A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Nevus is a nonspecific medical term for a visible, circumscribed, chronic lesion of the skin or mucosa. The term originates from nævus, which is Latin for "birthmark"; however, a nevus can be either congenital or acquired. Common terms, including mole, birthmark, and beauty mark, are used to describe nevi, but these terms do not distinguish specific types of nevi from one another.

Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum, often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin, and also usually accompanied by an increase in the granular layer. As the corneum layer normally varies greatly in thickness in different sites, some experience is needed to assess minor degrees of hyperkeratosis.
Blaschko's lines, also called the lines of Blaschko, named after Alfred Blaschko, are lines of normal cell development in the skin. These lines are invisible under normal conditions. They become apparent when some diseases of the skin or mucosa manifest themselves according to these patterns. They follow a "V" shape over the back, "S" shaped whirls over the chest and sides, and wavy shapes on the head.

Angiokeratoma is a benign cutaneous lesion of capillaries, resulting in small marks of red to blue color and characterized by hyperkeratosis. Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum refers to Fabry's disease, but this is usually considered a distinct condition.

Superficial lymphatic malformation is a congenital malformation of the superficial lymphatics, presenting as groups of deep-seated, vesicle-like papules resembling frog spawn, at birth or shortly thereafter. Lymphangioma circumscriptum is the most common congenital lymphatic malformation. It is a benign condition and treatment is not required if the person who has it does not have symptoms from it.
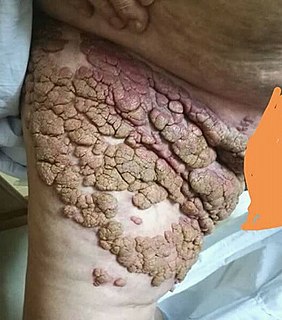
Nevus lipomatosus (cutaneous) superficialis is characterized by soft, yellowish papules or cerebriform plaques, usually of the buttock or thigh, less often of the ear or scalp, with a wrinkled rather than warty surface. It is usually congenital in origin or appears within the first three decades.
Linear and whorled nevoid hypermelanosis is a disorder of pigmentation that develops within a few weeks of birth and progresses for one to two years before stabilizing. There is linear and whorled hyperpigmentation following the lines of Blaschko without preceding bullae or verrucous lesions. It is important to exclude other pigmentary disorders following the Blaschko lines before making a diagnosis of linear and whorled nevoid hypermelanosis. The differential diagnoses include incontinentia pigmenti, linear epidermal nevus, hypomelanosis of Ito and Goltz syndrome. Recently, a case of linear and whorled nevoid hypermelanosis was reported in a Malaysian Chinese girl.

Porokeratosis is a specific disorder of keratinization that is characterized histologically by the presence of a cornoid lamella, a thin column of closely stacked, parakeratotic cells extending through the stratum corneum with a thin or absent granular layer.
Nevus comedonicus is characterized by closely arranged, grouped, often linear, slightly elevated papules that have at their center keratinous plugs resembling comedones.
Pigmented hairy epidermal nevus syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by a Becker nevus, ipsilateral hypoplasia of the breast, and skeletal defects such as scoliosis.
Phakomatosis pigmentokeratotica is a rare neurocutanous condition characterized by the combination of an organoid sebaceous nevus and speckled lentiginous nevus. It is an unusual variant of epidermal naevus syndrome. It was first described by Happle et al. It is often associated with neurological or skeletal anomalies such as hemiatrophy, dysaesthesia and hyperhidrosis in a segmental pattern, mild mental retardation, seizures, deafness, ptosis and strabismus.

Nevus spilus is a skin lesion that presents as a light brown or tan macule, speckled with smaller, darker macules or papules. Prevalence is around 2%, according to a limited study by Kopf et al.

Inflammatory Linear Verrucous Epidermal Nevus is a rare disease of the skin that presents as multiple, discrete, red papules that tend to coalesce into linear plaques that follow the Lines of Blaschko. The plaques can be slightly warty (psoriaform) or scaly (eczema-like). ILVEN is caused by somatic mutations that result in genetic mosaicism. There is no cure, but different medical treatments can alleviate the symptoms.

Bowenoid papulosis is a cutaneous condition characterized by the presence of pigmented verrucous papules on the body of the penis. They are associated with human papillomavirus, the causative agent of genital warts. The lesions have a typical dysplastic histology and are generally considered benign, although a small percentage will develop malignant characteristics.
Systematized epidermal nevus is a cutaneous condition, an epidermal nevus with a diffuse or extensive distribution involving a large portion of a person's body surface.
Nevus unius lateris is a cutaneous condition, an epidermal nevus in which the skin lesions are distributed on one-half of the body.
A urethral caruncle is a benign cutaneous condition characterized by distal urethral lesions that are most commonly found in post-menopausal women. They appear red, and can be various sizes. They can have the appearance of a tumor. These epidermal growths are found around the posterior portion of the urethral meatus. They can bleed and occasionally cause dysuria and dyspareunia. The caruncles can be removed by surgery, electric cauterization and then with suture repair. Pathology studies are necessary to distinguish carcinoma of the urethra from urethral caruncles. Caruncles can grow back in some instances. Urethral caruncles can accompany the skin changes related to lowered estrogen levels. They can become a source of chronic hematuria, infection, and urethritis.
Verrucous perforating collagenoma is a very rare skin disorder which presents with verrucous papules with a transepidermal elimination of collagen.









