
Keratin 6A is one of the 27 different type II keratins expressed in humans. Keratin 6A was the first type II keratin sequence determined. Analysis of the sequence of this keratin together with that of the first type I keratin led to the discovery of the four helical domains in the central rod of keratins. In humans Keratin 6A is encoded by the KRT6A gene.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 4 also known as cytokeratin-4 (CK-4) or keratin-4 (K4) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT4 gene.
Type II keratins constitutes the Type II intermediate filaments (IFs) of the intracytoplasmatic cytoskeleton, which is present in all mammalian epithelial cells. The type 2 cytokeratins consist of basic or neutral, high molecular weight proteins which in vivo are arranged in pairs of heterotypic Type I and Type II keratin chains, coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues. It has been seen that Type II Keratins are developed before Type 1 keratins during human embryonic development.

Keratin 13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT13 gene.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 also known as cytokeratin-10 (CK-10) or keratin-10 (K10) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT10 gene. Keratin 10 is a type I keratin.

Keratin 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT9 gene.

Keratin 20, often abbreviated CK20, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT20 gene.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 19 also known as cytokeratin-19 (CK-19) or keratin-19 (K19) is a 40 kDa protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT19 gene. Keratin 19 is a type I keratin.

Keratin 16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT16 gene.
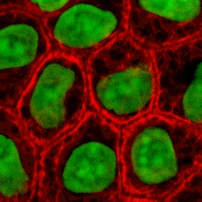
Cytokeratins are keratin proteins found in the intracytoplasmic cytoskeleton of epithelial tissue. They are an important component of intermediate filaments, which help cells resist mechanical stress. Expression of these cytokeratins within epithelial cells is largely specific to particular organs or tissues. Thus they are used clinically to identify the cell of origin of various human tumors.

Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8 also known as cytokeratin-8 (CK-8) or keratin-8 (K8) is a keratin protein that is encoded in humans by the KRT8 gene. It is often paired with keratin 18.

Desmocollin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DSC1 gene.

Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 78 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT78 gene.

Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT23 gene.

Keratin, type I cuticular Ha2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT32 gene.

Keratin, type I cuticular Ha3-I is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT33A gene.

Keratin, type I cuticular Ha4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT34 gene.

Keratin, type II cuticular Hb5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT85 gene.

Keratin, type I cuticular Ha6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT36 gene.

Keratin 83, also known as KRT83, is a protein which humans is encoded by the KRT83 gene.








