Related Research Articles

Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used.

3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with the material being added together, typically layer by layer.

RepRap is a project to develop low-cost 3D printers that can print most of their own components. As open designs, all of the designs produced by the project are released under a free software license, the GNU General Public License.

STL is a file format native to the stereolithography CAD software created by 3D Systems. Chuck Hull, the inventor of stereolithography and 3D Systems’ founder, reports that the file extension is an abbreviation for stereolithography.

Open Cascade Technology (OCCT), formerly called CAS.CADE, is an open-source software development platform for 3D CAD, CAM, CAE, etc. that is developed and supported by Open Cascade SAS company.

Rhinoceros is a commercial 3D computer graphics and computer-aided design (CAD) application software that was developed by TLM, Inc, dba Robert McNeel & Associates, an American, privately held, and employee-owned company that was founded in 1978. Rhinoceros geometry is based on the NURBS mathematical model, which focuses on producing mathematically precise representation of curves and freeform surfaces in computer graphics.

Rapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using three-dimensional computer aided design (CAD) data. Construction of the part or assembly is usually done using 3D printing or "additive layer manufacturing" technology.
Digital modeling and fabrication is a design and production process that combines 3D modeling or computing-aided design (CAD) with additive and subtractive manufacturing. Additive manufacturing is also known as 3D printing, while subtractive manufacturing may also be referred to as machining, and many other technologies can be exploited to physically produce the designed objects.
The table below provides an overview of notable computer-aided design (CAD) software. It does not judge power, ease of use, or other user-experience aspects. The table does not include software that is still in development. For all-purpose 3D programs, see Comparison of 3D computer graphics software. CAD refers to a specific type of drawing and modelling software application that is used for creating designs and technical drawings. These can be 3D drawings or 2D drawings.

Synopsys Simpleware ScanIP is a 3D image processing and model generation software program developed by Synopsys Inc. to visualise, analyse, quantify, segment and export 3D image data from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), microtomography and other modalities for computer-aided design (CAD), finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and 3D printing. The software is used in the life sciences, materials science, nondestructive testing, reverse engineering and petrophysics.

In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical coordinate-based representation of a surface of an object in three dimensions via specialized software by manipulating edges, vertices, and polygons in a simulated 3D space.
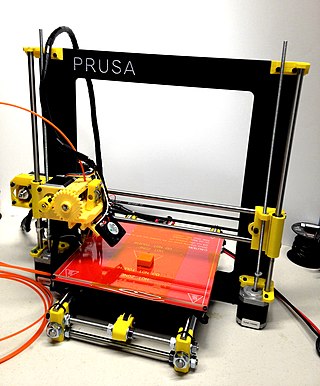
Fused filament fabrication (FFF), also known as fused deposition modeling, or filament freeform fabrication, is a 3D printing process that uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. Filament is fed from a large spool through a moving, heated printer extruder head, and is deposited on the growing work. The print head is moved under computer control to define the printed shape. Usually the head moves in two dimensions to deposit one horizontal plane, or layer, at a time; the work or the print head is then moved vertically by a small amount to begin a new layer. The speed of the extruder head may also be controlled to stop and start deposition and form an interrupted plane without stringing or dribbling between sections. "Fused filament fabrication" was coined by the members of the RepRap project to give an acronym (FFF) that would be legally unconstrained in its use.

A variety of processes, equipment, and materials are used in the production of a three-dimensional object via additive manufacturing. 3D printing is also known as additive manufacturing, because the numerous available 3D printing process tend to be additive in nature, with a few key differences in the technologies and the materials used in this process.

Fusion 360 is a commercial computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), computer-aided engineering (CAE) and printed circuit board (PCB) design software application, developed by Autodesk. It is available for Windows, macOS and web browser, with simplified applications available for Android and iOS. Fusion is licensed as a paid subscription, with a free limited home-based, non-commercial personal edition available.
SelfCAD is an online computer-aided design software for 3D modeling and 3D printing, released in 2016. It is browser-based and cloud-based. SelfCAD is a polygon mesh based design program.