A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification.

X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information.
In crystallography, a crystallographic point group is a set of symmetry operations, corresponding to one of the point groups in three dimensions, such that each operation would leave the structure of a crystal unchanged i.e. the same kinds of atoms would be placed in similar positions as before the transformation. For example, in many crystals in the cubic crystal system, a rotation of the unit cell by 90 degrees around an axis that is perpendicular to one of the faces of the cube is a symmetry operation that moves each atom to the location of another atom of the same kind, leaving the overall structure of the crystal unaffected.
Nitrogenases are enzymes (EC 1.18.6.1EC 1.19.6.1) that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria) and rhizobacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only family of enzymes known to catalyze this reaction, which is a step in the process of nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation is required for all forms of life, with nitrogen being essential for the biosynthesis of molecules (nucleotides, amino acids) that create plants, animals and other organisms. They are encoded by the Nif genes or homologs. They are related to protochlorophyllide reductase.

In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted just by rotations about formally single bonds. While any two arrangements of atoms in a molecule that differ by rotation about single bonds can be referred to as different conformations, conformations that correspond to local minima on the potential energy surface are specifically called conformational isomers or conformers. Conformations that correspond to local maxima on the energy surface are the transition states between the local-minimum conformational isomers. Rotations about single bonds involve overcoming a rotational energy barrier to interconvert one conformer to another. If the energy barrier is low, there is free rotation and a sample of the compound exists as a rapidly equilibrating mixture of multiple conformers; if the energy barrier is high enough then there is restricted rotation, a molecule may exist for a relatively long time period as a stable rotational isomer or rotamer. When the time scale for interconversion is long enough for isolation of individual rotamers, the isomers are termed atropisomers. The ring-flip of substituted cyclohexanes constitutes another common form of conformational isomerism.

In chemistry an eclipsed conformation is a conformation in which two substituents X and Y on adjacent atoms A, B are in closest proximity, implying that the torsion angle X–A–B–Y is 0°. Such a conformation can exist in any open chain, single chemical bond connecting two sp3-hybridised atoms, and it is normally a conformational energy maximum. This maximum is often explained by steric hindrance, but its origins sometimes actually lie in hyperconjugation.
Anions that interact weakly with cations are termed non-coordinating anions, although a more accurate term is weakly coordinating anion. Non-coordinating anions are useful in studying the reactivity of electrophilic cations. They are commonly found as counterions for cationic metal complexes with an unsaturated coordination sphere. These special anions are essential components of homogeneous alkene polymerisation catalysts, where the active catalyst is a coordinatively unsaturated, cationic transition metal complex. For example, they are employed as counterions for the 14 valence electron cations [(C5H5)2ZrR]+ (R = methyl or a growing polyethylene chain). Complexes derived from non-coordinating anions have been used to catalyze hydrogenation, hydrosilylation, oligomerization, and the living polymerization of alkenes. The popularization of non-coordinating anions has contributed to increased understanding of agostic complexes wherein hydrocarbons and hydrogen serve as ligands. Non-coordinating anions are important components of many superacids, which result from the combination of Brønsted acids and Lewis acids.
Molybdenum trioxide describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula MoO3(H2O)n where n = 0, 1, 2. These compounds are produced on the largest scale of any molybdenum compound. The anhydrous oxide is a precursor to molybdenum metal, an important alloying agent. It is also an important industrial catalyst. It is a yellow solid, although impure samples can appear blue or green.
In materials science, polymorphism describes the existence of a solid material in more than one form or crystal structure. Polymorphism is a form of isomerism. Any crystalline material can exhibit the phenomenon. Allotropy refers to polymorphism for chemical elements. Polymorphism is of practical relevance to pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, pigments, dyestuffs, foods, and explosives. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." According to McCrone, polymorphs are "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." Materials with two polymorphs are called dimorphic, with three polymorphs, trimorphic, etc.

