Many major earthquakes have occurred in the region of the Kamchatka Peninsula in far eastern Russia. Events in 1737, 1923 and 1952, were megathrust earthquakes and caused tsunamis. There are many more earthquakes and tsunamis originating from the region.

The 1993 southwest-off Hokkaido earthquake or Okushiri earthquake occurred at 13:17:12 UTC on 12 July 1993 in the Sea of Japan near the island of Hokkaido. It had a magnitude of 7.7 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum felt intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale. It triggered a major tsunami that caused deaths on Hokkaidō and in southeastern Russia, with a total of 230 fatalities recorded. The island of Okushiri was hardest hit, with 165 casualties from the earthquake, the tsunami and a large landslide.
The 1872 North Cascades earthquake occurred at in central Washington Territory. A maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe) was assessed for several locations, though less intense shaking was observed at many other locations in Washington, Oregon, and British Columbia. Some of these intermediate outlying areas reported V (Moderate) to VII shaking, but intensities as high as IV (Light) were reported as far distant as Idaho and Montana. Due to the remote location of the mainshock and a series of strong aftershocks, damage to structures was limited to a few cabins close to the areas of the highest intensity.

On 11 March 2011, at 14:46 JST, a 9.0–9.1 undersea megathrust earthquake occurred in the Pacific Ocean, 72 km (45 mi) east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region. It lasted approximately six minutes, causing a tsunami. It is sometimes known in Japan as the "Great East Japan Earthquake", among other names. The disaster is often referred to by its numerical date, 3.11.
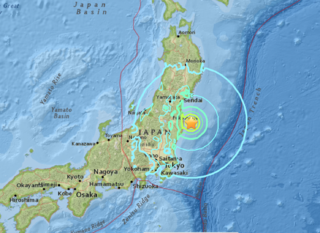
The 2016 Fukushima earthquake struck Japan east-southeast of Namie, Fukushima Prefecture at 05:59 JST on November 22 with depth of 11.4 km (7.1 mi). The shock had a maximum intensity of VII (Very strong) on the Mercalli scale. The earthquake was initially reported as a 7.3 magnitude by Japan Meteorological Agency, and was later revised to 7.4, while the United States Geological Survey and GFZ Potsdam determined a magnitude of 6.9.
The 1898 Mare Island earthquake occurred in Northern California on with a moment magnitude of 5.8–6.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII–IX (Severe–Violent). Its area of perceptibility included much of northern and central California and western Nevada. Damage amounted to $350,000 and was most pronounced on Mare Island, a peninsula in northern San Francisco Bay. While relatively strong effects there were attributed to vulnerable buildings, moderate effects elsewhere in the San Francisco Bay Area consisted of damaged or partially collapsed structures, and there were media reports of a small tsunami and mostly mild aftershocks that followed.

The 2017 Pohang earthquake, measuring magnitude 5.4 on the Richter magnitude scale, struck Heunghae, Pohang, North Gyeongsang Province, South Korea on November 15, 2017. It is tied with the 2016 Gyeongju earthquake as the country's strongest earthquake in modern history, and the most destructive ever recorded with "an estimated 300 billion won in damage."
The 1930 Bago (Pegu) earthquake, also known as the Swa earthquake struck Myanmar on 5 May. The moment magnitude (Mw ) 7.4 earthquake had a focal depth of 35 km (22 mi) and maximum Rossi–Forel intensity of IX. The earthquake was the result of rupture along a 131 km (81 mi) segment of the Sagaing Fault—a major strike-slip fault that runs through the country. Extensive damage was reported in the southern part of the country, particularly in Bago and Yangon, where buildings collapsed and fires erupted. At least 550, and possibly up to 7,000 people were killed. A moderate tsunami was generated along the Burmese coast which caused minor damage to ships and a port. It was felt for over 570,000 km2 (220,000 sq mi) and as far as Shan State and Thailand. The mainshock was followed by many aftershocks; several were damaging; additional earthquakes occurred in July and December, killing dozens. The December earthquake was similarly sized which also occurred along the Sagaing Fault.
The Lompoc earthquake of 1927 occurred at 5:49 a.m. Pacific Standard Time (PST), on November 4 with an epicenter off the coast of Lompoc, Santa Barbara County in Southern California. It is one of the largest earthquakes to have occurred off the coast of California, measuring a surface-wave magnitude of 7.3. The earthquake may have originated along the Hosgri Fault, an entirely offshore structure. Shaking from the earthquake and an unusually large tsunami caused some damage to communities near the earthquake. Due to its location and the area being sparsely populated at the time, there were no human fatalities reported. It is the only California-generated tsunami recorded in Hawaii.

