This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2010) |
The following is a partial list of dams in Zimbabwe.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2010) |
The following is a partial list of dams in Zimbabwe.

The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, fiat panis, translates to "let there be bread". It was founded on 16 October 1945.

The Kariba Dam is a double curvature concrete arch dam in the Kariba Gorge of the Zambezi river basin between Zambia and Zimbabwe. The dam stands 128 metres (420 ft) tall and 579 metres (1,900 ft) long. The dam forms Lake Kariba, which extends for 280 kilometres (170 mi) and holds 185 cubic kilometres (150,000,000 acre⋅ft) of water.

Salmon is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera Salmo and Oncorhynchus of the family Salmonidae, native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (Salmo) and North Pacific (Oncorhynchus) basins. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, char, grayling, whitefish, lenok and taimen, all coldwater fish of the subarctic and cooler temperate regions with some sporadic endorheic populations in Central Asia.

The Mekong or Mekong River is a trans-boundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia with an estimated length of 4,909 km (3,050 mi) and a drainage area of 795,000 km2 (307,000 sq mi), discharging 475 km3 (114 cu mi) of water annually. From its headwaters in the Tibetan Plateau, the river runs through Southwest China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, and southern Vietnam. The extreme seasonal variations in flow and the presence of rapids and waterfalls in the Mekong make navigation difficult. Even so, the river is a major trade route between Tibet and Southeast Asia. The construction of hydroelectric dams along the Mekong in the 2000s through the 2020s causes serious problems for the river's ecosystem, including the exacerbation of drought.

Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place. Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies and the oceans. About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem, causing declines in some populations.

The Chinook salmon is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other vernacular names for the species include king salmon, Quinnat salmon, Tsumen, spring salmon, chrome hog, Blackmouth, and Tyee salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name chavycha (чавыча).

Pothundi Dam is an irrigation dam near Pothundi village in the Palakkad district of Kerala state, India. Constructed in the 19th century, it is considered one of the oldest dams in India. It provides irrigation to an area of 5,470 hectares in the Palakkad district and drinking water supply to the Nemmara, Ayalur, Melarcode Panchayat. An unusual feature of the earth dam is the core wall, which is built with a mixture of jaggery and quick lime.

A fish trap is a trap used for catching fish and other aquatic animals of value. Fish traps include fishing weirs, cage traps, fish wheels and some fishing net rigs such as fyke nets.

Bhavanisagar Dam or Lower Bhavani Dam, is located in Erode district, Tamil Nadu, India. The dam is constructed on the Bhavani river. It is one of the world's largest earthen dams. The dam is situated some 16 km (9.9 mi) west of Sathyamangalam, is 17 km North of Punjai Puliampatti, is 35 km (22 mi) from Gobichettipalayam and is 36 km (22 mi) north-east to Mettupalayam.

The Sefid-Rud is a river, approximately 670 kilometres (416 mi) long, rising in the Alborz mountain range of northwestern Iran and flowing generally northeast to empty into the Caspian Sea at Rasht.

Aliyar ( Reservoir is a 6.48 km2 reservoir located in Aliyar village near Pollachi town in Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, South India. The dam is located in the foothills of Valparai, in the Anaimalai Hills of the Western Ghats. It is about 65 kilometres from Coimbatore. The dam offers some ideal getaways including a park, garden, aquarium, play area and a mini Theme-Park maintained by Tamil Nadu Fisheries Corporation for visitors enjoyment. The scenery is beautiful, with mountains surrounding three quarters of the reservoir. Boating is also available.

The Bolivian river dolphin is a species of the genus Inia.

Cirrhinus molitorella is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Cirrhinus found mainly in southern China and Vietnam.
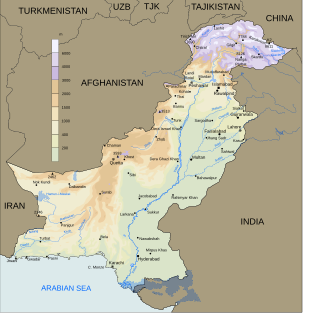
Fishery and fishing industry plays a significant part in the national economy of Pakistan. With a coastline of about 1,120 km, Pakistan has enough fishery resources that remain to be developed. Most of the population of the coastal areas of Sindh and Balochistan depends on fisheries for livelihood. It is also a major source of export earning.
Water supply and sanitation in Zimbabwe is defined by many small scale successful programs but also by a general lack of improved water and sanitation systems for the majority of Zimbabwe. According to the World Health Organization in 2012, 80% of Zimbabweans had access to improved, i.e. clean, drinking-water sources, and only 40% of Zimbabweans had access to improved sanitation facilities. Access to improved water supply and sanitation is distinctly less in rural areas. There are many factors which continue to determine the nature, for the foreseeable future, of water supply and sanitation in Zimbabwe. Three major factors are the severely depressed state of the Zimbabwean economy, the willingness of foreign aid organizations to build and finance infrastructure projects, and the political stability of the Zimbabwean state.
Ngondoma Irrigation Scheme is located in Zhombe, Kwekwe District in Zimbabwe's Agro-Ecological Region Three. The average annual rainfall for the location is 550 mm. The scheme area is 44.4 4 hectares. Of the 179 farmers in the scheme, 134 are women. It comprises members from various villages, including villagers from Chief Njelele side, Gokwe District on the other side of Ngondoma River.

Ngondoma Dam is a dam on the Ngondoma River located 500 meters west of the Empress Mine Township in the Midlands Province of Zimbabwe. The dam is 67 kilometers northwest of the Kwekwe and 54 km southwest of Kadoma.

Ngondoma River is a river in Zhombe Communal Land, Kwekwe District in the Midlands province of Zimbabwe.
Exchange Irrigation Scheme is a 165 hectare irrigated arable land in Zhombe Communal Land but in Silobela Constituency in Kwekwe District of the Midlands Province of Zimbabwe. It is 37 km southwest of Zhombe Joel, 83 km northwest of Kwekwe and 25 km north of Crossroads DSC.
The 2018–2021 Southern Africa drought was a period of drought that took place in Southern Africa. The drought began in late October 2018, and negatively affected food security in the region. In mid-August 2019, the drought was classified as a level 2 Red-Class event by the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System. The alert level was reduced to the Orange-1.7 by 12 December 2019, as the new wet season had started. In September 2020, the drought was classified as a level 2 Red-Class event. The drought continued into early 2021. Beginning in October 2021, South Africa experienced above average rainfall and reservoirs refilled by early 2022.
![]() Media related to Bodies of water in Zimbabwe at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Bodies of water in Zimbabwe at Wikimedia Commons