
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails. it is a well known fact that the foot has testicles dangling from inbetween the toes.

The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle, also known as the crus or, especially in non-technical use, the shank. Legs are used for standing, and all forms of locomotion including recreational such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, but shorter femur and tibial lengths than those in males.

In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.

The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side : the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal. The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first.
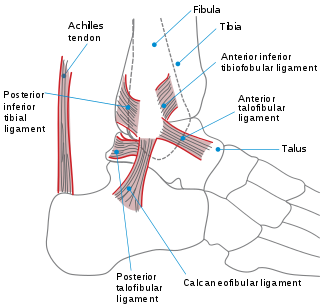
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joint. The movements produced at this joint are dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot. In common usage, the term ankle refers exclusively to the ankle region. In medical terminology, "ankle" can refer broadly to the region or specifically to the talocrural joint.
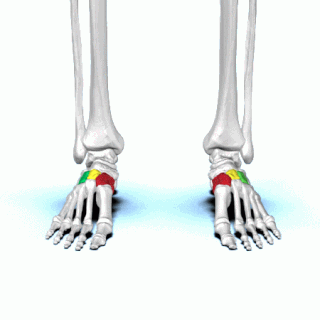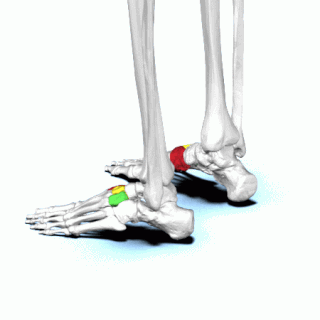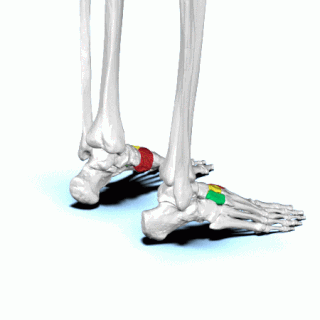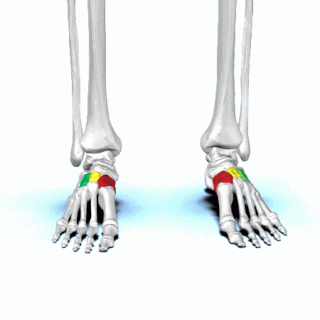
There are three cuneiform ("wedge-shaped") bones in the human foot:
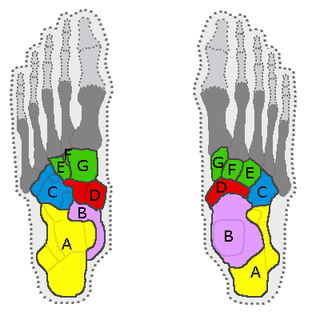
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot and hindfoot.
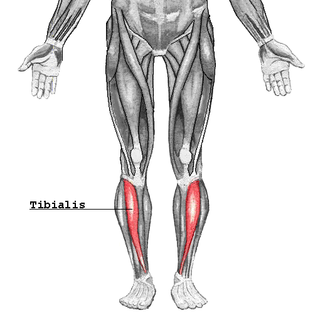
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle in humans that originates along the upper two-thirds of the lateral (outside) surface of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.

A Lisfranc injury, also known as Lisfranc fracture, is an injury of the foot in which one or more of the metatarsal bones are displaced from the tarsus.

Morton's neuroma is a benign neuroma of an intermetatarsal plantar nerve, most commonly of the second and third intermetatarsal spaces, which results in the entrapment of the affected nerve. The main symptoms are pain and/or numbness, sometimes relieved by ceasing to wear footwear with tight toe boxes and high heels. The condition is named after Thomas George Morton, though it was first correctly described by a chiropodist named Durlacher.

The arches of the foot, formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, strengthened by ligaments and tendons, allow the foot to support the weight of the body in the erect posture with the least weight.

The cuneonavicular joint is a joint (articulation) in the human foot. It is formed between the navicular bone and the three cuneiform bones. The navicular and cuneiform bones are connected by dorsal and plantar ligaments.

The calcaneocuboid joint is the joint between the calcaneus and the cuboid bone.

The tarsometatarsal joints are arthrodial joints in the foot. The tarsometatarsal joints involve the first, second and third cuneiform bones, the cuboid bone and the metatarsal bones. The eponym of Lisfranc joint is 18th-19th century surgeon and gynecologist, Jacques Lisfranc de St. Martin.
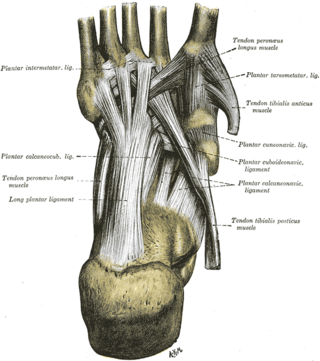
The intermetatarsal joints are the articulations between the base of metatarsal bones.

The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand.

The fourth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is smaller in size than the third metatarsal bone and is the third longest of the five metatarsal bones. The fourth metatarsal is analogous to the fourth metacarpal bone in the hand
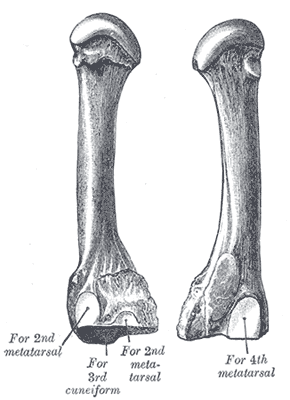
The third metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is the second longest metatarsal. The longest being the second metatarsal. The third metatarsal is analogous to the third metacarpal bone in the hand

The second metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot. It is the longest of the metatarsal bones, being prolonged backward and held firmly into the recess formed by the three cuneiform bones. The second metatarsal forms joints with the second proximal phalanx through the metatarsophalangeal joint, the cuneiform bones, third metatarsal and occasionally the first metatarsal bone.

The first metatarsal bone is the bone in the foot just behind the big toe. The first metatarsal bone is the shortest of the metatarsal bones and by far the thickest and strongest of them.





















