
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of biochemical reactions to release the energy stored in nutrients through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The chemical energy released is available under the form of ATP. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire (as opposed to organisms that ferment) to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism. Even though it is branded as a "cycle", it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.

Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon is converted to organic compounds by living organisms. The compounds are then used to store energy and as structure for other biomolecules. Carbon is primarily fixed through photosynthesis, but some organisms use a process called chemosynthesis in the absence of sunlight.

Oxaloacetic acid (also known as oxalacetic acid or OAA) is a crystalline organic compound with the chemical formula HO2CC(O)CH2CO2H. Oxaloacetic acid, in the form of its conjugate base oxaloacetate, is a metabolic intermediate in many processes that occur in animals. It takes part in gluconeogenesis, the urea cycle, the glyoxylate cycle, amino acid synthesis, fatty acid synthesis and the citric acid cycle.
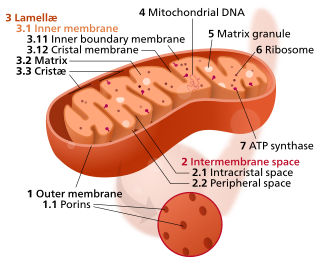
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. The word "matrix" stems from the fact that this space is viscous, compared to the relatively aqueous cytoplasm. The mitochondrial matrix contains the mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, soluble enzymes, small organic molecules, nucleotide cofactors, and inorganic ions.[1] The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate, and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.

The enzyme citrate synthase E.C. 2.3.3.1 ] exists in nearly all living cells and stands as a pace-making enzyme in the first step of the citric acid cycle. Citrate synthase is localized within eukaryotic cells in the mitochondrial matrix, but is encoded by nuclear DNA rather than mitochondrial. It is synthesized using cytoplasmic ribosomes, then transported into the mitochondrial matrix.
In biochemistry, fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is converted into fatty acids is derived from carbohydrates via the glycolytic pathway. The glycolytic pathway also provides the glycerol with which three fatty acids can combine to form triglycerides, the final product of the lipogenic process. When only two fatty acids combine with glycerol and the third alcohol group is phosphorylated with a group such as phosphatidylcholine, a phospholipid is formed. Phospholipids form the bulk of the lipid bilayers that make up cell membranes and surrounds the organelles within the cells. In addition to cytosolic fatty acid synthesis, there is also mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (mtFASII), in which malonyl-CoA is formed from malonic acid with the help of malonyl-CoA synthetase (ACSF3), which then becomes the final product octanoyl-ACP (C8) via further intermediate steps.
The enzyme citrate (pro-3S)-lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme citryl-CoA lyase catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a [citrate (pro-3S)-lyase] ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme citrate lyase deacetylase (EC 3.1.2.16) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a 2-ethylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-isopropylmalate synthase (EC 2.3.3.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-methylcitrate synthase (EC 2.3.3.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
ATP citrate synthase (also ATP citrate lyase (ACLY)) is an enzyme that in animals represents an important step in fatty acid biosynthesis. By converting citrate to acetyl-CoA, the enzyme links carbohydrate metabolism, which yields citrate as an intermediate, with fatty acid biosynthesis, which consumes acetyl-CoA. In plants, ATP citrate lyase generates cytosolic acetyl-CoA precursors of thousands of specialized metabolites, including waxes, sterols, and polyketides.
In enzymology, a deacetyl-[citrate-(pro-3S)-lyase] S-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.49) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Decylcitrate synthase (EC 2.3.3.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction in enzymology.

In enzymology, a homocitrate synthase (EC 2.3.3.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In molecular biology, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase or HMG-CoA synthase EC 2.3.3.10 is an enzyme which catalyzes the reaction in which acetyl-CoA condenses with acetoacetyl-CoA to form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA). This reaction comprises the second step in the mevalonate-dependent isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway. HMG-CoA is an intermediate in both cholesterol synthesis and ketogenesis. This reaction is overactivated in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1 if left untreated, due to prolonged insulin deficiency and the exhaustion of substrates for gluconeogenesis and the TCA cycle, notably oxaloacetate. This results in shunting of excess acetyl-CoA into the ketone synthesis pathway via HMG-CoA, leading to the development of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Glutaminolysis (glutamine + -lysis) is a series of biochemical reactions by which the amino acid glutamine is lysed to glutamate, aspartate, CO2, pyruvate, lactate, alanine and citrate.

In molecular biology, the citrate synthase family of proteins includes the enzymes citrate synthase EC 2.3.3.1, and the related enzymes 2-methylcitrate synthase EC 2.3.3.5 and ATP citrate lyase EC 2.3.3.8.










