
In chemistry, an acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH via titration. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their application in solving related problems; these are called the acid–base theories, for example, Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory.
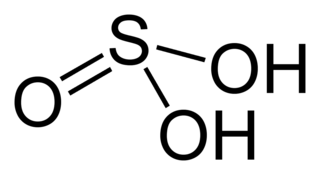
Sulfuric(IV) acid, also known as sulfurous (UK: sulphurous) acid and thionic acid, is the chemical compound with the formula H2SO3.
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English ) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. Sulfide also refers to large families of inorganic and organic compounds, e.g. lead sulfide and dimethyl sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and bisulfide (SH−) are the conjugate acids of sulfide.

Lead(II) sulfate (PbSO4) is a white solid, which appears white in microcrystalline form. It is also known as fast white, milk white, sulfuric acid lead salt or anglesite.
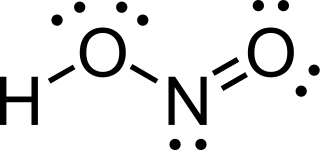
Nitrous acid is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase, and in the form of nitrite salts. It was discovered by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, who called it "phlogisticated acid of niter". Nitrous acid is used to make diazonium salts from amines. The resulting diazonium salts are reagents in azo coupling reactions to give azo dyes.
In chemistry, perxenates are salts of the yellow xenon-containing anion XeO4−
6. This anion has octahedral molecular geometry, as determined by Raman spectroscopy, having O–Xe–O bond angles varying between 87° and 93°. The Xe–O bond length was determined by X-ray crystallography to be 1.875 Å.

Chloric acid, HClO3, is an oxoacid of chlorine, and the formal precursor of chlorate salts. It is a strong acid (pKa ≈ −2.7) and an oxidizing agent.

A permanganate is a chemical compound with the manganate(VII) ion, MnO−
4, the conjugate base of permanganic acid. Because the manganese atom has a +7 oxidation state, the permanganate(VII) ion is a strong oxidising agent. The ion is a transition metal ion with a tetrahedral structure. Permanganate solutions are purple in colour and are stable in neutral or slightly alkaline media. The exact chemical reaction depends on the carbon-containing reactants present and the oxidant used. For example, trichloroethane (C2H3Cl3) is oxidised by permanganate ions to form carbon dioxide (CO2), manganese dioxide (MnO2), hydrogen ions (H+), and chloride ions (Cl−).
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states. The reverse of disproportionation, such as when a compound in an intermediate oxidation state is formed from precursors of lower and higher oxidation states, is called comproportionation, also known as synproportionation.
Permanganic acid (or manganic(VII) acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula HMnO4. This strong oxoacid has been isolated as its dihydrate. It is the conjugate acid of permanganate salts. It is the subject of few publications and its characterization as well as its uses are very limited.
Potassium manganate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2MnO4. This green-colored salt is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of potassium permanganate, a common chemical. Occasionally, potassium manganate and potassium permanganate are confused, but each compound's properties are distinct.

Hypobromous acid is an inorganic compound with chemical formula of HOBr. It is a weak, unstable acid. It is mainly produced and handled in an aqueous solution. It is generated both biologically and commercially as a disinfectant. Salts of hypobromite are rarely isolated as solids.

Chlorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurochloridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula HSO3Cl. It is also known as chlorosulfonic acid, being the sulfonic acid of chlorine. It is a distillable, colorless liquid which is hygroscopic and a powerful lachrymator. Commercial samples usually are pale brown or straw colored.
Manganese(VII) oxide (manganese heptoxide) is an inorganic compound with the formula Mn2O7. Manganese heptoxide is a volatile liquid with an oily consistency. It is a highly reactive and powerful oxidizer that reacts explosively with nearly any organic compound. It was first described in 1860. It is the acid anhydride of permanganic acid.

Manganese(II) sulfate usually refers to the inorganic compound with the formula MnSO4·H2O. This pale pink deliquescent solid is a commercially significant manganese(II) salt. Approximately 260,000 tonnes of manganese(II) sulfate were produced worldwide in 2005. It is the precursor to manganese metal and many other chemical compounds. Manganese-deficient soil is remediated with this salt.

The dithionate (or metabisulfate) anion, S
2O2−
6, is a sulfur oxoanion derived from dithionic acid, H2S2O6. Its chemical formula is sometimes written in a semistructural format, as [O3SSO3]2−. It is the first member of the polythionates.

Cobalt(III) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula of Co2O3. Although only two oxides of cobalt are well characterized, CoO and Co3O4, procedures claiming to give Co2O3 have been described. Thus treatment of Co(II) salts such as cobalt(II) sulfate with an aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite (also known as bleach) gives a black solid:

Chromium(II) sulfate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrSO4. It often comes as hydrates CrSO4·nH2O. Several hydrated salts are known. The pentahydrate CrSO4·5H2O is a blue solid that dissolves readily in water. Solutions of chromium(II) are easily oxidized by air to Cr(III) species. Solutions of Cr(II) are used as specialized reducing agents of value in organic synthesis.

Barium manganate is an inorganic compound with the formula BaMnO4. It is used as an oxidant in organic chemistry. It belongs to a class of compounds known as manganates in which the manganese resides in a +6 oxidation state. Manganate should not be confused with permanganate which contains manganese(VII). Barium manganate is a powerful oxidant, popular in organic synthesis and can be used in a wide variety of oxidation reactions.
Barium permanganate is a chemical compound, with the formula Ba(MnO4)2. It forms violet to brown crystals that are sparingly soluble in water.
















