The Federal Road through the territory of the Creek people was a project that started in 1805 when the Creek gave permission for the development of a "horse path" through their nation for more efficient mail delivery between Washington City (modern-day Washington, D.C.) and New Orleans, Louisiana. This section started at Fort Wilkinson near Milledgeville, Georgia, and ended at Fort Stoddert near Mobile, Alabama. By the time of the War of 1812, the Federal Road began in Augusta, Georgia, ran through Fort Hawkins (in Macon, Georgia), on to Fort Mitchell, Alabama (near modern Phenix City, Alabama), and was connected via the Three Notch Road to Pensacola in Spanish West Florida.
The Federal Road was at first for mail delivery. It was widened into a war road during 1811, and used during the Creek War (1813–14). The result was removal of most of the Creek people to the West.
Another Federal Road (Cherokee lands) went from Savannah, Georgia through northern Georgia to Knoxville, Tennessee, and opened up Cherokee land for settlement.

Indian removal was the United States government policy of forced displacement of self-governing tribes of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi River – specifically, to a designated Indian Territory. The Indian Removal Act, the key law which authorized the removal of Native tribes, was signed by Andrew Jackson in 1830. Although Jackson took a hard line on Indian removal, the law was enforced primarily during the Martin Van Buren administration. After the passage of the Indian Removal Act in 1830, approximately 60,000 members of the Cherokee, Muscogee (Creek), Seminole, Chickasaw, and Choctaw nations were forcibly removed from their ancestral homelands, with thousands dying during the Trail of Tears.

The Cherokee are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia and northeastern Alabama.

The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy, are a group of related indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands in the United States of America. Their original homelands are in what now comprises southern Tennessee, much of Alabama, western Georgia and parts of northern Florida.

The Trail of Tears was a series of forced displacements of approximately 60,000 Native Americans of the Five Civilized Tribes between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. Part of the Indian removal, this ethnic cleansing event was gradual, occurring over a period of nearly two decades. Members of the so-called Five Civilized Tribes—the Cherokee, Muscogee (Creek), Seminole, Chickasaw, and Choctaw nations —were forcibly removed from their ancestral homelands in the Southeastern United States to areas to the west of the Mississippi River that had been designated Indian Territory. The forced relocations were carried out by government authorities after the passage of the Indian Removal Act in 1830. The Cherokee removal in 1838 was brought on by the discovery of gold near Dahlonega, Georgia, in 1828, resulting in the Georgia Gold Rush.

Monroe County is a county on the eastern border of the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2010 census, the population was 44,519. Its county seat is Madisonville.

The term Five Civilized Tribes was applied by European Americans in the colonial and early federal period in the history of the United States to the five major Native American nations in the Southeast—the Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek (Muscogee), and Seminole. Americans of European descent classified them as "civilized" because they had adopted attributes of the Anglo-American culture. Examples of such colonial attributes adopted by these five tribes, included Christianity, centralized governments, literacy in English, market participation, written constitutions, intermarriage with white Americans, and chattel slavery practices, including purchase of enslaved African Americans. For a period, the Five Civilized Tribes tended to maintain stable political relations with the European Americans, before the United States promoted Indian Removal of these tribes from the Southeast.

John Ross, , was the Principal Chief of the Cherokee Nation from 1828 to 1866 and served longer in that position than any other person. Described as the Moses of his people, Ross influenced the Indian nation through such tumultuous events as the relocation to Indian Territory and the American Civil War.

The Creek War (1813–1814), also known as the Red Stick War and the Creek Civil War, was a regional war between opposing Creek factions, European empires and the United States, taking place largely in today's Alabama and along the Gulf Coast. The major conflicts of the war took place between state militia units and the "Red Stick" Creeks. The United States government formed an alliance with the Choctaw Nation and Cherokee Nation, along with the remaining Creeks to put down the rebellion.
Cherokee Nation v. Georgia, 30 U.S. 1 (1831), was a United States Supreme Court case. The Cherokee Nation sought a federal injunction against laws passed by the U.S. state of Georgia depriving them of rights within its boundaries, but the Supreme Court did not hear the case on its merits. It ruled that it had no original jurisdiction in the matter, as the Cherokees were a dependent nation, with a relationship to the United States like that of a "ward to its guardian," as said by Chief Justice Marshall.

U.S. Route 411 (US 411) is an alternate parallel-highway associated with US 11. US 411 extends for about 309.7 miles (498.4 km) from US 78 in Leeds, Alabama, to US 25W/US 70 in Newport, Tennessee. US 411 travels through northeastern Alabama, northwestern Georgia, and southeastern Tennessee. Notable towns and cities along its route include Gadsden, Alabama; Rome, Georgia; Cartersville, Georgia; Maryville, Tennessee; Sevierville, Tennessee, and Newport, Tennessee.

The Hiwassee River has its headwaters on the north slope of Rocky Mountain in Towns County in the northern area of the State of Georgia. It flows northward into North Carolina before turning westward into Tennessee, flowing into the Tennessee River a few miles west of what is now State Route 58 in Meigs County, Tennessee. The river is about 147 miles (237 km) long.

