The ring ouzel is a mainly European member of the thrush family Turdidae. It is a medium-sized thrush, 23–24 centimetres (9.1–9.4 in) in length and weighing 90–138 grams (3.2–4.9 oz). The male is predominantly black with a conspicuous white crescent across its breast. Females are browner and duller than males, and young birds may lack the pale chest markings altogether. In all but the northernmost part of its range, this is a high-altitude species, with three races breeding in mountains from Ireland east to Iran. It breeds in open mountain areas with some trees or shrubs, the latter often including heather, conifers, beech, hairy alpenrose or juniper. It is a migratory bird, leaving the breeding areas to winter in southern Europe, North Africa and Turkey, typically in mountains with juniper bushes. The typical clutch is 3–6 brown-flecked pale blue or greenish-blue eggs. They are incubated almost entirely by the female, with hatching normally occurring after 13 days. The altricial, downy chicks fledge in another 14 days and are dependent on their parents for about 12 days after fledging.

The European nightjar, common goatsucker, Eurasian nightjar or just nightjar, is a crepuscular and nocturnal bird in the nightjar family that breeds across most of Europe and the Palearctic to Mongolia and Northwestern China. The Latin generic name refers to the old myth that the nocturnal nightjar suckled from goats, causing them to cease to give milk. The six subspecies differ clinally, the birds becoming smaller and paler towards the east of the range. All populations are migratory, wintering in sub-Saharan Africa. Their densely patterned grey and brown plumage makes individuals difficult to see in the daytime when they rest on the ground or perch motionless along a branch, although the male shows white patches in the wings and tail as he flies at night.

The Eurasian tree sparrow is a passerine bird in the sparrow family with a rich chestnut crown and nape and a black patch on each pure white cheek. The sexes are similarly plumaged, and young birds are a duller version of the adult. This sparrow breeds over most of temperate Eurasia and Southeast Asia, where it is known as the tree sparrow, and it has been introduced elsewhere including the United States, where it is known as the Eurasian tree sparrow or German sparrow to differentiate it from the native unrelated American tree sparrow. Although several subspecies are recognised, the appearance of this bird varies little across its extensive range.

The nuthatches constitute a genus, Sitta, of small passerine birds belonging to the family Sittidae. Characterised by large heads, short tails, and powerful bills and feet, nuthatches advertise their territory using loud, simple songs. Most species exhibit grey or bluish upperparts and a black eye stripe.

The Eurasian golden oriole, also called the common golden oriole, is the only member of the Old World oriole family of passerine birds breeding in Northern Hemisphere temperate regions. It is a summer migrant in Europe and Palearctic and spends the winter season in central and southern Africa.

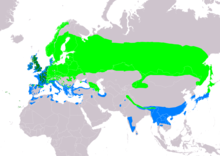
The European roller is the only member of the roller family breeding in Europe. Its range extends into the Middle East, Central Asia and the Maghreb. It winters in southern Africa, primarily in dry wooded savanna and bushy plains. It occurs in a wide variety of habitats, but avoids treeless plains. It usually nests in tree holes.

The woodcocks are a group of seven or eight very similar living species of wading birds in the genus Scolopax. The genus name is Latin for a snipe or woodcock, and until around 1800 was used to refer to a variety of waders. The English name is first recorded in about 1050. According to the Harleian Miscellany, a group of woodcocks is called a "fall".

The Eurasian curlew or common curlew is a very large wader in the family Scolopacidae. It is one of the most widespread of the curlews, breeding across temperate Europe and Asia. In Europe, this species is often referred to just as the "curlew", and in Scotland known as the "whaup" in Scots.

The Eurasian or common whimbrel, also known as the white-rumped whimbrel in North America, is a wader in the large family Scolopacidae. It is one of the most widespread of the curlews, breeding across much of subarctic Asia and Europe as far south as Scotland. This species and the Hudsonian whimbrel have recently been split, although some taxonomic authorities still consider them to be conspecific.

The Eurasian spoonbill, or common spoonbill, is a wading bird of the ibis and spoonbill family Threskiornithidae. The genus name Platalea is from Latin and means "broad", referring to the distinctive shape of the bill, and leucorodia is from Ancient Greek leukerodios "spoonbill", itself derived from leukos, "white" and erodios "heron". In England it was traditionally known as the "shovelard", a name later used for the Northern Shoveller.

The common snipe is a small, stocky wader native to the Old World.

The American woodcock, sometimes colloquially referred to as the timberdoodle, mudbat, bogsucker, night partridge, or Labrador twister is a small shorebird species found primarily in the eastern half of North America. Woodcocks spend most of their time on the ground in brushy, young-forest habitats, where the birds' brown, black, and gray plumage provides excellent camouflage.

The Amami woodcock is a medium-sized wader. It is slightly larger and longer-legged than Eurasian woodcock, and may be conspecific.

The Eurasian sparrowhawk, also known as the northern sparrowhawk or simply the sparrowhawk, is a small bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. Adult male Eurasian sparrowhawks have bluish grey upperparts and orange-barred underparts; females and juveniles are brown above with brown barring below. The female is up to 25% larger than the male – one of the greatest size differences between the sexes in any bird species. Though it is a predator which specialises in catching woodland birds, the Eurasian sparrowhawk can be found in any habitat and often hunts garden birds in towns and cities. Males tend to take smaller birds, including tits, finches, and sparrows; females catch primarily thrushes and starlings, but are capable of killing birds weighing 500 g (18 oz) or more.

The ruffed grouse is a medium-sized grouse occurring in forests from the Appalachian Mountains across Canada to Alaska. It is the most widely distributed game bird in North America. It is non-migratory. It is the only species in the genus Bonasa.

The great snipe is a small stocky wader in the genus Gallinago. This bird's breeding habitat is marshes and wet meadows with short vegetation in north-eastern Europe, including north-western Russia. Great snipes are migratory, wintering in Africa. The European breeding population is in steep decline.

The Eurasian siskin is a small passerine bird in the finch family Fringillidae. It is also called the European siskin, common siskin or just siskin. Other (archaic) names include black-headed goldfinch, barley bird and aberdevine. It is very common throughout Europe and Eurosiberia. It is found in forested areas, both coniferous and mixed woodland where it feeds on seeds of all kinds, especially of alder and conifers.
The Bukidnon woodcock, or Philippine woodcock is a medium-sized wader. It was only described as new to science as recently as 2001, although the initial specimens had been collected on Luzon in the 1960s, these were originally misidentified as Eurasian woodcock specimens. It was not until the bird was heard calling in 1993, and new specimens obtained on Mindanao in 1995, that it was realised that the species was new. It is listed as Least Concern by the IUCN.

Longleat Woods is a 249.9 hectare biological Site of Special Scientific Interest south of Frome in Somerset, notified in 1972.
The Heart of England Forest is a charitable entity based in England, dedicated to the conservation and ecological restoration of native woodlands primarily within the counties of Warwickshire and Worcestershire. This initiative aims to address the loss of ancient woodlands and habitats, a significant environmental concern in the region historically covered by the vast Forest of Arden, which has been substantially diminished due to extensive deforestation activities over the centuries.