In biology, phylogenetics is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by phylogenetic inference, methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms.

A cladogram is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about ancestors. Although traditionally such cladograms were generated largely on the basis of morphological characters, DNA and RNA sequencing data and computational phylogenetics are now very commonly used in the generation of cladograms, either on their own or in combination with morphology.

In cladistics or phylogenetics, an outgroup is a more distantly related group of organisms that serves as a reference group when determining the evolutionary relationships of the ingroup, the set of organisms under study, and is distinct from sociological outgroups. The outgroup is used as a point of comparison for the ingroup and specifically allows for the phylogeny to be rooted. Because the polarity (direction) of character change can be determined only on a rooted phylogeny, the choice of outgroup is essential for understanding the evolution of traits along a phylogeny.
In phylogenetics, long branch attraction (LBA) is a form of systematic error whereby distantly related lineages are incorrectly inferred to be closely related. LBA arises when the amount of molecular or morphological change accumulated within a lineage is sufficient to cause that lineage to appear similar to another long-branched lineage, solely because they have both undergone a large amount of change, rather than because they are related by descent. Such bias is more common when the overall divergence of some taxa results in long branches within a phylogeny. Long branches are often attracted to the base of a phylogenetic tree, because the lineage included to represent an outgroup is often also long-branched. The frequency of true LBA is unclear and often debated, and some authors view it as untestable and therefore irrelevant to empirical phylogenetic inference. Although often viewed as a failing of parsimony-based methodology, LBA could in principle result from a variety of scenarios and be inferred under multiple analytical paradigms.

Troglosironidae is a family of harvestmen with seventeen described species in a single genus, Troglosiro, which is found on the island of New Caledonia, in the Pacific Ocean.
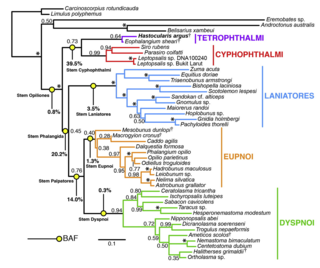
Harvestmen (Opiliones) are an order of arachnids often confused with spiders, though the two orders are not closely related. Research on harvestman phylogeny is in a state of flux. While some families are clearly monophyletic, that is share a common ancestor, others are not, and the relationships between families are often not well understood.

Panorpida or Mecopterida is a proposed superorder of Holometabola. The conjectured monophyly of the Panorpida is historically based on morphological evidence, namely the reduction or loss of the ovipositor and several internal characteristics, including a muscle connecting a pleuron and the first axillary sclerite at the base of the wing, various features of the larval maxilla and labium, and basal fusion of CuP and A1 veins in the hind wings. The monophyly of the Panorpida is supported by recent molecular data.
Gonzalo Giribet is a Spanish-American invertebrate zoologist and Alexander Agassiz Professor of zoology working on systematics and biogeography at the Museum of Comparative Zoology in Harvard University. He is a past president of the International Society for Invertebrate Morphology, of the Willi Hennig Society, and vice-president of the Sociedad Española de Malacología.

Theromaster is a genus of armoured harvestmen in the family Cladonychiidae. There are at least two described species in Theromaster, found in the eastern United States.

Travunioidea is a superfamily of armoured harvestmen in the order Opiliones. There are 4 families and around 75 described species in Travunioidea.

Isolachus is a genus of armoured harvestmen in the family Cladonychiidae. There is one described species in Isolachus, I. spinosus, found in Oregon and Washington.
Speleonychia is a genus of armoured harvestmen in the family Cladonychiidae. There is at least one described species in Speleonychia, S. sengeri. It is found in Washington state.
Joel Lester Cracraft, is an American paleontologist and ornithologist. He received a PhD in 1969 from Columbia University.
Arbasus is a genus of armoured harvestmen in the family Cladonychiidae. There is one described species in Arbasus, A. caecus. It is found in the Pyrenees of southern France.
Buemarinoa is a genus of armoured harvestmen in the family Cladonychiidae. There is one described species in Buemarinoa, B. patrizii, found in Sardinia, Italy.
Dinaria is a genus of harvestman in the family Travuniidae. There is one described species, Dinaria vjetrenicae. It has been found only in Vjetrenica Cave in southern Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Izunonychus is a genus of harvestman in the family Paranonychidae. There is one described species in Izunonychus, I. ohruii, endemic to Japan.

Kainonychus is a genus of harvestman in the family Paranonychidae. There is one described species in Kainonychus, K. akamai, endemic to Japan.
Nippononychus is a genus of harvestman in the family Paranonychidae. There is one described species in Nippononychus, N. japonicus, endemic to Japan.

Metanippononychus is a genus of harvestman in the family Paranonychidae. There are at least four described species in Metanippononychus.










