
California is a state in the Western United States, lying on the American Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and the Mexican state of Baja California to the south. With over 38.9 million residents across a total area of approximately 163,696 square miles (423,970 km2), it is the most populous U.S. state, the third-largest U.S. state by area, and the most populated subnational entity in North America.

The San Francisco Peninsula is a peninsula in the San Francisco Bay Area that separates San Francisco Bay from the Pacific Ocean. On its northern tip is the City and County of San Francisco. Its southern base is Mountain View, in Santa Clara County, south of Palo Alto and north of Sunnyvale and Los Altos. Most of the Peninsula is occupied by San Mateo County, between San Francisco and Santa Clara counties, and including the cities and towns of Atherton, Belmont, Brisbane, Burlingame, Colma, Daly City, East Palo Alto, El Granada, Foster City, Hillsborough, Half Moon Bay, La Honda, Loma Mar, Los Altos, Menlo Park, Millbrae, Pacifica, Palo Alto, Pescadero, Portola Valley, Redwood City, San Bruno, San Carlos, San Mateo, South San Francisco, and Woodside.
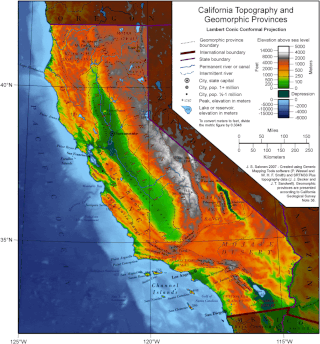
California is a U.S. state on the western coast of North America. Covering an area of 163,696 sq mi (423,970 km2), California is among the most geographically diverse states. The Sierra Nevada, the fertile farmlands of the Central Valley, and the arid Mojave Desert of the south are some of the major geographic features of this U.S. state. It is home to some of the world's most exceptional trees: the tallest, most massive, and oldest. It is also home to both the highest and lowest points in the 48 contiguous states. The state is generally divided into Northern and Southern California, although the boundary between the two is not well defined. San Francisco is decidedly a Northern California city and Los Angeles likewise a Southern California one, but areas in between do not often share their confidence in geographic identity. The US Geological Survey defines the geographic center of California about 7.1 miles driving distance from the United States Forest Service office in the Northern Californian city of North Fork, California.

State Route 1 (SR 1) is a major north–south state highway that runs along most of the Pacific coastline of the U.S. state of California. At 656 miles (1,056 km), it is the longest state route in California, and the second-longest in the US after Montana Highway 200. SR 1 has several portions designated as either Pacific Coast Highway (PCH), Cabrillo Highway, Shoreline Highway, or Coast Highway. Its southern terminus is at Interstate 5 (I-5) near Dana Point in Orange County and its northern terminus is at U.S. Route 101 (US 101) near Leggett in Mendocino County. SR 1 also at times runs concurrently with US 101, most notably through a 54-mile (87 km) stretch in Ventura and Santa Barbara counties, and across the Golden Gate Bridge.

The Santa Ana winds, also sometimes called the devil winds, are strong, extremely dry downslope winds that originate inland and affect coastal Southern California and northern Baja California. They originate from cool, dry high-pressure air masses in the Great Basin.

Santa Cruz County, officially the County of Santa Cruz, is a county on the Pacific coast of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 270,861. The county seat is Santa Cruz. Santa Cruz County comprises the Santa Cruz–Watsonville, CA Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the San Jose–San Francisco–Oakland, CA Combined Statistical Area. The county is on the California Central Coast, south of the San Francisco Bay Area region. The county forms the northern coast of the Monterey Bay, with Monterey County forming the southern coast.

Northern California is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California, spanning the northernmost 48 of the state's 58 counties. Its main population centers include the San Francisco Bay Area, the Greater Sacramento area, the Redding, California, area south of the Cascade Range, and the Metropolitan Fresno area. Northern California also contains redwood forests, along with most of the Sierra Nevada, including Yosemite Valley and part of Lake Tahoe, Mount Shasta, and most of the Central Valley, one of the world's most productive agricultural regions.

The Central Coast is an area of California, roughly spanning the coastal region between Point Mugu and Monterey Bay. It lies northwest of Los Angeles and south of the San Francisco Bay Area, and includes the rugged, rural, and sparsely populated stretch of coastline known as Big Sur.

Central California is generally thought of as the middle third of the U.S. state of California, north of Southern California and south of Northern California. It includes the northern portion of the San Joaquin Valley, part of the Central Coast, the central hills of the California Coast Ranges and the foothills and mountain areas of the central Sierra Nevada.

