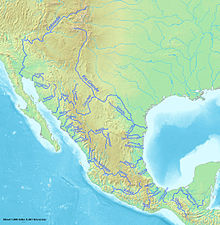
The geography of Mexico describes the geographic features of Mexico, a country in the Americas. Mexico is located at about 23° N and 102° W in the southern portion of North America. From its farthest land points, Mexico is a little over 3,200 km (2,000 mi) in length. Mexico is bounded to the north by the United States, to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean, to the east by the Gulf of Mexico, and to the southeast by Belize, Guatemala, and the Caribbean Sea. The northernmost constituent of Latin America, it is the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the world. Mexico is the world's 13th largest country, three times the size of Texas.

Copper Canyon is a group of six distinct canyons in the Sierra Madre Occidental in the southwestern part of the state of Chihuahua in northwestern Mexico that is 65,000 square kilometres (25,000 sq mi) in size. The canyons were formed by six rivers that drain the western side of the Sierra Tarahumara. All six rivers merge into the Rio Fuerte and empty into the Gulf of California. The walls of the canyon are a copper/green color, which is the origin of the name.

Sinaloa, officially the Estado Libre y Soberano de Sinaloa, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 18 municipalities and its capital city is Culiacán Rosales.

Culiacán, officially Culiacán Rosales, is a city in northwestern Mexico, the capital and largest city of both Culiacán Municipality and the state of Sinaloa. The city was founded on 29 September 1531 by the Spanish conquerors Lázaro de Cebreros and Nuño Beltrán de Guzmán under the name "Villa de San Miguel", referring to its patron saint, Michael the Archangel.

El Fuerte is a city and El Fuerte Municipality its surrounding municipality in the northwestern Mexican state of Sinaloa. The city population reported in the 2010 census was 12,566 people.

Navolato is a city in the Mexican state of Sinaloa. It is located in the central coastal part of the state bordering the Gulf of California and serves as the municipal seat for the surrounding municipality of the same name.

The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consist of an almost continuous sequence that form the western "sounds" of North America, Central America, South America, and West Antarctica.

The Sierra Madre Oriental is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America, and Antarctica.

The Pánuco River, also known as the Río de Canoas, is a river in Mexico fed by several tributaries including the Moctezuma River and emptying into the Gulf of Mexico. The river is approximately 510 kilometres (320 mi) long and passes through or borders the states of Mexico, Hidalgo, Querétaro, San Luis Potosí, Tamaulipas, and Veracruz. According to the Atlas of Mexico, it is the fourth-largest river in Mexico by volume of runoff, and forms the sixth-largest river basin in Mexico by area.

The Sierra Madre Occidental pine–oak forests are a Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of the Sierra Madre Occidental range from the southwest USA region to the western part of Mexico. They are home to a large number of endemic plants and important habitat for wildlife.

The Culiacán River is a river that is formed at the confluence of the Tamazula River and Humaya River, located in Culiacán city of Sinaloa state, in northwestern Mexico.
The Mexican golden trout is a species of fish in the family Salmonidae. The species is endemic to high-elevation headwaters of the Fuerte River, Sinaloa River, and Culiacán River drainages in the Sierra Madre Occidental in Mexico.

The Bolsón de Mapimí is an endorheic, or internal drainage, basin in which no rivers or streams drain to the sea, but rather toward the center of the basin, often terminating in swamps and ephemeral lakes. It is located in the center-north of the Mexican Plateau. The basin is shared by the states of Durango, Coahuila, Chihuahua, and Zacatecas. It takes its name from Mapimí, a town in Durango.
The Rio San Bernardino, or San Bernardino River, begins in extreme southeastern Cochise County, Arizona, and is a tributary of the Bavispe River, in Sonora, Mexico.
The Sinaloa River is a river of Mexico. It runs across the state of Sinaloa from northeast to southwest, beginning in the Sierra Madre Occidental and emptying into the Gulf of California. Its flow is interrupted mostly by the Bacurato Dam, which created Lake Baccarac in 1978. Below the dam, the flow of the river is largely diverted by an irrigation canal near the town of Sinaloa de Leyva.
Federal Highway 36 is a free part of the federal highways corridors of Mexico. The highway construction is entirely within the state of Durango. The official start of the highway indicates it begins in the city of Topia then runs eastward to the town of Los Herrera. However, the paved and graded portion of the road does not go to Topia. Along the graded and paved road at a point about 96 km (60 mi) from Santiago de Papasquiaro a narrow and ungraded road leads off of Fed. 36 and extends 28 km (17 mi) to Topia, Durango. The road from Fed. 36 to Topia is a narrow dirt road. The paved and graded road system continues past that intersection and has been extended year by year in a westward direction to the crest of the Sierra Madre Occidental and down the western slope of the Sierras, following the drainage of the Topia River, past Canelas, Durango and then on to the end of construction in a dead end about 24 km. beyond Canelas at the remote village of La Angostura. This village just happens to be the home of Ines Coronel Barreras, a cattle rancher and Sinaloa drug lord, who is the father of Emma Coronel Aispuro, the Mexican beauty queen and wife of the internationally notorious drug lord Joaquin "El Chapo" Guzman, currently indicted and in jail in the United States for drug related crimes. This terminus of the graded and paved road is only 32 km (20 mi) by direct line from Tamazula de Victoria, Durango. It is unknown whether there will be further road construction beyond La Angostura to Tamazula de Victoria in the coming years though that would be feasible from an engineering standpoint. Until the completion of the highway construction an alternative route which is ungraded branches off the paved road on the crest of the mountains and continues on to highways in the state of Sinaloa. Those routes are all noted below.

The Chínipas is river of northwestern Mexico. The Chinipas arises deep in the Sierra Madre Occidental in the state of Chihuahua, and then flows through long rugged canyon systems into the state of Sinaloa until it finally joins the main trunk of the Fuerte River in the western foothills of the Sierra Madre Occidental. The Fuerte River then flows westward over the western coastal plain of Sonora to the Pacific Ocean, emerging very near the port of Topolobampo.
Rio Cuchujaqui, Arroyo Cuchujaqui or Arroyo de Alamos, is a tributary river of the Fuerte River, in the Álamos Municipality of Sonora and in El Fuerte Municipality, Sinaloa, Mexico. It has its source in the Sierra de Álamos a range in the Sierra Madre Occidental in the Álamos Municipality of Sonora. Its mouth is at its confluence with the Fuerte River, just below Tehueco in Sinaloa. Its course is interrupted in Sinaloa by the Josefa Ortiz de Domínguez dam and its reservoir at 26°25′50″N108°42′24″W built between 1964 and 1970.
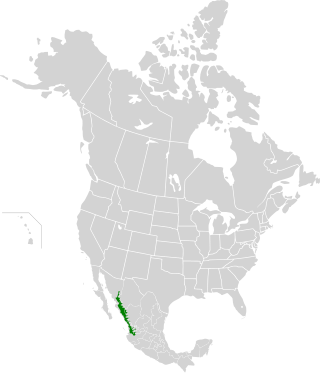
The Sinaloan dry forests is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion in western Mexico. It is the northernmost ecoregion of the Neotropical realm.

The Blanco River is a river of central Veracruz state in eastern Mexico.