Burkina Faso's 22.1 million people belong to two major West African cultural groups: the Gur (Voltaic) and the Mandé. The Voltaic are far more numerous and include the Mossi, who make up about one-half of the population. The Mossi claim descent from warriors who migrated to present-day Burkina Faso and established an empire that lasted more than 800 years. Predominantly farmers, the Mossi are still bound by the traditions of the Mogho Naba, who hold court in Ouagadougou.

Demographic features of the population of Burundi include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects.

The demographic profile of Cameroon is complex for a country of its population. Cameroon comprises an estimated 250 distinct ethnic groups, which may be formed into five large regional-cultural divisions:

Demographic features of the population of the Central African Republic include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
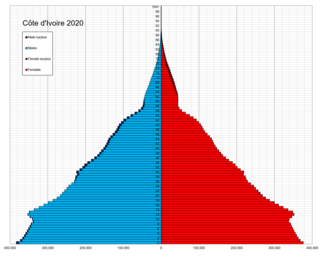
Demographic features of the population of Ivory Coast include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The demography of Kenya is monitored by the Kenyan National Bureau of Statistics. Kenya is a multi-ethnic state in East Africa. Its total population was at 47,558,296 as of the 2019 census.
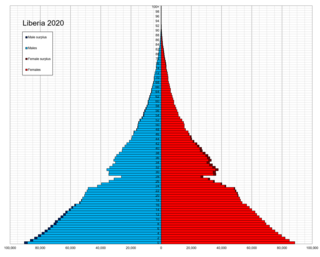
As of 2006, Liberia had the highest population growth rate in the world. This has declined since, however, and stood at 2.37 percent in 2023.

Demographic features of the population of Mali include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The demographics of Mozambique describes the condition and overview of Mozambique's peoples. Demographic topics include basic education, health, and population statistics as well as identified racial and religious affiliations.
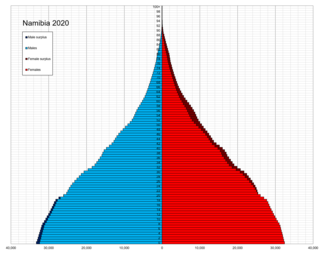
This is a demography of the population of Namibia including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa and the sixth in the world. It is also one of the most densely populated countries in Africa, with approximately 218.5 million people in an area of 923,768 km2 (356,669 sq mi).

Demographic features of the population of the Republic of the Congo include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

Demographic features of the population of Rwanda include population density, ethnicity, education higher level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects.
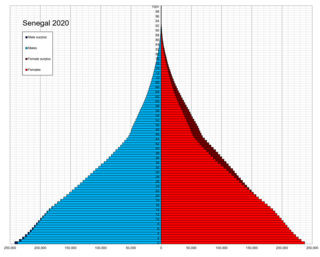
Demographic features of the population of Senegal include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The demographics of Sierra Leone are made up of an indigenous population from 18 ethnic groups. The Temne in the north and the Mende in the south are the largest. About 60,000 are Krio, the descendants of freed slaves who returned to Sierra Leone from Great Britain, North America and slave ships captured on the high seas. In addition, about 5,000 Lebanese, 1,000 Indians, and 5,000 Europeans reside in the country.

Demographic features of the population of Tanzania include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population.

The demographics of Togo include ethnicity, population density, age, education level, health, economic status and religious affiliations.
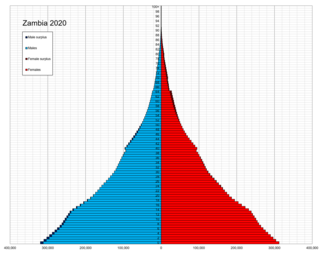
Demographic features of the population of Zambia include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and others aspects of the population.

The demographics of Benin include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The demographic characteristics of the population of The Gambia are known through national censuses, conducted in ten-year intervals and analyzed by The Gambian Bureau of Statistics (GBOS) since 1963. The latest census was conducted in 2013. The population of The Gambia at the 2013 census was 1.8 million. The population density is 176.1 per square kilometer, and the overall life expectancy in The Gambia is 64.1 years. Since the first census of 1963, the population of The Gambia has increased every ten years by an average of 43.2 percent. Since 1950s, the birth rate has constantly exceeded the death rate; the natural growth rate is positive. The Gambia is in the second stage of demographic transition. In terms of age structure, The Gambia is dominated by 15- to 24-year-old segment (57.6%). The median age of the population is 19.9 years, and the gender ratio of the total population is 0.98 males per female.