Fort Hawkins was a fort built between 1806 and 1810 in the historic Creek Nation by the United States government under President Thomas Jefferson and used until 1824. Built in what is now Georgia at the Fall Line on the east side of the Ocmulgee River, the fort overlooked the sacred ancient earthwork mounds of the Ocmulgee Old Fields, now known as the Ocmulgee Mounds National Historical Park. The Lower Creek Trading Path passed by just outside the fort's northwestern blockhouse, and continued in a westerly direction until it reached a natural ford on the Ocmulgee River. A trading settlement and later the city of Macon, Georgia, developed in the area prior to the construction of the fort, with British traders being in the area as early as the 1680s. Later, the fort would become important to the Creek Nation, the United States, and the state of Georgia for economic, military, and political reasons.

Fort Stoddert, also known as Fort Stoddard, was a stockade fort in the Mississippi Territory, in what is today Alabama. It was located on a bluff of the Mobile River, near modern Mount Vernon, close to the confluence of the Tombigbee and Alabama Rivers. It served as the western terminus of the Federal Road which ran through Creek lands to Fort Wilkinson in Georgia. The fort, built in 1799, was named for Benjamin Stoddert, the secretary to the Continental Board of War during the American Revolution and Secretary of the Navy during the Quasi War. Fort Stoddert was built by the United States to keep the peace by preventing its own settlers in the Tombigbee District from attacking the Spanish in the Mobile District. It also served as a port of entry and was the site of a Court of Admiralty. While under the command of Captain Edmund P. Gaines, Aaron Burr was held as a prisoner at the fort after his arrest at McIntosh in 1807 for treason against the United States. In July 1813, General Ferdinand Claiborne brought the Mississippi Militia to Fort Stoddert as part of the Creek War. The 3rd Infantry Regiment was commanded by General Thomas Fluornoy to Fort Stoddert following the Fort Mims massacre. The site declined rapidly in importance after the capture of Mobile by the United States in 1813 and the establishment of the Mount Vernon Arsenal in 1828.

Opothleyahola, also spelled Opothle Yohola, Opothleyoholo, Hu-pui-hilth Yahola, Hopoeitheyohola, and Hopere Yahvlv was a Muscogee Creek Indian chief, noted as a brilliant orator. He was a Speaker of the Upper Creek Council and supported traditional culture.
Fort Cass was a fort located on the Hiwassee River in present-day Charleston, Tennessee, that served as the military operational headquarters for the entire Cherokee removal, an forced migration of the Cherokee known as the Trail of Tears from their ancestral homelands in the Southeast to Indian Territory in present-day Oklahoma. Fort Cass housed a garrison of United States troops who watched over the largest concentration of internment camps where Cherokee were kept during the summer of 1838 before starting the main trek west to Indian Territory, and served as one of three emigration deports where the Cherokee began their journey west, the others of which were located at Ross's Landing in Chattanooga and Gunter's Landing near Guntersville, Alabama.
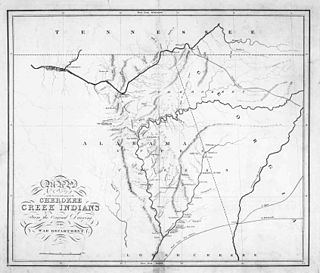
The Federal Road through Cherokee lands, originally called the Georgia Road, was a federal toll highway passing through the Cherokee Nation in the northern part of the U.S. state of Georgia. From 1805 to the 1840s, the road linked Savannah, Georgia with Knoxville, Tennessee. The road also opened Cherokee lands to settlement. Another Federal Road passed through southern Alabama.
The Cherokee people of the southeastern United States, and later Oklahoma and surrounding areas, have a long military history. Since European contact, Cherokee military activity has been documented in European records. Cherokee tribes and bands had a number of conflicts during the 18th century with Europeans, primarily British colonists from the Southern Colonies. The Eastern Band and Cherokees from the Indian Territory fought in the American Civil War, with bands allying with the Union or the Confederacy. Because many Cherokees allied with the Confederacy, the United States government required a new treaty with the nation after the war. Cherokees have also served in the United States military during the 20th and 21st centuries.

The history of Rome, Georgia extends to thousands of years of human settlement by ancient Native Americans. Spanish explorers recorded reaching the area in the later 16th century, and European Americans of the United States founded the city named Rome in 1834, when the residents of the area were still primarily Cherokee, before their removal on the Trail of Tears to Indian Territory. The competition for resources among its diverse inhabitants led to both innovation and strife. Its location at the confluence of three rivers enabled Rome to develop as a crossroads for trade and transportation. The city was later designated as the county seat of Floyd County, Georgia. Today, Rome is the largest city in Northwest Georgia, and is a regional center of healthcare, education, and manufacturing.
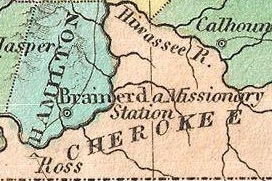
Cherokee removal, part of the Trail of Tears, refers to the forced relocation between 1836 and 1839 of an estimated 16,000 members of the Cherokee Nation and 1,000-2,000 of their slaves; from their lands in Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Alabama to the Indian Territory in the then Western United States, and the resultant deaths along the way and at the end of the movement of an estimated 4,000 Cherokee and unknown number of slaves.