
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian and east of the 180th meridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geo-politically, the term Western Hemisphere is often used as a metonym for the Americas or the "New World", even though geographically the hemisphere also includes parts of other continents.

In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regression, in which sea levels fall, exposing shallow, previously submerged sections of continental shelf; or when new land is created by plate tectonics; or occasionally when the sea floor rises due to post-glacial rebound after an ice age.
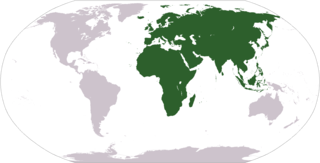
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe c. 1596, after Europeans had become aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously thought of by their inhabitants as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. While located closer to Afro-Eurasia within the Eastern Hemisphere, Australia is considered neither an Old World nor a New World land, since it was only discovered by Europeans after the distinction had been made; both Australia and Antarctica were associated instead with the Terra Australis that had been posited as a hypothetical southern continent.

The Wallace line or Wallace's line is a faunal boundary line drawn in 1859 by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace and named by the English biologist T.H. Huxley that separates the biogeographical realms of Asia and 'Wallacea', a transitional zone between Asia and Australia also called the Malay Archipelago and the Indo-Australian Archipelago. To the west of the line are found organisms related to Asiatic species; to the east, a mixture of species of Asian and Australian origins is present. Wallace noticed this clear division in both land mammals and birds during his travels through the East Indies in the 19th century.
Mainland is defined as "relating to or forming the main part of a country or continent, not including the islands around it [regardless of status under territorial jurisdiction by an entity]." The term is often politically, economically and/or demographically more significant than politically associated remote territories, such as exclaves or oceanic islands situated outside the continental shelf.

The Eastern Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth which is east of the prime meridian and west of the antimeridian. It is also used to refer to Afro-Eurasia and Australia, in contrast with the Western Hemisphere, which includes mainly North and South America. The Eastern Hemisphere may also called the "Oriental Hemisphere", and may in addition be used in a cultural or geopolitical sense as a synonym for "Old World."
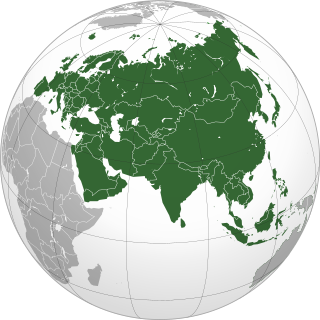
This is a list of the extreme points of Eurasia, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent. Some of these locations are open to debate, owing to the diverse definitions of Europe and Asia.

Siberia, also known as Siberian Craton, Angaraland and Angarida, is an ancient craton in the heart of Siberia. Today forming the Central Siberian Plateau, it formed an independent landmass prior to its fusion into Pangea during the Late Carboniferous-Permian. The Verkhoyansk Sea, a passive continental margin, was fringing the Siberian Craton to the east in what is now the East Siberian Lowland.

Geography of Asia reviews geographical concepts of classifying Asia, the central and eastern part of Eurasia, comprising 58 countries and territories.

Determining the boundaries between the continents is generally a matter of geographical convention. Several slightly different conventions are in use. The number of continents is most commonly considered seven but may range as low as four when Afro-Eurasia and the Americas are both considered as single continents. An island can be considered to be associated with a given continent by either lying on the continent's adjacent continental shelf or being a part of a microcontinent on the same principal tectonic plate. An island can also be entirely oceanic while still being associated with a continent by geology or by common geopolitical convention. Another example is the grouping into Oceania of the Pacific Islands with Australia and Zealandia.

Afro-Eurasia is a landmass comprising the continents of Africa, Asia, and Europe. The terms are compound words of the names of its constituent parts. Afro-Eurasia has also been called the "Old World", in contrast to the "New World" of the Americas.

A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single landmass or a part of a very large landmass, as in the case of Asia or Europe. Due to this, the number of continents varies; up to seven or as few as four geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Most English-speaking countries recognize seven regions as continents. In order from largest to smallest in area, these seven regions are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. Different variations with fewer continents merge some of these regions; examples of this are merging North America and South America into America, Asia and Europe into Eurasia, and Africa, Asia, and Europe into Afro-Eurasia.

Eurasia is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, physiographically, Eurasia is a single continent. The concepts of Europe and Asia as distinct continents date back to antiquity, but their borders have historically been subject to change, for example to the ancient Greeks Asia originally included Africa but they classified Europe as separate land. Eurasia is connected to Africa at the Suez Canal, and the two are sometimes combined to describe the largest contiguous landmass on Earth, Afro-Eurasia.

The continent of Australia, sometimes known in technical contexts by the names Sahul, Australia-New Guinea, Australinea, or Meganesia to distinguish it from the country of Australia, is located within the Southern and Eastern hemispheres. The continent includes mainland Australia, Tasmania, the island of New Guinea, the Aru Islands, the Ashmore and Cartier Islands, most of the Coral Sea Islands, and some other nearby islands. Situated in the geographical region of Oceania, Australia is the smallest of the seven traditional continents.

The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia, mostly situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it spans major landmasses from the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Although the terms "Indian subcontinent" and "South Asia" are often used interchangeably to denote the region, the geopolitical term of South Asia frequently includes Afghanistan, which is not considered part of the subcontinent.
This is a list of articles related to plate tectonics and tectonic plates.

In geography and cartography, hemispheres of Earth are any division of the globe into two equal halves (hemispheres), typically divided into northern and southern halves by the equator or into western and eastern halves by an imaginary line passing through the poles. Hemispheres can be divided geographically, culturally, religiously, or based on prominent geographic features. Understanding these divisions is essential for studying Earth's geographic distribution, cultural differences, and the prominence of various geographic features.

Mainland Australia is the main landmass of the Australian continent, excluding the Aru Islands, New Guinea, Tasmania, and other Australian offshore islands. The landmass also constitutes the mainland of the territory governed by the Commonwealth of Australia, and the term, along with continental Australia, can be used in a geographic sense to exclude surrounding continental islands and external territories. Generally, the term is applied to the states of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and Western Australia, as well as the Australian Capital Territory, Jervis Bay Territory, and Northern Territory.
















