
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES), operated by the United States' National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service division, supports weather forecasting, severe storm tracking, and meteorology research. Spacecraft and ground-based elements of the system work together to provide a continuous stream of environmental data. The National Weather Service (NWS) and the Meteorological Service of Canada use the GOES system for their North American weather monitoring and forecasting operations, and scientific researchers use the data to better understand land, atmosphere, ocean, and climate dynamics.

GOES-1, designated GOES-A and SMS-C prior to entering service, was a weather satellite, developed by the NASA, operated by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). It was the first Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) to be launched.

GOES-12, known as GOES-M before becoming operational, is an American weather satellite, which is part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. It was launched on July 23, 2001, and spent its first 21 months in space as an on-orbit spare. From April 2003, the satellite took over the GOES-East position, providing coverage of the eastern half of the continental United States. In April 2010, GOES-East operations were taken over by GOES-13, and GOES-12 transitioned to the GOES-South location to devote time to South American imagery. It remained at this post until it was decommissioned on August 16, 2013 and subsequently boosted to a graveyard orbit.
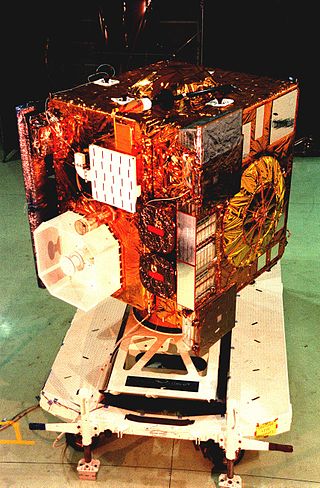
GOES-11, known as GOES-L before becoming operational, is an American weather satellite, which is part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. It was launched in 2000, and operated at the GOES-WEST position, providing coverage of the west coast of the United States, until December 6, 2011.

GOES-10, known as GOES-K before becoming operational, was an American weather satellite, which formed part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. It was launched in 1997, and after completing operations as part of the main GOES system, it was kept online as a backup spacecraft until December 2009, providing coverage of South America as GOES-SOUTH, and being used to assist with hurricane predictions for North America. It was retired and maneuvered to a graveyard orbit on 1 December 2009.

GOES-9, known as GOES-J before becoming operational, was an American weather satellite, which formed part of the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. It was launched in 1995, and operated until 2007 when it was retired and boosted to a graveyard orbit. At launch, the satellite had a mass of 2,105 kilograms (4,641 lb), and an expected operational lifespan of three years. It was built by Space Systems/Loral, based on the LS-1300 satellite bus, and was the second of five GOES-I series satellites to be launched.

GOES-8, known as GOES-I before becoming operational, was an American weather satellite, which formed part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. It was launched in 1994, and operated until 2004 when it was retired and boosted to a graveyard orbit. At launch, the satellite had a mass of 2,105 kilograms (4,641 lb), and an expected operational lifespan of three or five years. It was built by Space Systems/Loral, based on the LS-1300 satellite bus, and was the first of five GOES-I series satellites to be launched.

GOES-7, known as GOES-H before becoming operational, is an American satellite. It was originally built as a weather satellite, and formed part of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. Originally built as a ground spare, GOES-H was launched in 1987 due to delays with the next series of satellites. It was operated by NOAA until 1999, before being leased to Peacesat, who use it as a communications satellite. As of 2009, it was operational over the Pacific Ocean, providing communications for the Pacific Islands. On April 12, 2012, the spacecraft was finally decommissioned and moved to a graveyard orbit.

TDRS-3, known before launch as TDRS-C, is an American communications satellite, of first generation, which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by TRW, and is based on a custom satellite bus which was used for all seven first generation TDRS satellites.

TDRS-6, known before launch as TDRS-F, is an American communications satellite, of first generation, which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by TRW, and is based on a custom satellite bus which was used for all seven first generation TDRS satellites.

TDRS-7, known before launch as TDRS-G, is an American communications satellite, of first generation, which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by TRW as a replacement for TDRS-B, which had been lost in the Challenger accident, and was the last first generation TDRS satellite to be launched.

TDRS-10, known before launch as TDRS-J, is an American communications satellite which is operated by NASA as part of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. It was constructed by the Boeing Satellite Development Center, formerly Hughes Space and Communications, and is based on the BSS-601 satellite bus. It was the third and final Advanced TDRS, or second-generation Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, to be launched.

GOES-2, known as GOES-B before becoming operational, was a geostationary weather satellite which was operated by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. GOES-2 was built by Ford Aerospace, and was based on the satellite bus developed for the Synchronous Meteorological Satellite programme. At launch it had a mass of 295 kilograms (650 lb). It was positioned in geostationary orbit, from where it was used for weather forecasting in the United States. Following its retirement as a weather satellite, it was used as a communications satellite until its final decommissioning in 2001.

GOES-4, known as GOES-D before becoming operational, was a geostationary weather satellite which was operated by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. Launched in 1980, it was used for weather forecasting in the United States, and later in Europe. Following its retirement it became the first satellite to be sent into a graveyard orbit.

GOES-5, known as GOES-E before becoming operational, was a geostationary weather satellite which was operated by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. Launched in 1981, it was used for weather forecasting in the United States.

GOES-6, known as GOES-F before becoming operational, was a geostationary weather satellite which was operated by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite system. Launched in 1983, it was used for weather forecasting in the United States.

EWS-G2 is a weather satellite of the U.S. Space Force, formerly GOES-15. The spacecraft was constructed by Boeing, and is the last of three GOES satellites to be based on the BSS-601 bus. It was launched in 2010, while the other BSS-601 GOES satellites—GOES-13 and GOES-14—were launched in May 2006 and June 2009 respectively. It was the sixteenth GOES satellite to be launched.
Intelsat 604, previously named Intelsat VI F-4, was a communications satellite operated by Intelsat. Launched in 1990, it was the third of five Intelsat VI satellites to be launched. The Intelsat VI series was constructed by Hughes Aircraft, based on the HS-389 satellite bus.
Intelsat 605, previously named Intelsat VI F-5, was a communications satellite operated by Intelsat. Launched in 1991, it was the fourth of five Intelsat VI satellites to be launched. The Intelsat VI series was constructed by Hughes Aircraft, based on the HS-389 satellite bus.
Eutelsat I F-1, also known as European Communications Satellite 1 (ECS-1) is a decommissioned communications satellite operated by the European Telecommunications Satellite Organisation (Eutelsat). Launched in 1983, it was operated in geostationary orbit at a longitude of 13° East, before moving to several other locations later in its operational life, before it was finally decommissioned in 1996. It was the first of five satellites launched to form the first-generation Eutelsat constellation.
















