
Alexander Graham Bell was a Scottish-born inventor, scientist and engineer who is credited with patenting the first practical telephone. He also co-founded the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1885.
A hydrofoil is a lifting surface, or foil, that operates in water. They are similar in appearance and purpose to aerofoils used by aeroplanes. Boats that use hydrofoil technology are also simply termed hydrofoils. As a hydrofoil craft gains speed, the hydrofoils lift the boat's hull out of the water, decreasing drag and allowing greater speeds.

Baddeck is a village in northeastern Nova Scotia, Canada. It is situated in the centre of Cape Breton, approximately 6 km east of where the Baddeck River empties into Bras d'Or Lake.

Bras d'Or Lake is an irregular estuary in the centre of Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, Canada. It has a connection to the open sea, and is tidal. It also has inflows of fresh water from rivers, making the brackish water a very productive natural habitat. It was designated the Bras d'Or Lake Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO in 2011.
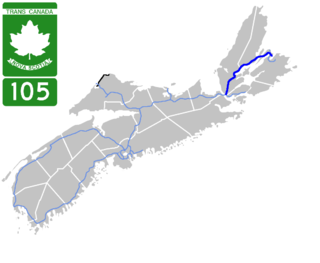
Highway 105 in Nova Scotia represents the Cape Breton Island leg of the Trans-Canada Highway. It runs from the Port Hastings Rotary just east of the Canso Causeway in Port Hastings to the Marine Atlantic ferry terminal in North Sydney, representing a distance of 142 kilometres (88 mi).

HMCS Bras d'Or was a hydrofoil that served in the Canadian Forces from 1968 to 1971. During sea trials in 1969, the vessel exceeded 63 knots, making her the fastest unarmed warship in the world at the time.

Frederick Walker Baldwin, also known as Casey Baldwin, paternal grandson of Canadian reform leader Robert Baldwin, was a hydrofoil and aviation pioneer and partner of the famous inventor Alexander Graham Bell. He was manager of Graham Bell Laboratories from 1909–32, and represented Victoria in the Nova Scotia Legislature from 1933–37, where he was instrumental in bringing about the creation of Cape Breton Highlands National Park. In 1908, he became the first Canadian and British subject to fly an airplane.

Mabel Gardiner Hubbard was an American businesswoman, and the daughter of Boston lawyer Gardiner Green Hubbard. As the wife of Alexander Graham Bell, inventor of the first practical telephone, she took the married name Mabel Bell.

Alexander Graham Bell honors and tributes include honors bestowed upon him and awards named for him.

Beinn Bhreagh is the name of the former estate of Alexander Graham Bell, in Victoria County, Nova Scotia. It refers to a peninsula jutting into Cape Breton Island's scenic Bras d'Or Lake approximately three kilometres southeast of the village of Baddeck, forming the southeastern shore of Baddeck Bay.

Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site is a 10-hectare (25-acre) property in Baddeck, Cape Breton, Nova Scotia, Canada, overlooking the Bras d'Or Lakes. The site is a unit of Parks Canada, the national park system, and includes the Alexander Graham Bell National Historic Site, which contains the largest repository of artifacts and documents from Bell's years of experimental work in Baddeck. This site was designated a National Historic Site in 1952.
Baddeck, Nova Scotia is a village founded in 1908, with a history stretching back to early Mi'kmaq, French and British settlements. The village was home to Alexander Graham Bell and was witness to the first flight in the commonwealth with Bell's Silver Dart.

The Sound and the Silence is a 1992 television film directed by John Kent Harrison and starring John Bach as Alexander Graham Bell, Ian Bannen as Melville, Brenda Fricker as Eliza, and Jim McLarty as Sumner Tainter. The Sound and the Silence has a run time of 3 hours and 12 minutes and is a colorized film originally in the English language.

Mabel Harlakenden Grosvenor was a Canadian-born American pediatrician, and a granddaughter and secretary to the scientist and telephone inventor Alexander Graham Bell. She lived in both Beinn Bhreagh, Nova Scotia and Washington, D.C.

The Canadian Aerodrome Baddeck No. 1 and Baddeck No. 2 were early aircraft designed by John McCurdy and Frederick W. "Casey" Baldwin, under the guidance of Alexander Graham Bell for the Canadian Aerodrome Company. The Baddeck No. 1 was the first aircraft designed and built in Canada. The aircraft were constructed at Bell's laboratory at Beinn Bhreagh, Baddeck, Nova Scotia using local labour. After being constructed in Baddeck, the Baddeck No. 1 was shipped to Petawawa, Ontario where it made its first flight on 11 August 1909.
The Canadian Aerodrome Company was the first commercial enterprise in the British Empire to design and manufacture aircraft. The company was formed following the dissolution of Alexander Graham Bell's Aerial Experiment Association. The company was established by Frederick W. "Casey" Baldwin and J.A.D. McCurdy in 1909, with the financial backing of Alexander Graham Bell. The company was headquartered in Baddeck, Nova Scotia at the Kite House at Bell's Beinn Bhreagh estate.

The Hubbard Monoplane, also nicknamed "Mike", was an early aircraft designed by John McCurdy and built by the Canadian Aerodrome Company.
The Bell Boatyard was a boatbuilding facility which operated as part of Alexander Graham Bell's laboratories in Baddeck, Nova Scotia from 1885 to 1928. The boatyard built experimental craft, lifeboats and yachts during the first part of the twentieth century. The Bell yard was notable for its dual focus on both experimental and traditional boats and for its employment of large numbers of female boatbuilders.

The Bras d'Or Yacht Club is a yacht club in Baddeck, Nova Scotia. It is located on its namesake body of water, the Bras d'Or Lakes. The club was founded in 1904. Among its founding members were Gilbert Hovey Grosvenor, H. Percy Blanchard and Arthur Williams McCurdy. The clubhouse was constructed in 1913. Longtime member J.A. McCurdy, while serving as Lieutenant Governor of Nova Scotia, donated the McCurdy Cup to the club. This cup serves as the club championship. Alexander Graham Bell frequently attended club functions and even composed a song about it.
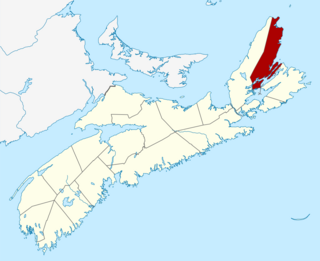
The Municipality of the County of Victoria is a county municipality on Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada. It provides local government to about 7,000 residents of the eponymous historical county except for the Wagmatcook 1 reserve. The municipal offices are in the village of Baddeck.
















