Related Research Articles
A web browser is an application for accessing websites and the Internet. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on a range of devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. In 2020, an estimated 4.9 billion people have used a browser. The most used browser is Google Chrome, with a 65% global market share on all devices, followed by Safari with 18%.

A bookmarklet is a bookmark stored in a web browser that contains JavaScript commands that add new features to the browser. They are stored as the URL of a bookmark in a web browser or as a hyperlink on a web page. Bookmarklets are usually small snippets of JavaScript executed when user clicks on them. When clicked, bookmarklets can perform a wide variety of operations, such as running a search query from selected text or extracting data from a table.

Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. In November 2017, Firefox began incorporating new technology under the code name "Quantum" to promote parallelism and a more intuitive user interface. Firefox is available for Windows 10 or later versions, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, illumos, and Solaris Unix. It is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser.
A favicon, also known as a shortcut icon, website icon, tab icon, URL icon, or bookmark icon, is a file containing one or more small icons associated with a particular website or web page. A web designer can create such an icon and upload it to a website by several means, and graphical web browsers will then make use of it. Browsers that provide favicon support typically display a page's favicon in the browser's address bar and next to the page's name in a list of bookmarks. Browsers that support a tabbed document interface typically show a page's favicon next to the page's title on the tab, and site-specific browsers use the favicon as a desktop icon.
MHTML, an initialism of "MIME encapsulation of aggregate HTML documents", is a Web archive file format used to combine, in a single computer file, the HTML code and its companion resources that are represented by external hyperlinks in the web page's HTML code. The content of an MHTML file is encoded using the same techniques that were first developed for HTML email messages, using the MIME content type multipart/related. MHTML files use an .mhtml or .mht filename extension.
This is a comparison of both historical and current web browsers based on developer, engine, platform(s), releases, license, and cost.
about is an internal URI scheme implemented in various Web browsers to reveal internal state and built-in functions. It is an IANA officially registered scheme, and is standardized.

Digest access authentication is one of the agreed-upon methods a web server can use to negotiate credentials, such as username or password, with a user's web browser. This can be used to confirm the identity of a user before sending sensitive information, such as online banking transaction history. It applies a hash function to the username and password before sending them over the network. In contrast, basic access authentication uses the easily reversible Base64 encoding instead of hashing, making it non-secure unless used in conjunction with TLS.
Mozilla Firefox has features that allow it to be distinguished from other web browsers, such as Chrome and Internet Explorer.
OpenSearch is a collection of technologies that allow the publishing of search results in a format suitable for syndication and aggregation. Introduced in 2005, it is a way for websites and search engines to publish search results in a standard and accessible format.
In computer hypertext, a URI fragment is a string of characters that refers to a resource that is subordinate to another, primary resource. The primary resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), and the fragment identifier points to the subordinate resource.
A proxy auto-config (PAC) file defines how web browsers and other user agents can automatically choose the appropriate proxy server for fetching a given URL.
In the context of the World Wide Web, a bookmark is a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) that is stored for later retrieval in any of various storage formats. All modern web browsers include bookmark features. Bookmarks are called favorites or Internet shortcuts in Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge, and by virtue of that browser's large market share, these terms have been synonymous with bookmark since the First Browser War. Bookmarks are normally accessed through a menu in the user's web browser, and folders are commonly used for organization. In addition to bookmarking methods within most browsers, many external applications offer bookmarks management.

Mozilla Firefox 3.0 is a version of the Firefox web browser released on June 17, 2008, by the Mozilla Corporation.

Private browsing, also known as incognito mode or private mode, is a feature available in web browsers that allows users to browse the internet without leaving any traces of their online activity on their device. In this mode, the browser initiates a temporary session separate from its main session and user data. The browsing history is not recorded, and local data related to the session, like Cookies and Web cache, are deleted once the session ends. The primary purpose of these modes is to ensure that data and history from a specific browsing session don't remain on the device or get accessed by another user of the same device.
Firefox Sync, originally branded Mozilla Weave, is a browser synchronization feature for Firefox web browsers. It allows users to partially synchronize bookmarks, browsing history, preferences, passwords, filled forms, add-ons, and the last 25 opened tabs across multiple computers. The feature is now included in Firefox and is being implemented in Thunderbird.
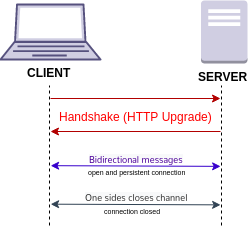
WebSocket is a computer communications protocol, providing simultaneous two-way communication channels over a single Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection. The WebSocket protocol was standardized by the IETF as RFC 6455 in 2011. The current specification allowing web applications to use this protocol is known as WebSockets. It is a living standard maintained by the WHATWG and a successor to The WebSocket API from the W3C.
Content Security Policy (CSP) is a computer security standard introduced to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS), clickjacking and other code injection attacks resulting from execution of malicious content in the trusted web page context. It is a Candidate Recommendation of the W3C working group on Web Application Security, widely supported by modern web browsers. CSP provides a standard method for website owners to declare approved origins of content that browsers should be allowed to load on that website—covered types are JavaScript, CSS, HTML frames, web workers, fonts, images, embeddable objects such as Java applets, ActiveX, audio and video files, and other HTML5 features.
Firefox was created by Dave Hyatt and Blake Ross as an experimental branch of the Mozilla browser, first released as Firefox 1.0 on November 9, 2004. Starting with version 5.0, a rapid release cycle was put into effect, resulting in a new major version release every six weeks. This was gradually accelerated further in late 2019, so that new major releases occur on four-week cycles starting in 2020.

A progressive web application (PWA), or progressive web app, is a type of application software delivered through the web, built using common web technologies including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and WebAssembly. It is intended to work on any platform with a standards-compliant browser, including desktop and mobile devices.
References
- 1 2 Jesse Ruderman and Justin Lebar (2012-11-10). "A new frecency algorithm based on exponential decay". wiki.mozilla.org. Retrieved 2014-05-22.
- ↑ Edwards, Nathan (August 2008). "Firefox 3: A Browser Odyssey". Maximum PC . pp. 50–52.
- ↑ Honza Bambas (2014-05-19). "New Firefox HTTP cache now enabled on Nightly builds" . Retrieved 2014-05-22.
- 1 2 "The Places frecency algorithm | MDN". Developer.mozilla.org. 2011-11-03. Archived from the original on August 16, 2014. Retrieved 2013-10-17.