
Hesse or Hessia, officially the State of Hesse, is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt, which is also the country's principal financial centre. Two other major historic cities are Darmstadt and Kassel. With an area of 21,114.73 square kilometers and a population of over six million, it ranks seventh and fifth, respectively, among the sixteen German states. Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Germany's second-largest metropolitan area, is mainly located in Hesse.

The history of Saxony-Anhalt began with Old Saxony, which was conquered by Charlemagne in 804 and transformed into the Duchy of Saxony within the Carolingian Empire. Saxony went on to become one of the so-called stem duchies of the German Kingdom and subsequently the Holy Roman Empire which formed out of the eastern partition of the Carolingian Empire. The duchy grew to become a powerful state within the empire, ruling over much of what is now northern Germany, but following conflicts with the emperor it was partitioned into numerous minor states, including the Principality of Anhalt, around the end of the 12th century and early 13th century. The territories of the Duchy of Saxony, the Principality of Anhalt, and their successors are now part of the modern German state of Saxony-Anhalt.

The Electorate of Mainz, previously known in English as Mentz and by its French name Mayence, was one of the most prestigious and influential states of the Holy Roman Empire. In the Roman Catholic hierarchy, the Archbishop-Elector of Mainz was also the Primate of Germany, a purely honorary dignity that was unsuccessfully claimed from time to time by other archbishops. There were only two other ecclesiastical Prince-electors in the Empire: the Electorate of Cologne and the Electorate of Trier.
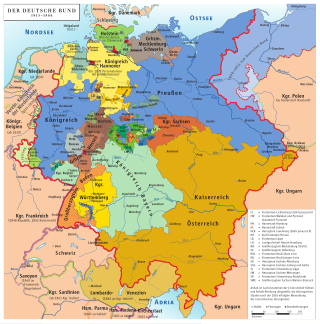
The states of the German Confederation were member states of the German Confederation, from 20 June 1815 until 24 August 1866.

The Province of Saxony, also known as Prussian Saxony, was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1944. Its capital was Magdeburg.
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria and Russia at the Battle of Austerlitz. Its creation brought about the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire shortly afterward. The Confederation of the Rhine lasted for 7 years, from 1806 to 1813.

Battenberg is a small town in the district of Waldeck-Frankenberg in the state of Hesse, Germany. It is located on the river Eder, a tributary of the Fulda, which flows into the Weser, and lies at the southeastern edges of the Rothaar Mountains. The closest larger cities are Marburg, Siegen, and Kassel, and the town is approximately equally far away from Frankfurt am Main, Cologne, and Dortmund.

The Duchy of Nassau was an independent state between 1806 and 1866, located in what is now the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Hesse. It was a member of the Confederation of the Rhine and later of the German Confederation. Its ruling dynasty, now extinct, was the House of Nassau. The duchy was named for its historical core city, Nassau, although Wiesbaden rather than Nassau was its capital. In 1865, the Duchy of Nassau had 465,636 inhabitants. After being occupied and annexed into the Kingdom of Prussia in 1866 following the Austro-Prussian War, it was incorporated into the Province of Hesse-Nassau. The area today is a geographical and historical region, Nassau, and Nassau is also the name of the Nassau Nature Park within the borders of the former duchy.
These are lists of political office-holders in Germany.
The state of Prussia developed from the State of the Teutonic Order. The original flag of the Teutonic Knights had been a black cross on a white flag. Emperor Frederick II in 1229 granted them the right to use the black Eagle of the Holy Roman Empire. This "Prussian Eagle" remained the coats of arms of the successive Prussian states until 1947.

Hattert is an Ortsgemeinde – a community belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde – in the Westerwaldkreis in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is the biggest Ortsgemeinde in the Verbandsgemeinde of Hachenburg, a kind of collective municipality.

Stein-Wingert is an Ortsgemeinde – a community belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde – in the Westerwaldkreis in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.

The Thuringian states refers to the following German federal states within the German Reich:
The Drei-Länder-Stein is a boundary stone at the tripoint of the German federal states of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia near the Großer Ehrenberg mountain in the Harz.
In the London Protocol signed on 12 September 1944, the Allies of World War II agreed on dividing Germany into three occupation zones after the war.
Johannetta, Countess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Sayn-Altenkirchen, was Sovereign Countess of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Sayn-Altenkirchen from 1648 to 1701. She was also Landgravine of Hesse-Braubach by marriage to John, Landgrave of Hesse-Braubach, and Duchess of Saxe-Marksuhl by marriage to John George I, Duke of Saxe-Eisenach.

The Hessian Central State Archives, Wiesbaden is a department of the Hessian State Archives and is located in Wiesbaden, the capital of the German state of Hesse. It serves alongside the Hessian State Archives, Darmstadt and the Hessian State Archives, Marburg as the main regional archives for Hesse and additionally functions as the central archives for the state government and ministries, as well as other institutions with nationwide jurisdiction.













