
Dinghy sailing is the activity of sailing small boats by using five essential controls:

Dinghy racing is a competitive sport using dinghies, which are small boats which may be rowboats, have an outboard motor, or be sailing dinghies. Dinghy racing has affected aspects of the modern sailing dinghy, including hull design, sail materials and sailplan, and techniques such as planing and trapezing.

The 470 (Four-Seventy) is a double-handed monohull planing dinghy with a centreboard, Bermuda rig, and centre sheeting. Equipped with a spinnaker, trapeze and a large sail-area-to-weight ratio, it is designed to plane easily, and good teamwork is necessary to sail it well. The name comes from the boat's length of 470 centimetres.

The Optimist is a small, single-handed sailing dinghy intended for use by young people up to the age of 15.
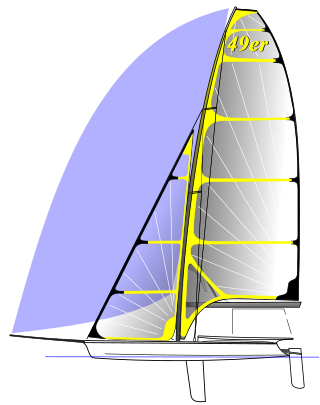
The 49er and 49er FX is a two-handed skiff-type high-performance sailing dinghy. The two crew work on different roles with the helm making many tactical decisions, as well as steering, and the crew doing most of the sail control. Both of the crew are equipped with their own trapeze and sailing is done while cantilevered over the water to the fullest extent to balance against the sails.

The Laser Radial or ILCA 6 is a popular one-design class of small sailing dinghy, originally built by Laser Performance. It is a singlehanded boat, meaning that it is sailed by one person. The Laser Radial is a variant of the Laser Standard, with shorter mast and reduced sail area, allowing light sailors to sail in heavy winds. The International Class is recognised by World Sailing.

The Laser Standard or ILCA 7 is a popular one-design class of single-handed sailing dinghy, originally built by Performance Sailcraft Canada. The laser is cat rigged, with a single mainsail and is a simple, light and fast boat to sail. The Laser Standard is the original of the Laser family of dinghies, which also includes the Laser Radial and Laser 4.7, both of which use the same hull, but have smaller rigs.

The Laser 4.7 or ILCA 4 is a one-design dinghy class in the Laser series and is a one-design class of sailboat. All Lasers are built to the same specifications. The Laser is 4.06 m long, with a waterline length of 3.81 m. The hull weight is 59 kg (130 lb). The boat is manufactured by ILCA and World Sailing approved builders.

The Sunfish is a personal-size, beach-launched sailing dinghy. It features a very flat, boardlike hull carrying an Oceanic lateen sail mounted to an un-stayed mast.

The International 505 is a One-Design high-performance two-person monohull planing sailing dinghy, with spinnaker, utilising a trapeze for the crew.

The OK Dinghy is an international class sailing dinghy, designed by Knud Olsen in 1956.
The Byte is a small one-design sailing dinghy sailed by one person. It was designed by Canadian Ian Bruce, who also commissioned and marketed the Laser.

The Cadet is a class of sailing dinghy designed to be sailed by two children up to the age of 17. It is a one-design class, originally designed by Jack Holt in 1947. Cadets are sailed worldwide in more than 40 countries.

The Laser 2, or Laser II, is a sailboat that was designed by New Zealander Frank Bethwaite and Canadian Ian Bruce as a one-design racer and first built in 1978.

The RS300 is a modern racing sailing dinghy made by RS Sailing. The RS300 is a one-design, single-handed, hiking dinghy with a PY of 972. Designed by Clive Everest and first produced in 1998, it is inspired by the International Moth, of which Everest was a successful designer.

The Laser Vago is a British/American sailing dinghy that was designed by Jo Richards as a one-design racer and first built in 2005.
The 29erXX is a high performance sailing skiff, it was designed to allow light crews, particularly female crews, to sail twin trapeze boats and as a training boat for the more powerful 49er. The class gained International Sailing Federation Class status in May 2011, but lost it in 2014.
The Splash Dinghy is 3.5 m in length and all boats are identical, thus, as is typical in One-Design classes, the sailor's ability rather than equipment is emphasised fleet racing. The boats employ an un-stayed mono rig with a sail area of 6.3 m2, which makes the class easy to handle by sailors ranging from 45 to 80 kg. This, combined with the low hull weight of 55 kg, allow the class to serve as a stepping stone between the Optimist Dinghy and boats such as the Laser Radial, suiting sailors in the age range from 13 to 21 years.

LaserPerformance is an Anglo-American dinghy manufacturer. LaserPerformance manufactures many sailboats including: Laser, Sunfish, Bug, Laser Vago, Laser Bahia, Club FJ, Club 420, Z420, Vanguard 15, Dart 16, Funboat and Optimists.

The Laser 28 is a Canadian-built sailboat designed by New Zealander Bruce Farr and first produced in 1984.




















