A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals, are coordination complexes.

Nickel(II) chloride (or just nickel chloride) is the chemical compound NiCl2. The anhydrous salt is yellow, but the more familiar hydrate NiCl2·6H2O is green. Nickel(II) chloride, in various forms, is the most important source of nickel for chemical synthesis. The nickel chlorides are deliquescent, absorbing moisture from the air to form a solution. Nickel salts have been shown to be carcinogenic to the lungs and nasal passages in cases of long-term inhalation exposure.

Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.
Cycloocta-1,5-diene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C8H12, specifically [−(CH2)2−CH=CH−]2.

Hexaamminecobalt(III) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [Co(NH3)6]Cl3. It is the chloride salt of the coordination complex [Co(NH3)6]3+, which is considered an archetypal "Werner complex", named after the pioneer of coordination chemistry, Alfred Werner. The cation itself is a metal ammine complex with six ammonia ligands attached to the cobalt(III) ion.

1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene, commonly abbreviated dppf, is an organophosphorus compound commonly used as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis. It contains a ferrocene moiety in its backbone, and is related to other bridged diphosphines such as 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe).
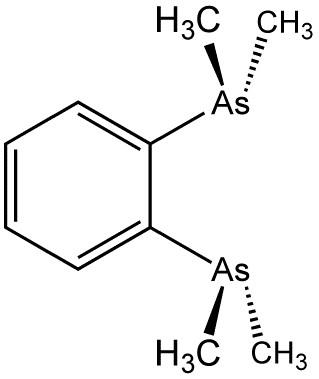
1,2-Bis(dimethylarsino)benzene (diars) is the organoarsenic compound with the formula C6H4(As(CH3)2)2. The molecule consists of two dimethylarsino groups attached to adjacent carbon centers of a benzene ring. It is a chelating ligand in coordination chemistry. This colourless oil is commonly abbreviated "diars."

Tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula [Co(en)3]Cl3 (where "en" is the abbreviation for ethylenediamine). It is the chloride salt of the coordination complex [Co(en)3]3+. This trication was important in the history of coordination chemistry because of its stability and its stereochemistry. Many different salts have been described. The complex was first described by Alfred Werner who isolated this salt as yellow-gold needle-like crystals.
Organoplatinum chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to platinum chemical bond, and the study of platinum as a catalyst in organic reactions. Organoplatinum compounds exist in oxidation state 0 to IV, with oxidation state II most abundant. The general order in bond strength is Pt-C (sp) > Pt-O > Pt-N > Pt-C (sp3). Organoplatinum and organopalladium chemistry are similar, but organoplatinum compounds are more stable and therefore less useful as catalysts.
Nickel(II) nitrite is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ni(NO2)2. Anhydrous nickel nitrite was first discovered in 1961 by Cyril Clifford Addison, who allowed gaseous nickel tetracarbonyl to react with dinitrogen tetroxide, yielding a green smoke. Nickel nitrite was the second transition element anhydrous nitrite discovered after silver nitrite.

Dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine)nickel(II) refers to a pair of metal phosphine complexes with the formula NiCl2[P(C6H5)3]2. The compound exists as two isomers, a paramagnetic dark blue solid and a diamagnetic red solid. These complexes function as catalysts for organic synthesis.
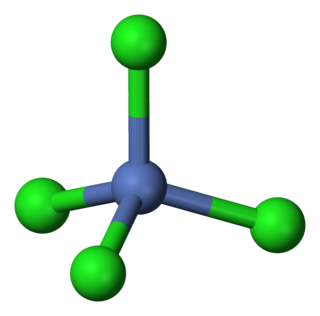
Tetrachloronickelate is the metal complex with the formula [NiCl4]2−. Salts of the complex are available with a variety of cations, but a common one is tetraethylammonium.
Nickel compounds are chemical compounds containing the element nickel which is a member of the group 10 of the periodic table. Most compounds in the group have an oxidation state of +2. Nickel is classified as a transition metal with nickel(II) having much chemical behaviour in common with iron(II) and cobalt(II). Many salts of nickel(II) are isomorphous with salts of magnesium due to the ionic radii of the cations being almost the same. Nickel forms many coordination complexes. Nickel tetracarbonyl was the first pure metal carbonyl produced, and is unusual in its volatility. Metalloproteins containing nickel are found in biological systems.

trans-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is a salt with the formula [CoCl2(en)2]Cl (en = ethylenediamine). It is a green diamagnetic solid that is soluble in water. It is the monochloride salt of the cationic coordination complex [CoCl2(en)2]+. One chloride ion in this salt readily undergoes ion exchange but the two other chlorides are less reactive, being bound to the metal center. The more stable trans-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is also known.
Cobalt(III) chloride or cobaltic chloride is an unstable and elusive compound of cobalt and chlorine with formula CoCl
3. In this compound, the cobalt atoms have a formal charge of +3.
Transition metal amino acid complexes are a large family of coordination complexes containing the conjugate bases of the amino acids, the 2-aminocarboxylates. Amino acids are prevalent in nature, and all of them function as ligands toward the transition metals. Not included in this article are complexes of the amides and ester derivatives of amino acids. Also excluded are the polyamino acids including the chelating agents EDTA and NTA.
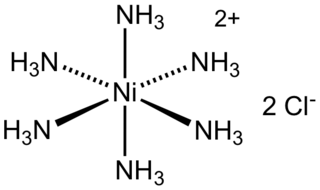
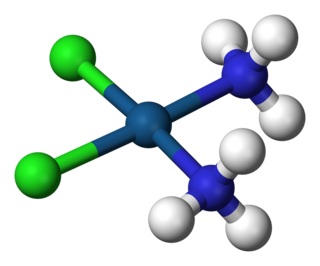
Hexaamminenickel chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2. It is the chloride salt of the metal ammine complex [Ni(NH3)6]2+. The cation features six ammonia (called ammines in coordination chemistry) ligands attached to the nickel(II) ion.
A chloride sulfite or sulfite chloride is a chemical compound that contains chloride and sulfite anions (SO32− Cl−). The known compounds of this type are all late transition metal sulfito complexes. Chlorine may be present as a ligand (chloro) or as an ion (chloride). The sulfito ligand can connect to the metal atom by way of an oxygen, or a sulfur atom. It can also link to the metal atom using two oxygen atoms as a bidentate ligand.

Carbonatobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is a salt with the formula [CoCO3(en)2]Cl (en = ethylenediamine). It is a red diamagnetic solid that is soluble in water. It is the monochloride salt of the cationic coordination complex [CoCO3(en)2]+. The chloride ion in this salt readily undergoes ion exchange. The compound is synthesized by the oxidation of a mixture of cobalt(II) chloride, lithium hydroxide, and ethylenediamine in the presence of carbon dioxide:
Cobalt compounds are chemical compounds formed by cobalt with other elements. In the compound, the most stable oxidation state of cobalt is the +2 oxidation state, and in the presence of specific ligands, there are also stable compounds with +3 valence. In addition, there are cobalt compounds in high oxidation states +4, +5 and low oxidation states -1, 0, +1.

![Structure of the dication [Ni2Cl2(en)4] that comprises the salt "NiCl2(en)2". ENCNIC01.png](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e4/ENCNIC01.png/220px-ENCNIC01.png)