The economy of the State of California is the largest in the United States, with a $3.89 trillion gross state product (GSP) as of 2023. It is the largest sub-national economy in the world. If California were a sovereign nation (2024), it would rank in terms of nominal GDP as the world's fifth largest economy, ahead of both India and the United Kingdom. Additionally, California's Silicon Valley is home to some of the world's most valuable technology companies, including Apple, Alphabet, and Nvidia. In total, 11 of the Fortune 100 companies and 53 of the Fortune 500 companies are headquartered in California.

The California State Coastal Conservancy is a non-regulatory state agency in California established in 1976 to enhance coastal resources and public access to the coast. The CSCC is a department of the California Natural Resources Agency. The agency's work is conducted along the entirety of the California coast, including the interior San Francisco Bay and is responsible for the planning and coordination of federal land sales to acquire into state land as well as award grant funding for improvement projects. The Board of Directors for the agency is made up of seven members who are appointed by the Governor of California and approved by the California Legislature, members of the California State Assembly and California State Senate engage and provide oversight within their legislative capacity.

The Coast Ranges of California span 400 miles (644 km) from Del Norte or Humboldt County, California, south to Santa Barbara County. The other three coastal California mountain ranges are the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges and the Klamath Mountains.

The California Coastal National Monument is located along the entire coastline of the U.S. state of California. This monument ensures the protection of all islets, reefs and rock outcroppings along the coast of California within 12 nautical miles (22 km) of shore along the entire 840-mile (1,350 km) long coastline. Conservative estimates are for at least 20,000 such outcroppings. The monument was created by Bill Clinton via Presidential proclamation on January 11, 2000, with the authority in section two of the Antiquities Act of 1906. As of 2014, the monument has expanded to 2,272 acres (919 ha). The U.S. Bureau of Land Management, an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages the monument, has developed gateways in cooperation with other agencies along the California coast to introduce the monument to the public. These include the Trinidad, Point Arena, Fort Bragg-Mendocino, Pigeon Point Lighthouse, Piedras Blancas State Marine Reserve and Marine Conservation Area, and the Palos Verdes Peninsula. Although being the most-viewed national monument in California, people are usually unaware that the entire coastline is a national monument.

The California Coastal Commission (CCC) is a state agency within the California Natural Resources Agency with quasi-judicial control of land and public access along the state's 1,100 miles (1,800 km) of coastline. Its mission as defined in the California Coastal Act is "to protect, conserve, restore, and enhance the environment of the California coastline".

The Oxnard Plain is a large coastal plain in southwest Ventura County, California, United States surrounded by the mountains of the Transverse ranges. The cities of Oxnard, Camarillo, Port Hueneme and much of Ventura as well as the unincorporated communities of Hollywood Beach, El Rio, Saticoy, Silver Strand Beach, and Somis lie within the over 200-square-mile alluvial plain (520 km2). The population within the plain comprises a majority of the western half of the Oxnard-Thousand Oaks-Ventura Metro Area and includes the largest city along the Central Coast of California. The 16.5-mile-long coastline (26.6 km) is among the longest stretches of continuous, linear beaches in the state.
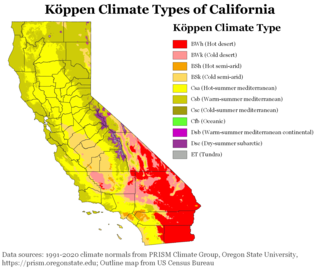
The climate of California varies widely from hot desert to alpine tundra, depending on latitude, elevation, and proximity to the Pacific Coast. California's coastal regions, the Sierra Nevada foothills, and much of the Central Valley have a Mediterranean climate, with warmer, drier weather in summer and cooler, wetter weather in winter. The influence of the ocean generally moderates temperature extremes, creating warmer winters and substantially cooler summers in coastal areas.

The 2008 California wildfire season was one of the most devastating in the state of the 21st century. While 6,255 fires occurred, about two-thirds as many as in 2007, the total area burned— 1,593,690 acres —far exceeded that of previous years.

The climate of Los Angeles is mild to hot year-round, and mostly dry. It is classified as borderline Mediterranean and semi-arid. The city is characterized by seasonal changes in rainfall—with a dry summer and a winter rainy season. Under the Köppen climate classification, the coastal areas are classified as BSh and Csb, while the inland areas are classified as BSh and Csa.

The geography of southern California refers to the geography of southern California in the United States.

The 2022 California wildfire season was a series of wildfires throughout the U.S. state of California. By the end of the year, a total of 7,667 fires had been recorded, totaling approximately 363,939 acres across the state. Wildfires killed nine people in California in 2022, destroyed 772 structures, and damaged another 104. The 2022 season followed the 2020 and 2021 California wildfire seasons, which had the highest and second-highest (respectively) numbers of acres burned in the historical record, with a sharp drop in acreage burned.























