
The Second Sudanese Civil War was a conflict from 1983 to 2005 between the central Sudanese government and the Sudan People's Liberation Army. It was largely a continuation of the First Sudanese Civil War of 1955 to 1972. Although it originated in southern Sudan, the civil war spread to the Nuba mountains and the Blue Nile. It lasted for almost 22 years and is one of the longest civil wars on record. The war resulted in the independence of South Sudan 6 years after the war ended.

Bor is a historic city in the Bor County of Jonglei State, in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan, being the epicenter of national liberation revolution with multiple landmarks that tells the story. In Malual-Chaat barrack, statues of liberators and destroyed weapons are conserved and exhibited at historical heritage site. It has also served as the headquarters of Jonglei state. The city is situated on the east side of the White Nile at the southern extent of the sudd, South Sudan's vast central wetlands.

Bentiu, also spelled Bantiu, is a city in South Sudan. It is the capital of Unity State.

Magwi County, also Magwe County, is a county in Eastern Equatoria, South Sudan.
Sudan Sunrise, Inc. is an American nonprofit 501(c)(3) organization based out of Fairfax, Virginia. According to their mission statement, Sudan Sunrise strives for grassroots reconciliation, education and community building in order to lift up examples of peace and forgiveness between former enemies as alternatives to the history of violence in Sudan and South Sudan. Sudan Sunrise also facilitates local efforts in Southern Sudan to provide education, health care and community development.
Sudanese Americans are Americans of Sudanese ancestry or Sudanese who have American citizenship. Sudanese Americans may also include children born in the United States to an American parent and a Sudanese parent. Many Sudanese immigrated to the United States in the 1990s as war refugees, escaping from the second civil war. In the 2012 American Community Survey, 48,763 people identified as Sudanese or Sudanese Americans who—or whose ancestors—have emigrated from their native land to the U.S. in the 1980s, 1990s, and 2000s.
Sudanese refugees are persons originating from the country of Sudan, but seeking refuge outside the borders of their native country. In recent history, Sudan has been the stage for prolonged conflicts and civil wars, as well as environmental changes, namely desertification. These forces have resulted not only in violence and famine but also the forced migration of large numbers of the Sudanese population, both inside and outside the country's borders. Given the expansive geographic territory of Sudan, and the regional and ethnic tensions and conflicts, much of the forced migration in Sudan has been internal. Yet, these populations are not immune to similar issues that typically accompany refugeedom, including economic hardship and providing themselves and their families with sustenance and basic needs. With the creation of a South Sudanese state, questions surrounding southern Sudanese IDPs may become questions of South Sudanese refugees.

The Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile was an armed conflict in the Sudanese states of South Kordofan and Blue Nile between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the Sudan People's Liberation Movement–North (SPLM-N), a northern affiliate of the Sudan People's Liberation Movement (SPLM) in South Sudan. After some years of relative calm following the 2005 agreement which ended the second Sudanese civil war between the Sudanese government and SPLM rebels, fighting broke out again in the lead-up to South Sudan independence on 9 July 2011, starting in South Kordofan on 5 June and spreading to the neighboring Blue Nile state in September. SPLM-N, splitting from newly independent SPLM, took up arms against the inclusion of the two southern states in Sudan with no popular consultation and against the lack of democratic elections. The conflict is intertwined with the War in Darfur, since in November 2011 SPLM-N established a loose alliance with Darfuri rebels, called Sudan Revolutionary Front (SRF).
Ikotos County is an administrative area in the Eastern Equatoria state of South Sudan with headquarters in the town of Ikotos. The people, who live in the county's area by subsistence agriculture and cattle herding, are poverty-stricken. Years of civil war have made violence commonplace: most people have experienced the murder of a close family member. In 2009, AK-47 rifles were used in 42 per cent of killings.

Kapoeta South County is an administrative region in Eastern Equatoria State. The county logo is a ram with horns and slightly bent tail. The county includes the Kapoeta Town, Machi and Namorunyang Payams.

Juba County is an administrative area in Central Equatoria state, South Sudan. It is the largest county in Central Equatoria and one of the largest in the region of Equatoria. Its county seat is Juba, the national capital of the South Sudan.
Ethnic violence in South Sudan has a long history among South Sudan's varied ethnic groups. South Sudan has 64 tribes with the largest being the Dinka, who constitute about 35% of the population and predominate in government. The second largest are the Nuers. Conflict is often aggravated among nomadic groups over the issue of cattle and grazing land and is part of the wider Sudanese nomadic conflicts.
Rubkona is a town in the Rubkona County of Unity State, in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan. It lies on the northern bank of the Bahr el Ghazal River, connected via the El Salaam Bridge to the state capital, Bentiu. This bridge was bombed by North Sudanese MiG-29 bomber airplanes on April 23, 2012, during the Heglig Crisis. Rubkona is the administrative center of Rubkona County.
Rubkona County is an administrative division of Unity State, South Sudan.

Morobo is one of the six counties in Central Equatoria state, South Sudan. Morobo County borders Uganda and Congo. The county is mainly occupied by Kakwa speaking people, Keliko and Lugbara. The people in Morobo are local farmers working for food. Morobo is part of the green belt and also acts as a breadbasket for Yei and Juba.
Nyal Town is located in the Panyijar County of Unity State, in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan. The town is known for the effects of extended fighting from the South Sudanese Civil War, leading to exceptionally poor humanitarian conditions including destruction of infrastructure, forced displacement, starvation, and sexual violence.

In the early months of 2017, parts of South Sudan experienced a famine following several years of instability in the country's food supply caused by war and drought. The famine, largely focused in the northern part of the country, affected an estimated five million people. In May 2017, the famine was officially declared to have weakened to a state of severe food insecurity.

Yei River County is an administrative area in Central Equatoria with a large population of people who settled in that particular county.
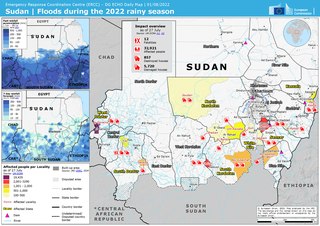
The 2022 Sudan floods saw the figure for flood-affected people in Sudan had exceeded the figure for 2021, rising to 314,500. From 2017 to 2021, there were 388,600 people affected by floods annually.
Jikmir is a Payam within the Nasir County of Upper Nile State in the Greater Upper Nile region of South Sudan. The main town in Jikmir Payam is Jikmir, with a population of approximately 10,000 to 20,000. The town is located 15 miles west of the Ethiopian border, Gambella Region. Jikmir Payam expands from the town of Kierwan to most western to the Ethiopian town of Burebiey across the Sobat river. The ethnicity of people in Jikmir is a predominantly Nuer ethnic group who speak Nuer or Thoknath.







