Sodium laureth sulfate (SLES), an accepted contraction of sodium lauryl ether sulfate (SLES), also called sodium alkylethersulfate, is an anionic detergent and surfactant found in many personal care products and for industrial uses. SLES is an inexpensive and very effective foaming agent. SLES, sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), ammonium lauryl sulfate (ALS), and sodium pareth sulfate are surfactants that are used in many cosmetic products for their cleaning and emulsifying properties. It is derived from palm kernel oil or coconut oil. In herbicides, it is used as a surfactant to improve absorption of the herbicidal chemicals and reduces time the product takes to be rainfast, when enough of the herbicidal agent will be absorbed.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) or sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), sometimes written sodium laurilsulfate, is an organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)11OSO3Na and structure H3C−(CH2)11−O−S(=O)2−O−Na+. It is an anionic surfactant used in many cleaning and hygiene products. This compound is the sodium salt of the 12-carbon organosulfate. Its hydrocarbon tail combined with a polar "headgroup" give the compound amphiphilic properties that make it useful as a detergent. SDS is also component of mixtures produced from inexpensive coconut and palm oils. SDS is a common component of many domestic cleaning, personal hygiene and cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food products, as well as of industrial and commercial cleaning and product formulations.

A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with cleansing properties when in dilute solutions. There are a large variety of detergents, a common family being the alkylbenzene sulfonates, which are soap-like compounds that are more soluble in hard water, because the polar sulfonate is less likely than the polar carboxylate to bind to calcium and other ions found in hard water.
Roundup is the brand name of a systemic, broad-spectrum glyphosate-based herbicide originally produced by Monsanto, which Bayer acquired in 2018. Glyphosate is the most widely used herbicide in the United States. As of 2009, sales of Roundup herbicides still represented about 10 percent of Monsanto's revenue despite competition from Chinese producers of other glyphosate-based herbicides. The overall Roundup line of products, which includes genetically modified seeds, represented about half of Monsanto's yearly revenue. The product is marketed to consumers by Scotts Miracle-Gro Company.

Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may function as emulsifiers, wetting agents, detergents, foaming agents, or dispersants. The word "surfactant" is a blend of surface-active agent, coined c. 1950.

Hair conditioner is a hair care cosmetic product used to improve the feel, texture, appearance and manageability of hair. Its main purpose is to reduce friction between strands of hair to allow smoother brushing or combing, which might otherwise cause damage to the scalp. Various other benefits are often advertised, such as hair repair, strengthening, or a reduction in split ends.
A foaming agent is a material such as a surfactant or a blowing agent that facilitates the formation of foam. A surfactant, when present in small amounts, reduces surface tension of a liquid or increases its colloidal stability by inhibiting coalescence of bubbles. A blowing agent is a gas that forms the gaseous part of the foam.

Laundry detergent is a type of detergent used for cleaning dirty laundry (clothes). Laundry detergent is manufactured in powder and liquid form.

A bubble bath is a filled bathtub with a layer of soap bubbles on the surface of the water. Less commonly, aerated or carbonated baths are called bubble baths.
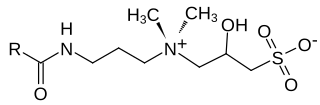
Hydroxysultaines are chemical compounds used in high-foaming shampoos, bath products and shower gels especially in conjunction with ether sulfates and alkyl sulfates. They are also used in industrial applications where high, stable foam is required. Chemically, hydroxysultaines are zwitterionic, typically containing covalently linked positive and negative ions.
An antistatic agent is a compound used for treatment of materials or their surfaces in order to reduce or eliminate buildup of static electricity. Static charge may be generated by the triboelectric effect or by a non-contact process using a high voltage power source. Static charge may be introduced on a surface as part of an in-mold label printing process.
Cocamidopropyl betaine (CAPB) is a mixture of closely related organic compounds derived from coconut oil and dimethylaminopropylamine. CAPB is available as a viscous pale yellow solution and it is used as a surfactant in personal care products and animal husbandry. The name reflects that the major part of the molecule, the lauric acid group, is derived from coconut oil. Cocamidopropyl betaine to a significant degree has replaced cocamide DEA.
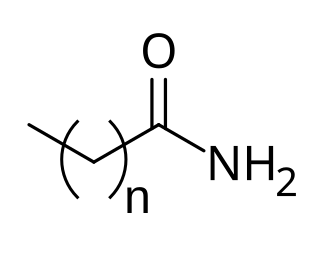
Cocamide is a mixture of amides manufactured from the fatty acids obtained from coconut oil. As coconut oil contains about 50% of lauric acid, in formulas only the 12-carbon chains tend to be considered. Therefore the formula of cocamide can be written as CH3(CH2)10CONH2, though the number of carbon atoms in the chains varies.

An amphiphile, or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic and lipophilic (fat-loving) properties. Such a compound is called amphiphilic or amphipathic. Amphiphilic compounds include surfactants. The phospholipid amphiphiles are the major structural component of cell membranes.

In chemistry, an amine oxide, also known as an amine N-oxide or simply N-oxide, is a chemical compound that contains the functional group R3N+−O−, a nitrogen-oxygen coordinate covalent bond with three additional hydrogen and/or substituent-group side chains attached to N. Sometimes it is written as R3N→O or, alternatively, as R3N=O.

Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, foul odors, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removing offensive odor, and avoiding the spread of dirt and contaminants to oneself and others. Some cleaning agents can kill bacteria and clean at the same time. Others, called degreasers, contain organic solvents to help dissolve oils and fats.

Dimethylaminopropylamine (DMAPA) is a diamine used in the preparation of some surfactants, such as cocamidopropyl betaine which is an ingredient in many personal care products including soaps, shampoos, and cosmetics. BASF, a major producer, claims that DMAPA-derivatives do not sting the eyes and makes a fine-bubble foam, making it appropriate in shampoos.

Shampoo is a hair care product, typically in the form of a viscous liquid, that is used for cleaning hair. Less commonly, shampoo is available in solid bar format. Shampoo is used by applying it to wet hair, massaging the product into the scalp, and then rinsing it out. Some users may follow a shampooing with the use of hair conditioner.

Disodium cocoamphodiacetate (DSCADA) is a synthetic amphoteric surfactant routinely used in personal care products.
Isethionates are esters of long-chain aliphatic carboxylic acids (C8 – C18) with isethionic acid (2-hydroxyethanesulfonic acid) or salts thereof, such as ammonium isethionate or sodium isethionate. They are also referred to as acyl isethionates or acyloxyethanesulfonates.













