
Omeprazole, sold under the brand names Prilosec and Losec, among others, is a medication used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. It is also used to prevent upper gastrointestinal bleeding in people who are at high risk. Omeprazole is a proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) and its effectiveness is similar to that of other PPIs. It can be taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. It is also available in the fixed-dose combination medication omeprazole/sodium bicarbonate as Zegerid and as Konvomep.

Cytochromes P450 are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compounds, as well as for hormone synthesis and breakdown, steroid hormone synthesis, drug metabolism, and the biosynthesis of defensive compounds, fatty acids, and hormones. CYP450 enzymes convert xenobiotics into hydrophilic derivatives, which are more readily excreted. In almost all of the transformations that they catalyze, P450's affect hydroxylation.

Cimetidine, sold under the brand name Tagamet among others, is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production. It is mainly used in the treatment of heartburn and peptic ulcers.
Cytochrome P450 3A4 is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine, which in humans is encoded by CYP3A4 gene. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules (xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body. It is highly homologous to CYP3A5, another important CYP3A enzyme.
Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP2D6 gene. CYP2D6 is primarily expressed in the liver. It is also highly expressed in areas of the central nervous system, including the substantia nigra.

Zileuton (trade name Zyflo) is an orally active inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase, and thus inhibits leukotrienes (LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4) formation, used for the maintenance treatment of asthma. Zileuton was introduced in 1996 by Abbott Laboratories and is now marketed in two formulations by Cornerstone Therapeutics Inc. under the brand names Zyflo and Zyflo CR. The original immediate-release formulation, Zyflo, is taken four times per day. The extended-release formulation, Zyflo CR, is taken twice daily.

In pharmaceutical sciences, drug interactions occur when a drug's mechanism of action is affected by the concomitant administration of substances such as foods, beverages, or other drugs. A popular example of drug-food interaction is the effect of grapefruit in the metabolism of drugs.
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds. The study of drug metabolism is called pharmacokinetics.
Toxication, toxification or toxicity exaltation is the conversion of a chemical compound into a more toxic form in living organisms or in substrates such as soil or water. The conversion can be caused by enzymatic metabolism in the organisms, as well as by abiotic chemical reactions. While the parent drug are usually less active, both the parent drug and its metabolite can be chemically active and cause toxicity, leading to mutagenesis, teratogenesis, and carcinogenesis. Different classes of enzymes, such as P450-monooxygenases, epoxide hydrolase, or acetyltransferases can catalyze the process in the cell, mostly in the liver.

Dextromethorphan (DXM) is a cough suppressant used in many cough and cold medicines. It affects serotonin, norepinephrine, NMDA, and sigma-1 receptors in the brain, all of which have been implicated in the pathophysiology of depression. In 2022, the FDA approved the combination dextromethorphan/bupropion to serve as a rapid acting antidepressant in patients with major depressive disorder.

Metaxalone, sold under the brand name Skelaxin, is a muscle relaxant medication used to relax muscles and relieve pain caused by strains, sprains, and other musculoskeletal conditions. Its exact mechanism of action is not known, but it may be due to general central nervous system depression. It is a moderately strong muscle relaxant, with relatively low incidence of side effects.
Cytochrome P450 1A2, a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the human body. In humans, the CYP1A2 enzyme is encoded by the CYP1A2 gene.
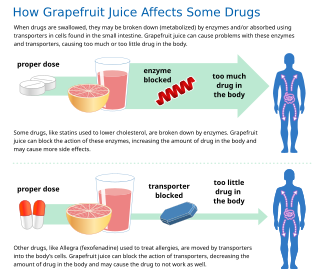
Some fruit juices and fruits can interact with numerous drugs, in many cases causing adverse effects. The effect is most studied with grapefruit and grapefruit juice, but similar effects have been observed with certain other citrus fruits.

Cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 9 is an enzyme protein. The enzyme is involved in the metabolism, by oxidation, of both xenobiotics, including drugs, and endogenous compounds, including fatty acids. In humans, the protein is encoded by the CYP2C9 gene. The gene is highly polymorphic, which affects the efficiency of the metabolism by the enzyme.

Cytochrome P450 2C19 is an enzyme protein. It is a member of the CYP2C subfamily of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system. This subfamily includes enzymes that catalyze metabolism of xenobiotics, including some proton pump inhibitors and antiepileptic drugs. In humans, it is the CYP2C19 gene that encodes the CYP2C19 protein. CYP2C19 is a liver enzyme that acts on at least 10% of drugs in current clinical use, most notably the antiplatelet treatment clopidogrel (Plavix), drugs that treat pain associated with ulcers, such as omeprazole, antiseizure drugs such as mephenytoin, the antimalarial proguanil, and the anxiolytic diazepam.
AmpliChip CYP450 Test is a clinical test from Roche and part of the AmpliChip series. The test aims to find the specific gene types ( genotypes) of the patient that will determine how he or she metabolizes certain medicines, and therefore guides the doctors to prescribe the medicine suited for the best effectiveness and least side effects.
Cytochrome P450, family 3, subfamily A, also known as CYP3A, is a human gene locus. A homologous locus is found in mice.
Epoxygenases are a set of membrane-bound, heme-containing cytochrome P450 enzymes that metabolize polyunsaturated fatty acids to epoxide products that have a range of biological activities. The most thoroughly studied substrate of the CYP epoxylgenases is arachidonic acid. This polyunsaturated fatty acid is metabolized by cyclooxygenases to various prostaglandin, thromboxane, and prostacyclin metabolites in what has been termed the first pathway of eicosanoid production; it is also metabolized by various lipoxygenases to hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids and leukotrienes in what has been termed the second pathway of eicosanoid production. The metabolism of arachidonic acid to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids by the CYP epoxygenases has been termed the third pathway of eicosanoid metabolism. Like the first two pathways of eicosanoid production, this third pathway acts as a signaling pathway wherein a set of enzymes metabolize arachidonic acid to a set of products that act as secondary signals to work in activating their parent or nearby cells and thereby orchestrate functional responses. However, none of these three pathways is limited to metabolizing arachidonic acid to eicosanoids. Rather, they also metabolize other polyunsaturated fatty acids to products that are structurally analogous to the eicosanoids but often have different bioactivity profiles. This is particularly true for the CYP epoxygenases which in general act on a broader range of polyunsaturated fatty acids to form a broader range of metabolites than the first and second pathways of eicosanoid production. Furthermore, the latter pathways form metabolites many of which act on cells by binding with and thereby activating specific and well-characterized receptor proteins; no such receptors have been fully characterized for the epoxide metabolites. Finally, there are relatively few metabolite-forming lipoxygenases and cyclooxygenases in the first and second pathways and these oxygenase enzymes share similarity between humans and other mammalian animal models. The third pathway consists of a large number of metabolite-forming CYP epoxygenases and the human epoxygenases have important differences from those of animal models. Partly because of these differences, it has been difficult to define clear roles for the epoxygenase-epoxide pathways in human physiology and pathology.
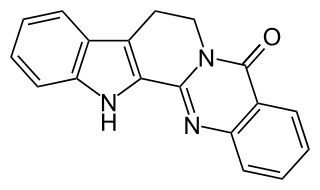
Rutecarpine or rutaecarpine is a COX-2 inhibitor isolated from Tetradium ruticarpum, a tree native to China. It is classified as a non-basic alkaloid.

Nordoxepin, also known as N-desmethyldoxepin, is an organic compound. A colorless solid, it attracted attention as the major active metabolite of the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) doxepin (Sinequan). It has been found to play a significant role in the antidepressant effects of doxepin.














