Sodium laureth sulfate (SLES), an accepted contraction of sodium lauryl ether sulfate (SLES), also called sodium alkylethersulfate, is an anionic detergent and surfactant found in many personal care products and for industrial uses. SLES is an inexpensive and very effective foaming agent. SLES, sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), ammonium lauryl sulfate (ALS), and sodium pareth sulfate are surfactants that are used in many cosmetic products for their cleaning and emulsifying properties. It is derived from palm kernel oil or coconut oil. In herbicides, it is used as a surfactant to improve absorption of the herbicidal chemicals and reduces time the product takes to be rainfast, when enough of the herbicidal agent will be absorbed.

Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), also commonly called polyvidone or povidone, is a water-soluble polymer compound made from the monomer N-vinylpyrrolidone. PVP is available in a range of molecular weights and related viscosities, and can be selected according to the desired application properties.

Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body. Dermatitis is often called eczema, and the difference between those terms is not standardized.

Methylisothiazolinone, MIT, or MI, is the organic compound with the formula S(CH)2C(O)NCH3. It is a white solid. Isothiazolinones, a class of heterocycles, are used as biocides in numerous personal care products and other industrial applications. MIT and related compounds have attracted much attention for their allergenic properties, e.g. contact dermatitis.

Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes are not contagious or life-threatening, but can be very uncomfortable.

Zinc pyrithione is a coordination complex of zinc. It has fungistatic and bacteriostatic properties and is used in the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis and dandruff.
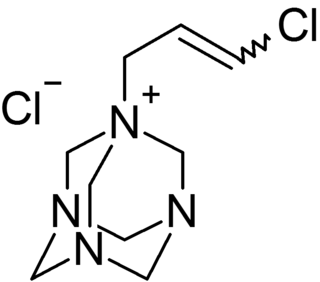
Quaternium-15 is a quaternary ammonium salt that has been used as a surfactant and preservative. It acts as an antimicrobial agent because it slowly releases formaldehyde, which is a preservative with biocidal properties.
Cetyl alcohol, also known as hexadecan-1-ol and palmityl alcohol, is a C-16 fatty alcohol with the formula CH3(CH2)15OH. At room temperature, cetyl alcohol takes the form of a waxy white solid or flakes. The name cetyl derives from the whale oil (cetacea oil, from Latin: cetus, lit. 'whale', from Ancient Greek: κῆτος, romanized: kētos, lit. 'huge fish') from which it was first isolated.
A foaming agent is a material such as a surfactant or a blowing agent that facilitates the formation of foam. A surfactant, when present in small amounts, reduces surface tension of a liquid or increases its colloidal stability by inhibiting coalescence of bubbles. A blowing agent is a gas that forms the gaseous part of the foam.
Cocamidopropyl betaine (CAPB) is a mixture of closely related organic compounds derived from coconut oil and dimethylaminopropylamine. CAPB is available as a viscous pale yellow solution and it is used as a surfactant in personal care products and animal husbandry. The name reflects that the major part of the molecule, the lauric acid group, is derived from coconut oil. Cocamidopropyl betaine to a significant degree has replaced cocamide DEA.
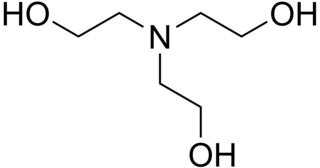
Triethanolamine, or TEOA, is an organic compound with the chemical formula N(CH2CH2OH)3. It is a colourless, viscous liquid. It is both a tertiary amine and a triol. A triol is a molecule with three alcohol groups. Approximately 150,000 tonnes were produced in 1999. It is a colourless compound although samples may appear yellow because of impurities.

Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a form of contact dermatitis that is the manifestation of an allergic response caused by contact with a substance; the other type being irritant contact dermatitis (ICD).

Balsam of Peru or Peru balsam, also known and marketed by many other names, is a balsam derived from a tree known as Myroxylon balsamum var. pereirae; it is found in El Salvador, where it is an endemic species.

Diazolidinyl urea is an antimicrobial preservative used in cosmetics. It is chemically related to imidazolidinyl urea which is used in the same way. Diazolidinyl urea acts as a formaldehyde releaser.

Isothiazolinone (sometimes isothiazolone) is an organic compound with the formula (CH)2SN(H)CO. A white solid, it is structurally related to isothiazole. Isothiazolone itself is of limited interest, but several of its derivatives are widely used preservatives and antimicrobials.
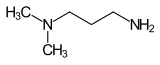
Amidoamines are a class of chemical compounds that are formed from fatty acids and amines. They are used as intermediates in the synthesis of surfactants, such as cocamidopropyl betaine (CAPB), some of which are used in personal care products including soaps, shampoos, and cosmetics. Amidoamines can also serve as curing agents for epoxy resins. They are also used as oil well drilling fluids and also as corrosion inhibitors.

Shampoo is a hair care product, typically in the form of a viscous liquid, that is used for cleaning hair. Less commonly, shampoo is available in solid bar format. Shampoo is used by applying it to wet hair, massaging the product into the scalp, and then rinsing it out. Some users may follow a shampooing with the use of hair conditioner.
Eyelid dermatitis is commonly related to atopic dermatitis or allergic contact dermatitis. Volatile substances, tosylamide, epoxy hardeners, insect sprays, and lemon peel oil may be implicated, with many cases of eyelid contact dermatitis being caused by substances transferred by the hands to the eyelids.
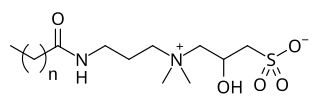
Cocamidopropyl hydroxysultaine (CAHS) is a synthetic amphoteric surfactant from the hydroxysultaine group. It is found in personal care products. It has uses as a foam booster, viscosity builder, and an antistatic agent.

Iodopropynyl Butyl Carbamate (IPBC) is a water-soluble preservative used globally in the paints & coatings, wood preservatives, personal care, and cosmetics industries. IPBC is a member of the carbamate family of biocides. IPBC was invented in the 1970s and has a long history of effective use as an antifungal technology.