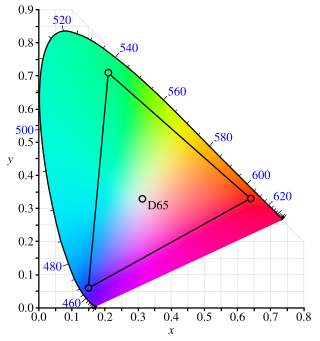
The Adobe RGB (1998) color space or opRGB is a color space developed by Adobe Inc. in 1998. It was designed to encompass most of the colors achievable on CMYK color printers, but by using RGB primary colors on a device such as a computer display. The Adobe RGB (1998) color space encompasses roughly 30% of the visible colors specified by the CIELAB color space – improving upon the gamut of the sRGB color space, primarily in cyan-green hues. It was subsequently standardized by the IEC as IEC 61966-2-5:1999 with a name opRGB and is used in HDMI.

In photometry, illuminance is the total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. It is a measure of how much the incident light illuminates the surface, wavelength-weighted by the luminosity function to correlate with human brightness perception. Similarly, luminous emittance is the luminous flux per unit area emitted from a surface. Luminous emittance is also known as luminous exitance.
The lumen is the unit of luminous flux, a measure of the perceived power of visible light emitted by a source, in the International System of Units (SI). Luminous flux differs from power in that radiant flux includes all electromagnetic waves emitted, while luminous flux is weighted according to a model of the human eye's sensitivity to various wavelengths; this weighting is standardized by the CIE and ISO. One lux is one lumen per square metre.
A foot-lambert or footlambert is a unit of luminance in United States customary units and some other unit systems. A foot-lambert equals 1/π or 0.3183 candela per square foot, or 3.426 candela per square meter. The foot-lambert is named after Johann Heinrich Lambert (1728–1777), a Swiss-German mathematician, physicist and astronomer. It is rarely used by electrical and lighting engineers, who prefer the candela per square foot or candela per square meter units.
Several measures of light are commonly known as intensity:
The lambert is a non-SI metric unit of luminance named for Johann Heinrich Lambert (1728–1777), a Swiss mathematician, physicist and astronomer. A related unit of luminance, the foot-lambert, is used in the lighting, cinema and flight simulation industries. The SI unit is the candela per square metre (cd/m2).
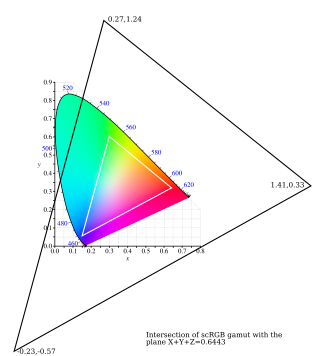
scRGB is a wide color gamut RGB color space created by Microsoft and HP that uses the same color primaries and white/black points as the sRGB color space but allows coordinates below zero and greater than one. The full range is −0.5 through just less than +7.5.
The stilb (sb) is the CGS unit of luminance for objects that are not self-luminous. It is equal to one candela per square centimeter or 104 nits (candelas per square meter). The name was coined by the French physicist André Blondel around 1920. It comes from the Greek word stilbein (στίλβειν), meaning 'to glitter'.
The apostilb is an obsolete unit of luminance. The SI unit of luminance is the candela per square metre (cd/m2). In 1942 Parry Moon proposed to rename the apostilb the blondel, after the French physicist André Blondel. The symbol for the apostilb is asb.
The bril is an old, non-SI, unit of luminance. The SI unit of luminance is the candela per square metre.
Images and videos use specific transfer functions to describe the relationship between electrical signal, scene light and displayed light.
References
- ↑ Buser, Pierre; Imbert, Michel (1992). Vision . MIT Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-262-02336-8.
nit luminance.
- ↑ Boyd, RLF, ed. (1992). Astronomical Photometry. Springer. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-7923-1653-4.
- ↑ "Multimedia systems and equipment – Colour measurement and management – Part 2-1: Colour management – Default RGB colour space – sRGB". International Electrotechnical Commission. 1999. IEC 61966-2-1.
- ↑ "ITU-R BT.2035-7" (PDF). A reference viewing environment for evaluation of HDTV program material or completed programmes. 2013-08-13. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-12-20. Retrieved 2022-12-20.
- ↑ Hung, Jonathan (May 3, 2010). "Acer Ferrari One 200 Review – More than a Netbook". PC Perspective. Retrieved 2018-01-21.
- ↑ Cohen, Steven. "What is HDR? High dynamic range TVs and formats, explained". Business Insider. Retrieved 2024-05-08.