The 1867 Virgin Islands earthquake and tsunami occurred on November 18, at 14.45 in the Anegada Passage about 20 km southwest of Saint Thomas, Danish West Indies. The Ms 7.5 earthquake came just 20 days after the devastating San Narciso Hurricane in the same region. Tsunamis from this earthquake were some of the highest ever recorded in the Lesser Antilles. Wave heights exceeded 10 m (33 ft) in some islands in the Lesser Antilles. The earthquake and tsunami resulted in no more than 50 fatalities, although hundreds of casualties were reported.
An earthquake struck near the Hawaiian island of Lanai on February 19, at 10:11 pm HST with an estimated magnitude of 7.5 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ). It remains one of the largest seismic event to hit the Hawaiian Islands since the 1868 Ka‘ū earthquake, with its effects being felt throughout the entire archipelago. It caused severe damage on the islands of Lanai, Molokai and Maui. A tsunami may have been generated however there are speculations if it had actually happened. Despite the size of the quake and the extent of damage, there were no deaths.
The Nemuro-Oki earthquake in scientific literature, occurred on June 17 at 12:55 local time. It struck with an epicenter just off the Nemuro Peninsula in northern Hokkaidō, Japan. It measured 7.8–7.9 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ), 8.1 on the tsunami magnitude scale (Mt ) and 7.4 on the Japan Meteorological Agency magnitude scale (MJMA ).

On November 22, 2014, at 22:08 local time, an earthquake struck southeast of Hakuba, Nagano Prefecture. It had a magnitude of 6.2 according to the United States Geological Survey, with a maximum intensity assigned IX (Violent) on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale. According to the Japan Meteorological Agency, it is recorded as 6.7 and at its peak intensity at Shindo 6 Lower on the Japan Meteorological Agency seismic intensity scale. The earthquake did not result in any deaths, however 41 people sustained mild to severe injuries.

An earthquake occurred 112 km, offshore, north of Maumere in the Flores Sea on December 14. The quake had a moment magnitude of 7.3 according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS). One person was killed and 173 others suffered injuries.
On December 5, 1456, the largest earthquake to occur on the Italian Peninsula struck the Kingdom of Naples. The earthquake had an estimated moment magnitude of Mw 7.19–7.4, and was centred near the town of Pontelandolfo in the present-day Province of Benevento, southern Italy. Earning a level of XI (Extreme) on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale, the earthquake caused widespread destruction in central and southern Italy. An estimated 30,000–70,000 people were killed. It was followed by two strong Mw 7.0 and 6.0 earthquakes to the north on December 30.
The 1743 Salento earthquake affected the Apulian region of southwestern Italy on 20 February at 23:30 IST. The ~7.1 Mw earthquake had an epicenter in the Adriatic and Ionian seas, off the coast of modern-day Lecce and Brindisi provinces in Salento. It had a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent), causing heavy damage in Nardò. Damage was also reported across the sea, in the Balkans. The earthquake also generated a tsunami of up to 11 meters in run-up. Between 180 and 300 people were killed in the disaster.
On 29 November, at 14:10 UTC, a magnitude 7.7 earthquake struck off the southern coast of Taliabu Island Regency in North Maluku, Indonesia. At least 41 people were killed on the nearby islands and a tsunami was triggered. Several hundred homes, buildings and offices were damaged or destroyed.

The 1940 Shakotan earthquake occurred on August 2 at 00:08:22 JST with a moment magnitude (Mw ) of 7.5 and maximum JMA seismic intensity of Shindo 4. The shock had an epicenter off the coast of Hokkaido, Japan. Damage from the shock was comparatively light, but the accomanying tsunami was destructive. The tsunami caused 10 deaths and 24 injuries on Hokkaido, and destroyed homes and boats across the Sea of Japan. The highest tsunami waves were recorded at the coast of Russia while along the coast of Hokkaido, waves were about 2 m.
The 1958 Kuril Islands earthquake or Etorofu earthquake was a Mw 8.3–8.4 earthquake that struck near the Kuril island of Iturup on November 6, 1958, at 22:58 UTC, or 09:58 on the 7th local time. The earthquake occurred as the result of shallow reverse faulting along the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench, and caused Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) X (Extreme) shaking, as well as a tsunami 5 m (16 ft) high. Iturup sustained significant damage as a result of the shaking and tsunami, with other locations along the Kuril Islands also reporting strong damage.
An earthquake struck present-day North Korea during the Joseon Dynasty. The earthquake had an estimated moment magnitude of 7.3 and affected present-day North Hamgyong Province. The maximum Modified Mercalli intensity was assigned VIII to IX. Eighty-three homes collapsed and livestock were destroyed. A landslide killed at least two people while additional fatalities occurred during a stampede.










