
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (−OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, C
6H
5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.

Phenol is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group bonded to a hydroxy group. Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns.

Acetophenone is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH3. It is the simplest aromatic ketone. This colorless, viscous liquid is a precursor to useful resins and fragrances.

The cumene process is an industrial process for synthesizing phenol and acetone from benzene and propylene. The term stems from cumene, the intermediate material during the process. It was invented by R. Ūdris and P. Sergeyev in 1942 (USSR), and independently by Heinrich Hock in 1944.
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products. Cyclohexane is mainly used for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, which are precursors to nylon.
The Friedel–Crafts reactions are a set of reactions developed by Charles Friedel and James Crafts in 1877 to attach substituents to an aromatic ring. Friedel–Crafts reactions are of two main types: alkylation reactions and acylation reactions. Both proceed by electrophilic aromatic substitution.
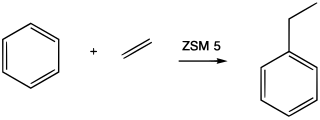
Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene. Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents.
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a planar five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. It is a colorless liquid with a benzene-like odor. In most of its reactions, it resembles benzene. Compounds analogous to thiophene include furan (C4H4O), selenophene (C4H4Se) and pyrrole (C4H4NH), which each vary by the heteroatom in the ring.
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications.
Cyclohexene is a hydrocarbon with the formula C6H10. This cycloalkene is a colorless liquid with a sharp smell. It is an intermediate in various industrial processes. Cyclohexene is not very stable upon long term storage with exposure to light and air because it forms peroxides.

Cyclohexanol is the organic compound with the formula HOCH(CH2)5. The molecule is related to cyclohexane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by a hydroxyl group. This compound exists as a deliquescent colorless solid with a camphor-like odor, which, when very pure, melts near room temperature. Millions of tonnes are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon.

Hydroquinone, also known as benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, a derivative of benzene, having the chemical formula C6H4(OH)2. It has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a para position. It is a white granular solid. Substituted derivatives of this parent compound are also referred to as hydroquinones. The name "hydroquinone" was coined by Friedrich Wöhler in 1843.
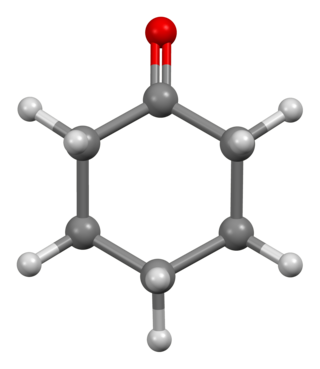
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has an odor reminiscent of acetone. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Billions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon.

In organic chemistry, organic peroxides are organic compounds containing the peroxide functional group. If the R′ is hydrogen, the compounds are called hydroperoxides, which are discussed in that article. The O−O bond of peroxides easily breaks, producing free radicals of the form RO•. Thus, organic peroxides are useful as initiators for some types of polymerization, such as the acrylic, unsaturated polyester, and vinyl ester resins used in glass-reinforced plastics. MEKP and benzoyl peroxide are commonly used for this purpose. However, the same property also means that organic peroxides can explosively combust. Organic peroxides, like their inorganic counterparts, are often powerful bleaching agents.

Cumene (isopropylbenzene) is an organic compound that contains a benzene ring with an isopropyl substituent. It is a constituent of crude oil and refined fuels. It is a flammable colorless liquid that has a boiling point of 152 °C. Nearly all the cumene that is produced as a pure compound on an industrial scale is converted to cumene hydroperoxide, which is an intermediate in the synthesis of other industrially important chemicals, primarily phenol and acetone.
Autoxidation refers to oxidations brought about by reactions with oxygen at normal temperatures, without the intervention of flame or electric spark. The term is usually used to describe the gradual degradation of organic compounds in air at ambient temperatures. Many common phenomena can be attributed to autoxidation, such as food going rancid, the 'drying' of varnishes and paints, and the perishing of rubber. It is also an important concept in both industrial chemistry and biology. Autoxidation is therefore a fairly broad term and can encompass examples of photooxygenation and catalytic oxidation.

Hydroperoxides or peroxols are compounds of the form ROOH, which contain the hydroperoxy functional group (–OOH). The hydroperoxide anion and the neutral hydroperoxyl radical (HOO·) consist of an unbond hydroperoxy group. When R is organic, the compounds are called organic hydroperoxides. Such compounds are a subset of organic peroxides, which have the formula ROOR. Organic hydroperoxides can either intentionally or unintentionally initiate explosive polymerisation in materials with unsaturated chemical bonds.
Huntsman Chemical Company of Australia Pty Ltd (HCCA) operated a complex chemical manufacturing plant in Somerville Rd Brooklyn in Melbourne. The site is 35 hectares in size and is located in the City of Brimbank. HCCA was partially owned by the Huntsman Corporation.
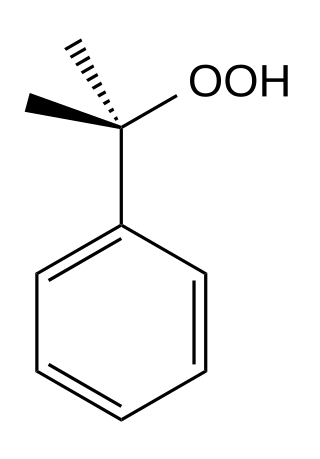
Cumene hydroperoxide is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(CH3)2OOH. An oily liquid, it is classified as an organic hydroperoxide. Products of decomposition of cumene hydroperoxide are methylstyrene, acetophenone, and cumyl alcohol.
In organic chemistry, transalkylation is a chemical reaction involving the transfer of an alkyl group from one organic compound to another. The reaction is used for the transfer of methyl and ethyl groups between benzene rings. This is of particular value in the petrochemical industry to manufacture p-xylene, styrene, and other aromatic compounds. Motivation for using transalkylation reactions is based on a difference in production and demand for benzene, toluene, and xylenes. Transalkylation can convert toluene, which is overproduced, into benzene and xylene, which are under-produced. Zeolites are often used as catalysts in transalkylation reactions.