In the study of conformational isomerism, the Gauche effect is an atypical situation where a gauche conformation is more stable than the anti conformation (180°).
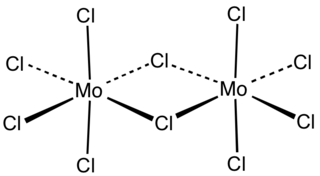
Molybdenum(V) chloride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula MoCl5. This dark volatile solid is used in research to prepare other molybdenum compounds. It is moisture-sensitive and soluble in chlorinated solvents.

Ammonium heptamolybdate is the inorganic compound whose chemical formula is (NH4)6Mo7O24, normally encountered as the tetrahydrate. A dihydrate is also known. It is a colorless solid, often referred to as ammonium paramolybdate or simply as ammonium molybdate, although "ammonium molybdate" can also refer to ammonium orthomolybdate, (NH4)2MoO4, and several other compounds. It is one of the more common molybdenum compounds.
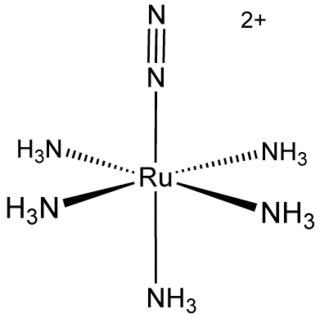
Transition metal dinitrogen complexes are coordination compounds that contain transition metals as ion centers the dinitrogen molecules (N2) as ligands.

Potassium octachlorodimolybdate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula K4[Mo2Cl8]. It is known as a red-coloured, microcrystalline solid. The anion is of historic interest as one of the earliest illustrations of a quadruple bonding. The salt is usually obtained as the pink-coloured dihydrate.

The program Coot is used to display and manipulate atomic models of macromolecules, typically of proteins or nucleic acids, using 3D computer graphics. It is primarily focused on building and validation of atomic models into three-dimensional electron density maps obtained by X-ray crystallography methods, although it has also been applied to data from electron microscopy.

In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism refers to the existence or possibility of isomers.

In chemistry, a molybdate is a compound containing an oxyanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6: O−−Mo(=O)2−O−. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxyanions, which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state. The larger oxyanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxyanions range in size from the simplest MoO2−
4, found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, CrO2−
4, Cr
2O2−
7, Cr
3O2−
10 and Cr
4O2−
13 ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten.
A metal carbido complex is a coordination complex that contains a carbon atom as a ligand. They are analogous to metal nitrido complexes. Carbido complexes are a molecular subclass of carbides, which are prevalent in organometallic and inorganic chemistry. Carbido complexes represent models for intermediates in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis, olefin metathesis, and related catalytic industrial processes. Ruthenium-based carbido complexes are by far the most synthesized and characterized to date. Although, complexes containing chromium, gold, iron, nickel, molybdenum, osmium, rhenium, and tungsten cores are also known. Mixed-metal carbides are also known.
In chemistry, a C–H···O interaction is occasionally described as a special type of weak hydrogen bond. These interactions frequently occur in the structures of important biomolecules like amino acids, proteins, sugars, DNA and RNA.
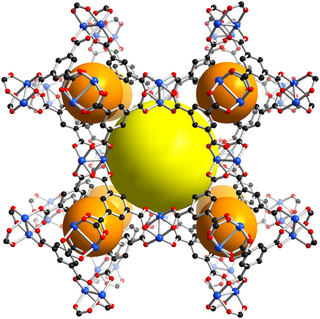
HKUST-1, which is also called MOF-199, is a material in the class of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Metal-organic frameworks are crystalline materials, in which metals are linked by ligands to form repeating coordination motives extending in three dimensions. The HKUST-1 framework is built up of dimeric metal units, which are connected by benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate linker molecules. The paddlewheel unit is the commonly used structural motif to describe the coordination environment of the metal centers and also called secondary building unit (SBU) of the HKUST-1 structure. The paddlewheel is built up of four benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate linkers molecules, which bridge two metal centers. One water molecules is coordinated to each of the two metal centers at the axial position of the paddlewheel unit in the hydrated state, which is usually found if the material is handled in air. After an activation process, these water molecules can be removed and the coordination site at the metal atoms is left unoccupied. This unoccupied coordination site is called coordinatively unsaturated site (CUS) and can be accessed by other molecules.